If you're still relying on yesterday’s cybersecurity tools, 2025 will likely be your wake-up call. The digital threat landscape is not only growing more complex—it’s evolving with machine speed. Cybercriminals are no longer lone hackers in basements; they’re well-funded, highly organised entities that leverage automation, artificial intelligence, and social engineering at scale.
While many organisations remain stuck with static defences and reactive strategies, cyber adversaries are moving with greater agility and intelligence. In this new era, cybersecurity isn’t just an IT issue—it’s a strategic imperative demanding boardroom attention.

Top 12 Cyber Security Threats in 2025
1. Advanced Phishing & AI-Powered Social Engineering
Phishing attacks in 2025 are more than just clumsy email scams. They are precision-crafted, AI-generated campaigns that can replicate voices, mimic executive behavior, and forge digital assets with unnerving accuracy. Technologies like deepfake audio and image generation have turned social engineering into a high-tech con job.
What’s at Stake:
-
Credential theft leading to system breaches
-
Financial fraud through business email compromise (BEC)
-
Executive impersonation and reputational harm
Prevention Tips:
-
Train employees regularly on the latest phishing tactics.
-
Deploy AI-based email security tools that detect spoofing and anomalies.
-
Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all systems.
-
Implement a “zero trust” approach to sensitive transactions.
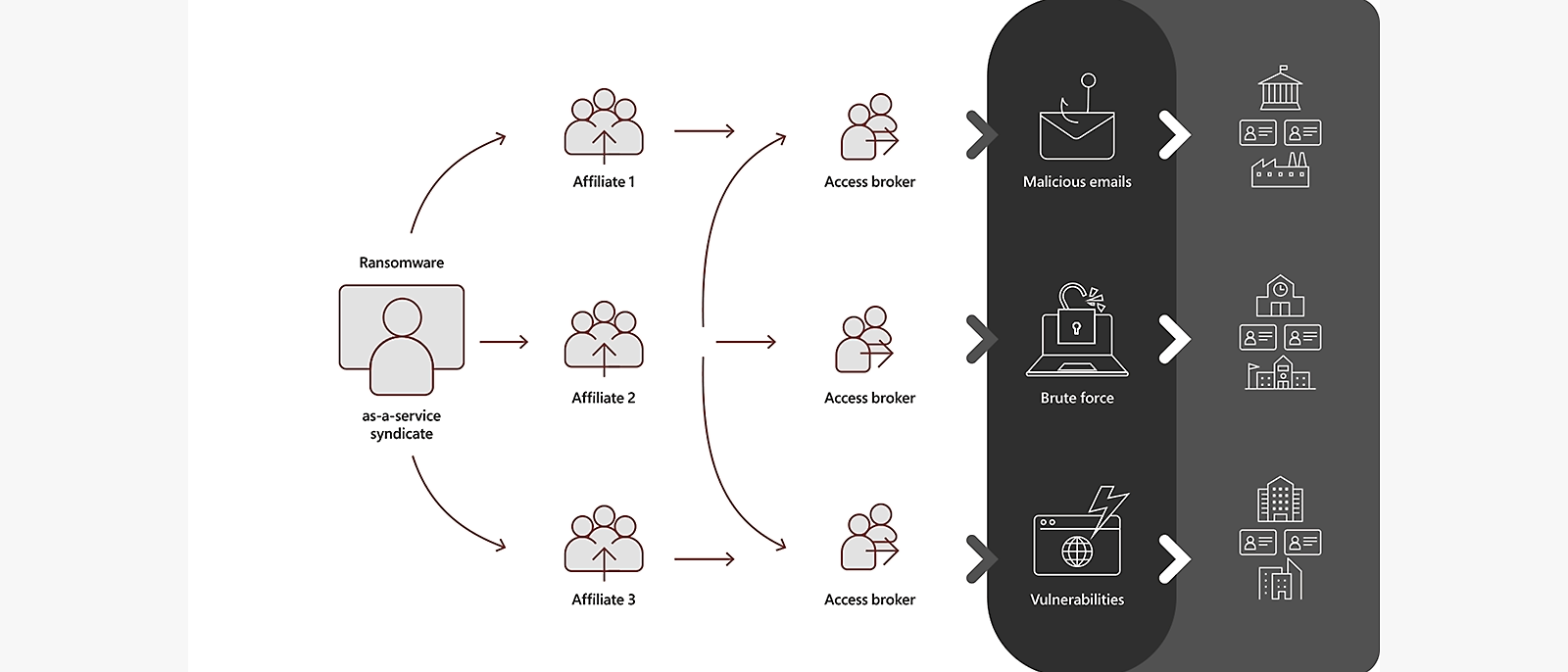
2. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Cybercrime on Subscription
Ransomware has been democratised. Cybercriminals with no technical expertise can now rent ransomware toolkits complete with user guides and customer support. This industrialisation of ransomware has led to more frequent, more costly, and more sophisticated attacks.
What’s at Stake:
-
Average downtime of 21+ days
-
Triple extortion tactics: data encryption, leaks, and public auctions
-
Long-term reputational and legal consequences
Prevention Tips:
-
Maintain regular, encrypted backups and test recovery procedures.
-
Segment your networks to contain breaches.
-
Use behavioural endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools.
-
Monitor the dark web for leaked credentials
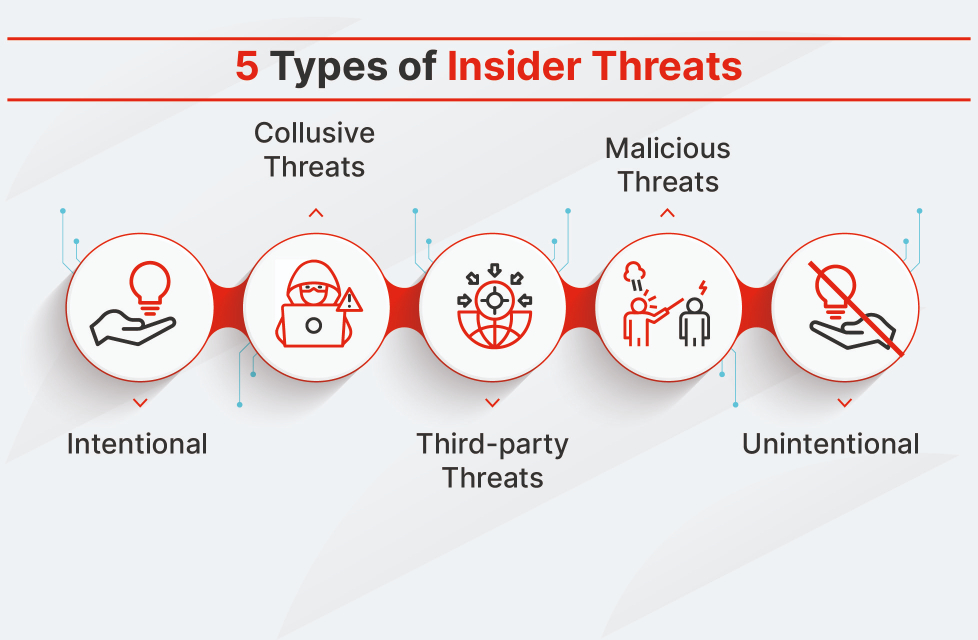
3. Insider Threats: Dangers from Within
Insiders—whether careless, compromised, or malicious—represent a growing risk. They often operate under the radar, using legitimate access to exfiltrate data or sabotage systems. Insider threats account for over 30% of all breaches.
What’s at Stake:
-
Breach of sensitive or proprietary data
-
Operational disruptions and compliance violations
-
Diminished trust among customers and stakeholders
Prevention Tips:
-
Enforce the principle of least privilege (POLP)
-
Monitor access logs and flag unusual behaviour
-
Conduct exit audits and revoke access immediately upon termination.
-
Invest in user behaviour analytics (UBA)
4. Cloud Misconfigurations: The Digital Achilles’ Heel
Cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer scalability but come with risks, especially when misconfigured. Common mistakes include open storage buckets, lax API security, and poor identity management.
What’s at Stake:
-
60% surge in cloud-related breaches year-over-year
-
Exposure of proprietary or regulated data
-
Regulatory fines and erosion of customer trust
Prevention Tips:
-
Conduct regular cloud configuration audits.
-
Use automated tools for continuous compliance checks.
-
Enable multi-factor authentication and strong encryption.
-
Implement a shared responsibility model with cloud providers

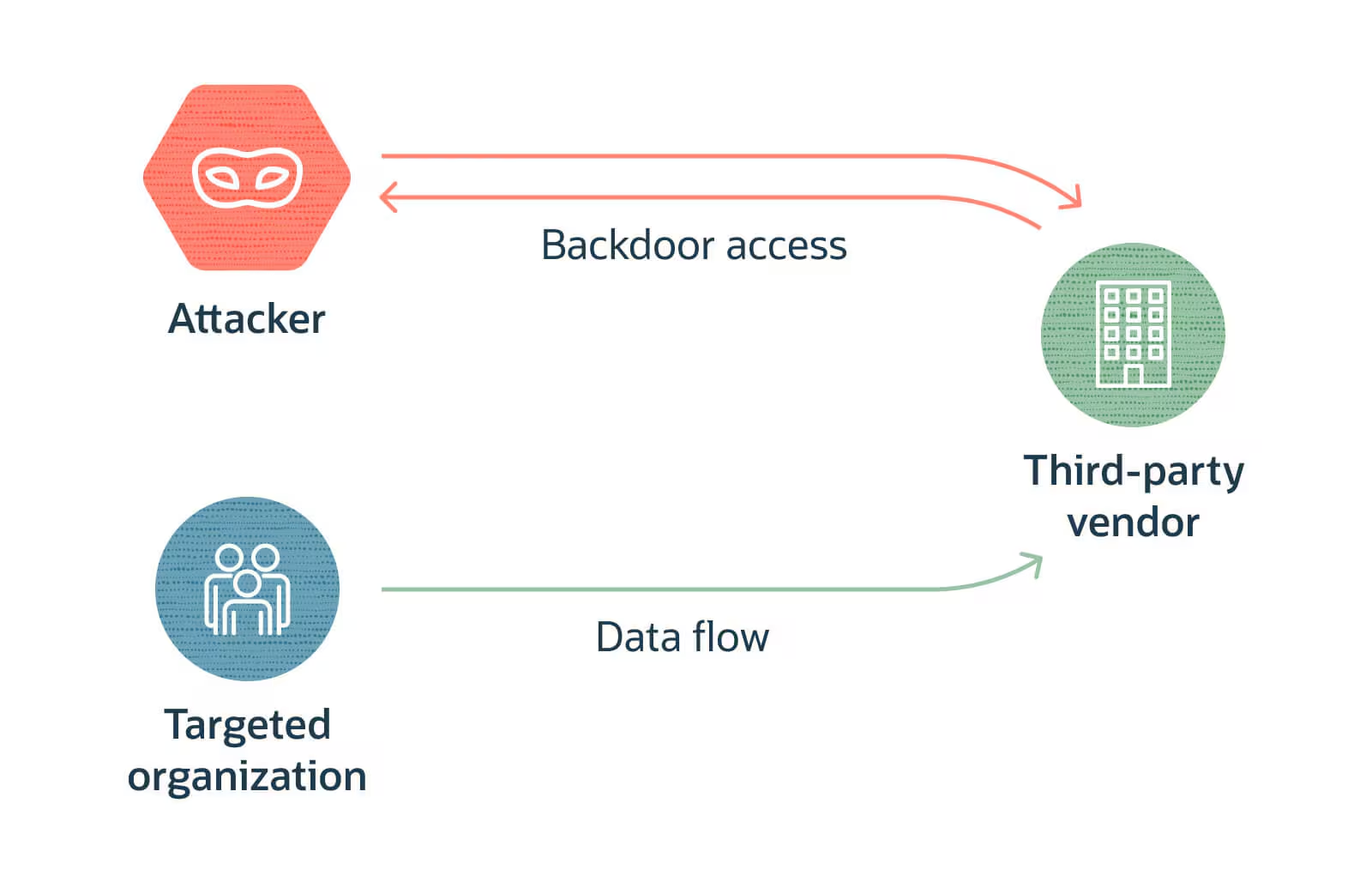
5. Supply Chain & Third-Party Attacks
Cybercriminals are no longer attacking you directly—they’re infiltrating your vendors, suppliers, and contractors to gain indirect access. These breach-by-proxy methods are notoriously difficult to detect and remediate.
What’s at Stake:
-
Compromise of critical systems without direct attack
-
Cross-network malware propagation
-
Major reputational damage from third-party failures
Prevention Tips:
-
Vet all vendors for cybersecurity standards.
-
Limit third-party access to only necessary systems.
-
Require contractual cybersecurity clauses and regular audits.
-
Use zero-trust architecture for third-party integrations
6. AI-Powered Cyberattacks: When Machines Attack
Cybercriminals now use AI to identify vulnerabilities, evade detection, and automate attacks. AI-generated phishing messages are 300% more effective, particularly against small and mid-sized enterprises.
What’s at Stake:
-
Highly adaptive, hard-to-detect threats
-
Accelerated attack timelines
-
Widespread and automated exploitation
Prevention Tips:
-
Invest in AI-driven defence tools that match the sophistication of attackers.
-
Stay current with emerging AI threat intelligence.
-
Incorporate AI into SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) platforms.
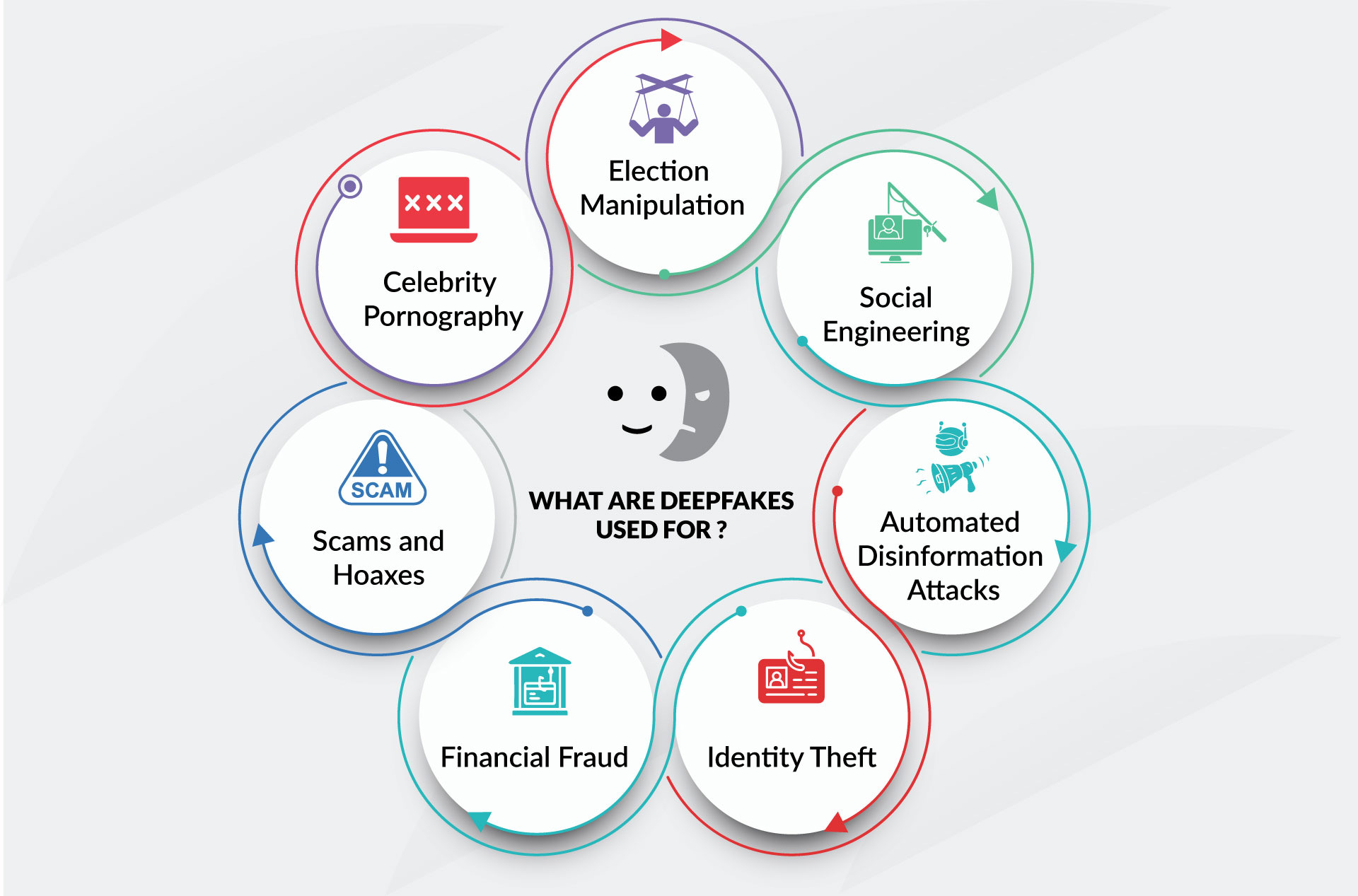
7. Deepfake Technology: Seeing Is No Longer Believing
Deepfakes aren’t just a novelty—they're a threat. By 2025, it’s expected there will be over 8 million deepfake assets in circulation, up from 500,000 in 2023. These can convincingly impersonate executives or public figures to manipulate employees or the public.
What’s at Stake:
-
Executive impersonation and financial fraud
-
Public misinformation and brand manipulation
-
Internal confusion during crises
Prevention Tips:
-
Use biometric verification and secondary authentication methods.
-
Train staff to verify unusual requests via trusted, out-of-band channels
-
Employ content authentication tools that can detect synthetic media.
8. IoT Device Exploitation: A Backdoor to Your Network
From smart locks to industrial sensors, IoT devices are now everywhere. But most were not built with security in mind. Nearly 67% of small businesses report IoT-related security incidents, yet less than a quarter have a formal IoT security policy.
What’s at Stake:
-
Network infiltration through weak or unpatched devices
-
Data leakage via unencrypted communications
-
Compromise of critical infrastructure
Prevention Tips:
-
Change default credentials and disable unused services.
-
Apply firmware updates regularly.
-
Segment IoT devices from your core business network
-
Use intrusion detection systems (IDS) specific to IoT
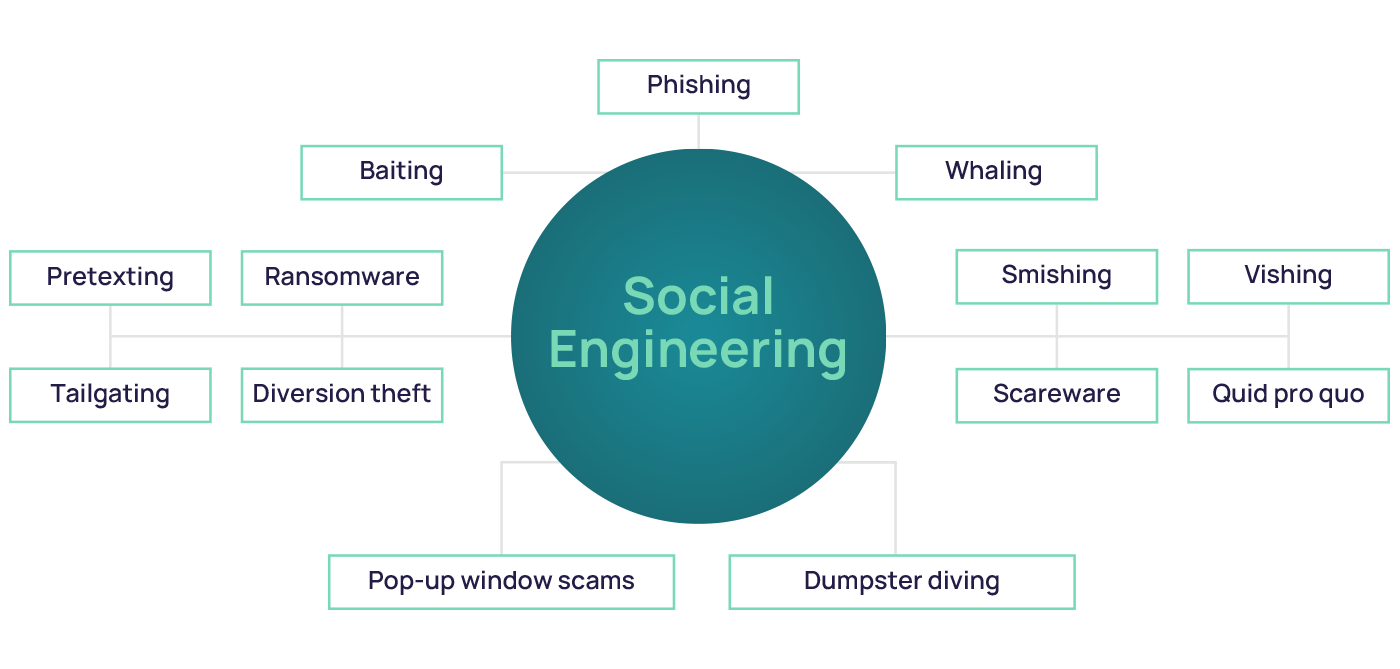
9. Social Engineering Attacks: Hacking the Human Mind
Cyberattacks increasingly bypass firewalls by manipulating people. Social engineering spans:
-
Phishing: Malicious emails or websites
-
Vishing: Voice impersonation calls
-
Smishing: Text-message-based lures
-
Baiting: Fake USBs or free software offers
What’s at Stake:
-
Unauthorised access to systems and data
-
Identity theft and financial losses
-
Malware infections
Prevention Tips:
-
Conduct continuous security awareness training.
-
Simulate phishing campaigns to test employee responses.
-
Use spam filters and domain verification protocols (like DMARC)
10. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks flood networks with traffic, shutting down services and overwhelming servers. Smaller businesses are especially vulnerable, often lacking the infrastructure to withstand these barrages.
What’s at Stake:
-
Downtime and operational paralysis
-
Lost revenue and customer trust
-
Damage to critical systems
Prevention Tips:
-
Use cloud-based DDoS protection services.
-
Establish traffic rate limits and monitoring.
-
Partner with ISPs or hosting providers that offer DDoS mitigation
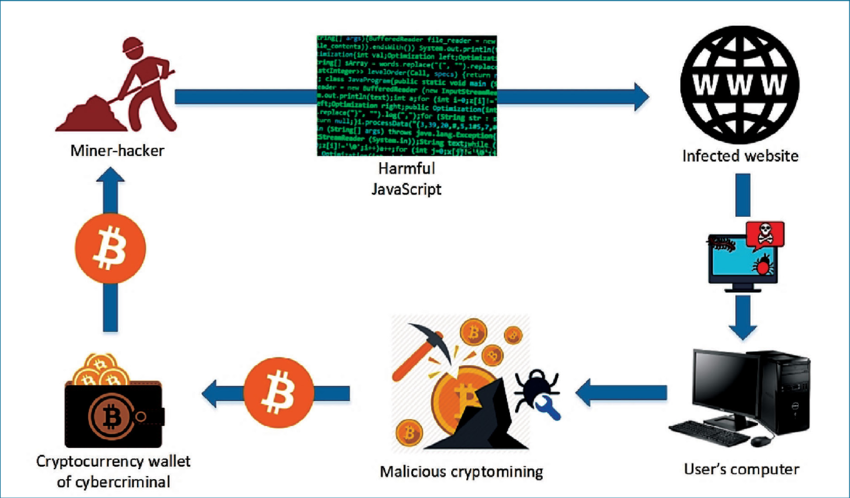
11. Cryptojacking: Hijacking for Hidden Profits
Instead of stealing data, cryptojacking hijacks your devices to mine cryptocurrency. While subtle, this can slow operations, increase energy costs, and damage hardware over time.
What’s at Stake:
-
Increased operating expenses
-
System slowdowns and hardware failure
-
Productivity losses
Prevention Tips:
-
Monitor CPU and network usage for anomalies.
-
Use endpoint protection that detects browser-based mining scripts.
-
Block known cryptojacking URLs and extensions
12. Fileless Malware: The Invisible Enemy
Unlike traditional malware, fileless malware operates directly in memory, evading signature-based detection tools. It often exploits legitimate system tools like PowerShell or WMI.
What’s at Stake:
-
Nearly undetectable breaches
-
Persistent, hard-to-remove infections
-
Compromise of mission-critical applications
Prevention Tips:
-
Deploy behavioural analytics for anomaly detection.
-
Limit script-based execution rights.
-
Regularly audit system processes and memory usage

Stay Ahead, Not Just Afloat
Cybersecurity in 2025 is no longer about patching holes—it’s about anticipating storms. The organisations that survive and thrive will be the ones that shift from reactive to proactive security. This means embedding cybersecurity into your culture, investing in intelligent defence systems, and treating digital risk like business risk.
In a world where trust is a target, resilience is your best weapon.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved. Powered by Vygr Media.
























