Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is rapidly reshaping business operations by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks through software robots or "bots" that mimic human actions within digital systems. This technology is becoming a strategic driver of digital transformation, enabling organizations to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve accuracy across various industries.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA involves deploying software bots to automate routine tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, report generation, and customer service queries. Unlike traditional automation that often requires complex programming and system changes, RPA can be implemented quickly with minimal IT intervention, working seamlessly alongside existing systems like CRMs and ERPs.
Key Benefits of RPA in Business
-
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: By automating mundane and repetitive tasks, RPA frees employees to focus on complex, strategic activities, boosting overall productivity.
-
Cost Reduction: Automation reduces the need for manual labor, minimizing operational costs and human errors.
-
Improved Accuracy: Bots perform tasks consistently without fatigue, enhancing data accuracy and compliance.
-
Faster Process Execution: Automated workflows accelerate business processes, improving turnaround times and customer satisfaction.
Emerging Trends Shaping RPA in 2025
1. Hyperautomation and AI Integration
By 2025, hyperautomation-combining RPA with Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and process mining-will dominate the automation landscape. This approach automates entire workflows rather than isolated tasks, creating self-operating systems that require minimal human intervention. AI-enhanced RPA bots will handle unstructured data, understand natural language, and make real-time decisions, enabling automation of complex processes like document analysis and predictive maintenance.
2. Expansion Across Industries

While finance and IT have traditionally led RPA adoption, 2025 will see RPA penetrate new sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, unlocking operational efficiencies and innovation opportunities in these fields.
3. Rise of Low-Code Platforms and Lifecycle Management
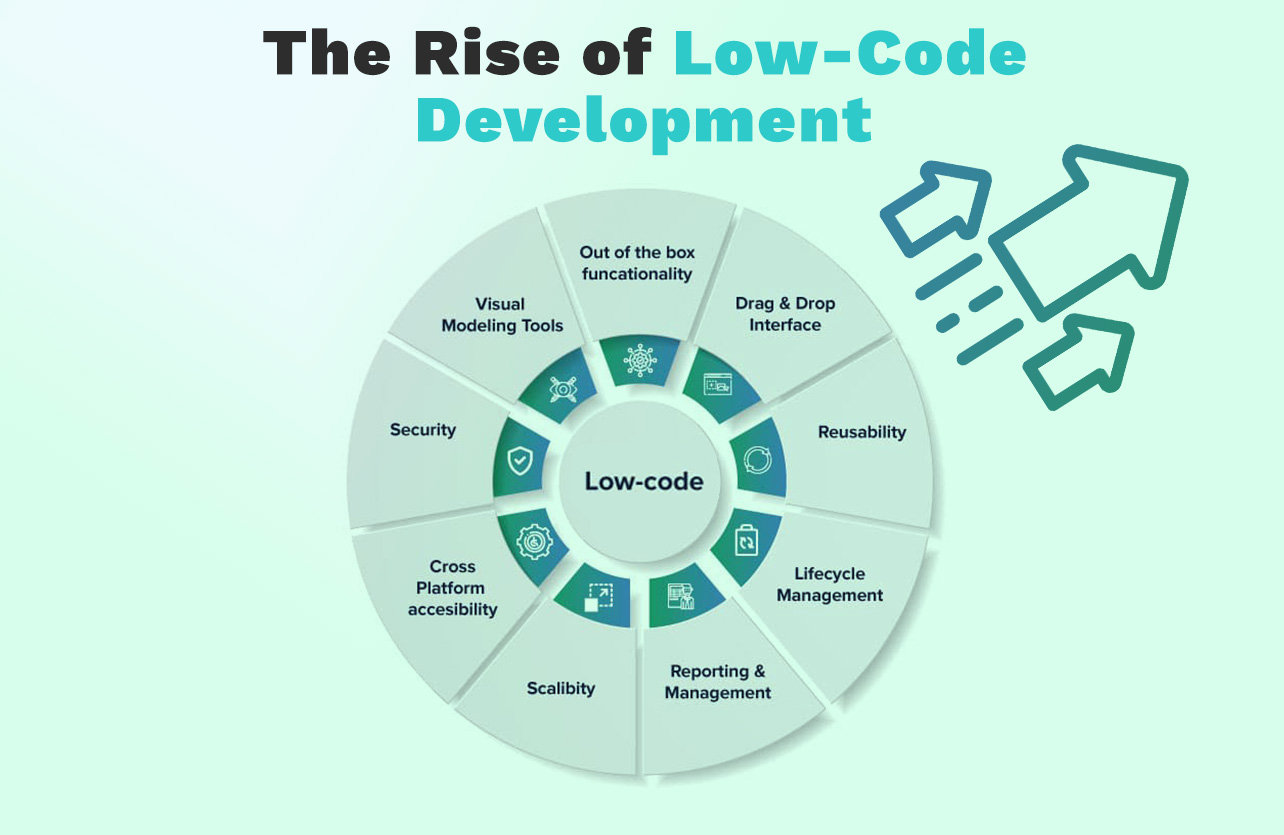
Low-code RPA platforms are making automation accessible to non-technical users, accelerating deployment and scaling. Additionally, effective RPA lifecycle management is becoming crucial to maximize return on investment and sustain automation success over time.
Practical Applications of RPA in Business
-
Data Entry and Processing: Automating data extraction, validation, and entry reduces errors and speeds up workflows.
-
Invoice and Billing Automation: Bots generate and send invoices automatically, improving cash flow and customer relations.
-
Report Generation: RPA consolidates data from multiple sources to produce timely and accurate reports, aiding informed decision-making.
-
Customer Support: Automated handling of routine queries enhances response times and customer experience.
Choosing the Right RPA Tools

The market offers a range of RPA tools tailored for different business needs-from startups to large enterprises. Leading platforms like UiPath, Blue Prism, and Automation Anywhere provide scalable solutions that integrate easily with existing systems, enabling businesses to optimize workflows and achieve operational excellence.
Robotic Process Automation is no longer just a cost-cutting tool but a vital component of digital transformation strategies. With advancements in AI and hyperautomation, RPA is set to revolutionize how businesses operate by automating complex processes, expanding into new industries, and enabling greater agility and competitiveness in 2025 and beyond.
This comprehensive overview highlights how RPA empowers businesses to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and drive innovation in an increasingly digital world.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.
























