In 2025, cybersecurity is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Once considered too insignificant to target, small businesses are now squarely in the crosshairs of cybercriminals. With the average cost of a data breach ranging from $120,000 to a staggering $1.24 million for SMBs, the stakes couldn’t be higher.
Many SMEs continue to operate under the illusion that they’re too small to attract hackers. That myth is not only outdated—it’s dangerous. In reality, 43% of all cyberattacks now target small businesses, largely because of their limited resources, lack of preparedness, and weak security infrastructure.

Why Cybercriminals Love Targeting Small Businesses
Cyber attackers see SMEs as low-hanging fruit. While enterprise giants may have dedicated security teams and millions to spend on cybersecurity, small businesses often:
-
Use outdated software and weak passwords
-
Lack employee training in spotting scams
-
Have no formal cybersecurity or incident response plan
-
Rely on basic or “DIY” IT solutions with glaring vulnerabilities
Even a single successful attack can lead to financial devastation, legal consequences, reputational loss, and business interruption that can take months—or years—to recover from..
Top Cybersecurity Threats Facing Small Businesses Today
Cyber threats have evolved rapidly, and small businesses face a broad spectrum of risks beyond the well-known ransomware and phishing scams. Key challenges include:
1. Poor Infrastructure Visibility
Attackers are shifting from traditional devices (laptops, desktops) to cloud environments like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and AWS, which saw a 95% increase in breaches in 2022 compared to the previous year. Additionally, Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as printers and smart cameras are becoming common entry points.
Case in point: In November 2024, a global botnet called “Matrix” exploited unpatched IoT devices using Mirai malware to launch widespread DDoS attacks, disrupting online operations worldwide.
2. Lack of Strategic Cybersecurity Guidance
Only 14% of small businesses have a cybersecurity plan. Many rely on piecemeal “DIY” solutions or basic IT provider services that fail to cover real risks comprehensively. Without expert insight, security efforts are fragmented and insufficient.
3. Inconsistent and Delayed Patching
Approximately 60% of breaches exploit unpatched vulnerabilities, with attackers now compromising systems in under six minutes due to AI-driven tools. Monthly patching schedules are outdated; continuous vulnerability management with daily scans and prioritized remediation is essential.
4. Weak Incident Response Planning
Nearly 47% of SMBs lack an incident response plan. This absence can turn minor incidents into full-blown crises, causing prolonged downtime and escalating costs. On average, organizations take 204 days to identify a breach and an additional 73 days to contain it.
5. Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware remains a significant threat with SMBs increasingly targeted via supply chain compromises. In 2023, 52% of global organizations reported ransomware impacting their supply chains, and ransom demands averaged $1.54 million.
6. Phishing and Vishing Attacks
Human error continues to be a leading cause of breaches, with 74% of data breaches involving phishing or vishing (voice phishing). Attackers are using sophisticated, targeted social engineering tactics based on public data from LinkedIn, company websites, and more.
Affordable and Practical Cybersecurity Solutions for Small Businesses
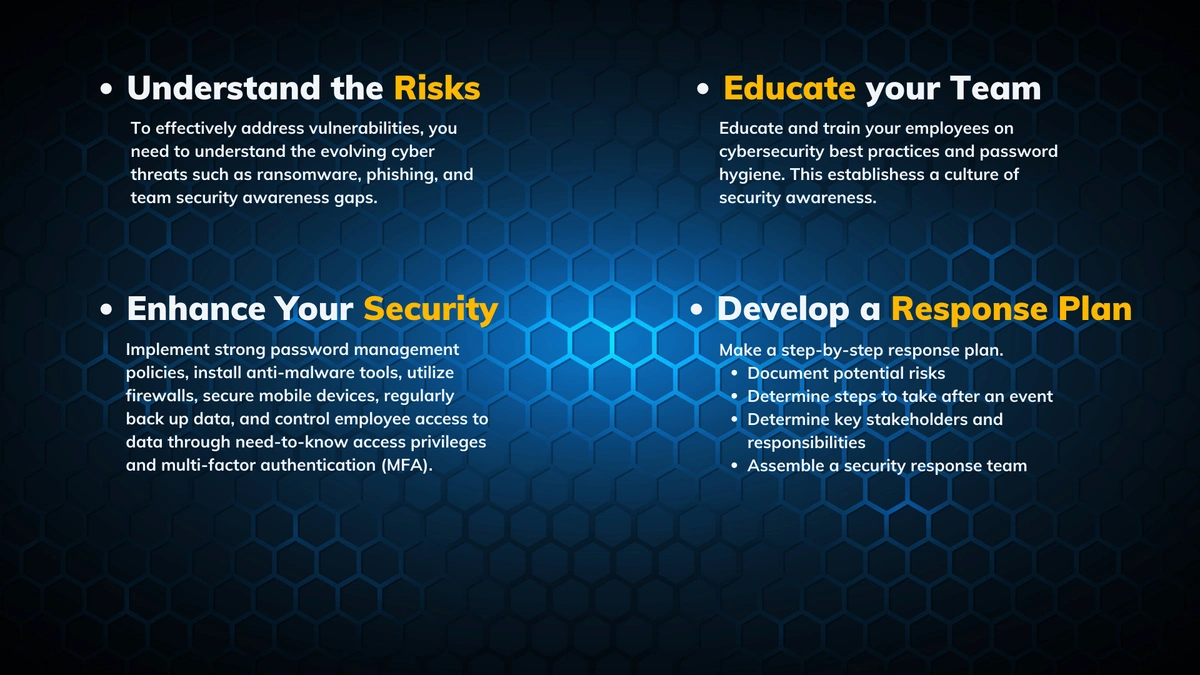
The good news? Small businesses don’t need expensive IT teams or complex tools to secure their operations. Implementing fundamental measures can drastically reduce risk and protect business continuity.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security beyond passwords, blocking unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised. Use app-based MFA tools like Google Authenticator.
-
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management: Automate updates and prioritize patches based on risk, not just severity scores. Weekly patching and continuous vulnerability scanning are vital.
-
Secure Wi-Fi and Network Segmentation: Avoid using public Wi-Fi for business tasks. Use VPNs when necessary and set up isolated guest Wi-Fi networks to protect internal systems.
-
Data Backups: Follow the 3-2-1 rule — three copies of your data, stored on two local devices and one off-site. Encrypt backups and test restore procedures regularly to mitigate ransomware damage.
-
Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Use reputable tools like Microsoft Defender or Bitdefender with real-time scanning and regular updates to detect threats early.
-
Password Management: Deploy password managers like LastPass or Bitwarden to generate and securely store strong, unique passwords for all accounts.
-
Employee Cybersecurity Training: Since 82% of data breaches involve human error, train employees on identifying phishing scams, practicing good password hygiene, and understanding company cybersecurity policies.
-
Incident Response Planning: Develop clear roles and communication protocols for breach detection, containment, and recovery. Test plans regularly with tabletop exercises.
-
Security Risk Assessments: Use frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework or CIS Top 18 Critical Security Controls to identify vulnerabilities and prioritize remediation.
-
Overarching Security Policies: Create simple, clear policies covering password usage, device management, data handling, and phishing response, updated annually.
Infact, some traders have started using tools like ItalbitPro to execute their trades better.
Training Your Team: The First Line of Cyber Defense
Even the most advanced cybersecurity tools are ineffective without knowledgeable employees. Training your team to recognize and avoid threats like phishing emails and suspicious links is crucial.
-
Conduct regular phishing simulation tests and quizzes.
-
Teach password best practices and encourage multi-factor authentication.
-
Limit data access based on job roles to minimize internal risk.
-
Establish and communicate a clear cybersecurity policy everyone must follow.
The Hidden and Devastating Costs of Cyber Attacks
Many small businesses take cybersecurity seriously only after experiencing an attack. By then, the consequences can be dire:
-
Financial Losses: Downtime, lost sales, expensive repairs, and ransom payments.
-
Legal Penalties: Violations of data privacy laws can result in significant fines.
-
Reputational Damage: Customer trust erosion leads to long-term revenue declines.
-
Operational Disruptions: Cyber incidents may halt business operations for days or weeks.
Preventive investment in cybersecurity tools and training is far more cost-effective than paying the price of recovery.
Why Cybersecurity Is a Leadership Responsibility
Cybersecurity is not just an IT issue — it’s a core business leadership responsibility. Small business owners must lead the charge by:
-
Prioritizing cybersecurity in business planning.
-
Allocating resources for security tools and training.
-
Promoting a culture of security awareness throughout the organization.
Taking proactive steps now will help safeguard your business against the growing tide of cyber threats.
Final Thoughts: Stay Vigilant, Stay Secure
Small businesses are more vulnerable than ever to increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. However, by understanding these risks and implementing practical, affordable security measures, you can protect your business assets, maintain customer trust, and ensure operational resilience.
Start today with the fundamentals — multi-factor authentication, regular patching, employee training, and robust backup strategies. Regularly reassess your security posture and adapt to evolving threats.
Remember: In cybersecurity, prevention is always cheaper than recovery.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.





















