SpaceX's Starship rocket, owned by Elon Musk, achieved a major milestone with its first fully successful test flight last week. After an hour-long sub-orbital journey, both the booster and spacecraft made controlled splashdowns. This marks the fourth launch attempt for the colossal Starship.
The Super Heavy booster separated and landed softly in the Gulf of Mexico, while the Starship spacecraft traveled halfway around the globe before splashing down in the Indian Ocean. This success moves SpaceX closer to its goal of creating a fully reusable rocket system, poised to revolutionize space travel and exploration, benefiting astronomy and planetary science.
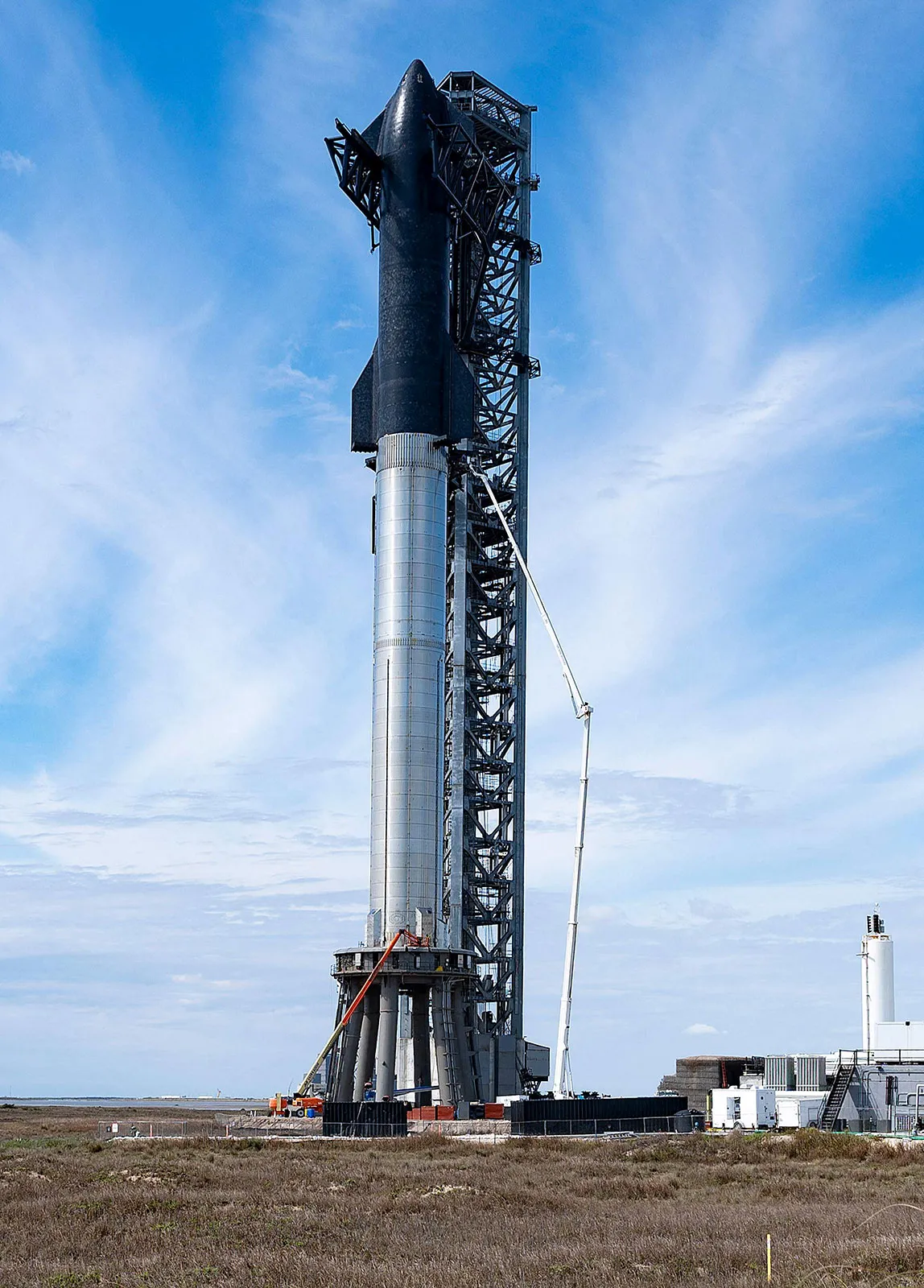

What is Starship?
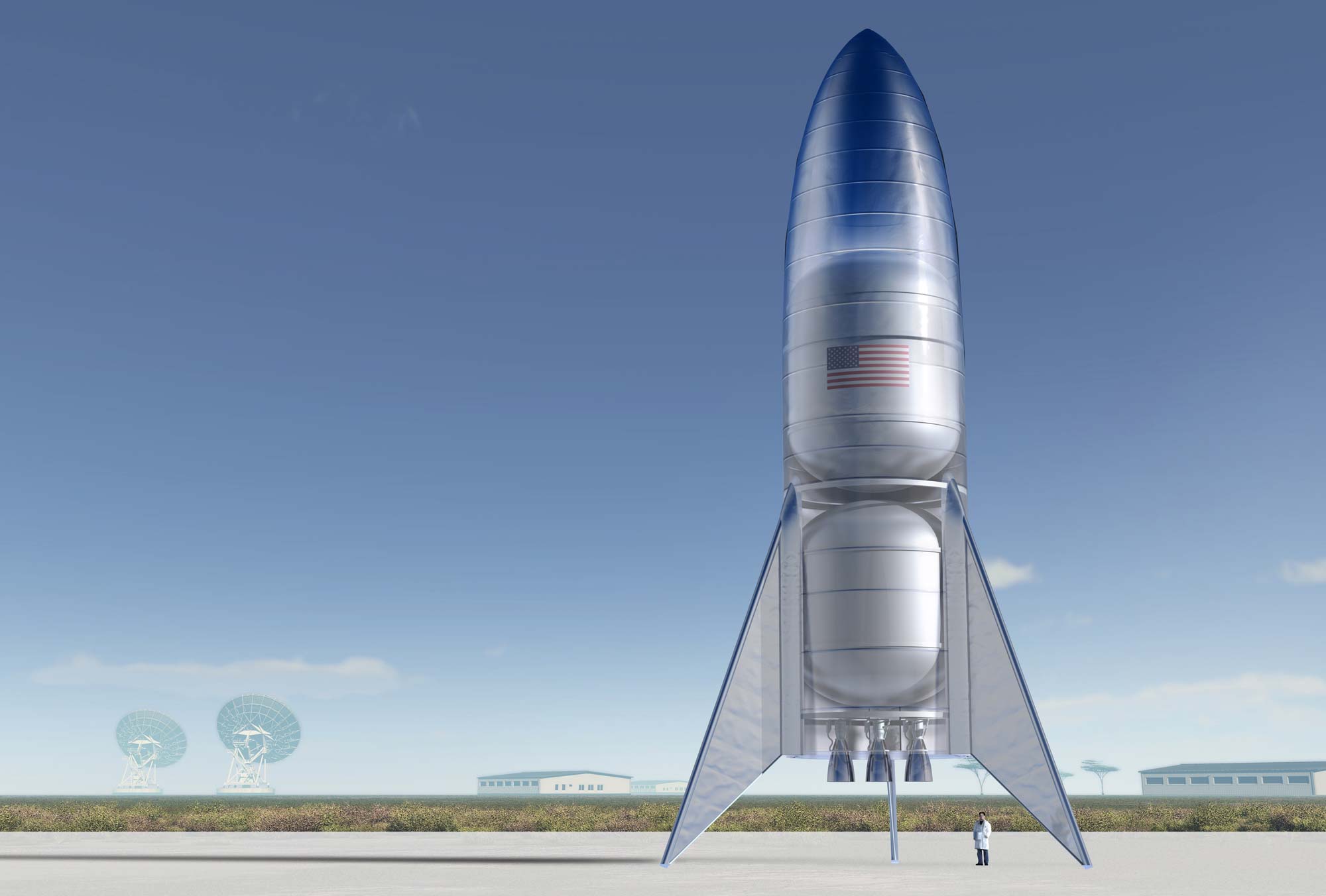
Starship is a groundbreaking two-stage rocket designed for carrying crew and cargo to destinations like Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Standing at nearly 120 meters, it surpasses even the Saturn V, which took astronauts to the Moon and was 111 meters tall. For comparison, the Qutab Minar is 72.5 meters tall.
The Super Heavy booster, equipped with 33 Raptor engines, generates a staggering 74 meganewtons of thrust. This dwarfs NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) with 39 meganewtons and Saturn V with 35 meganewtons. These Raptor engines operate on a 3.6:1 ratio of liquid oxygen and liquid methane, enabling efficient combustion.
SpaceX aims to make the Super Heavy booster fully reusable, capable of re-entering Earth's atmosphere and landing back at the launch site. The Starship spacecraft, with its six Raptor engines and four landing fins, is also designed for full reusability.

How can Starship reduce the cost of space travel?
Starship, developed by SpaceX, promises to revolutionize space travel by significantly reducing its costs. There are three key features driving this reduction:
-
Firstly, Starship is projected to carry up to 150 tonnes of payload to low-Earth orbit, and a minimum of 100 tonnes to destinations like the Moon and Mars. This payload capacity surpasses any previous lunar soft-landing missions.
-
Secondly, SpaceX is engineering Starship's upper stage to be refuelled in Earth orbit by other Starships. This innovation resembles refuelling an airplane, enabling swift deployment and enhancing the spacecraft's value by accommodating increased payload capacity and advanced scientific instruments.
-
Thirdly, Starship's design prioritizes full reusability, distinguishing it from traditional launch systems. Rather than discarding hardware elements, Starship retrieves them for reuse, minimizing costs associated with manufacturing and refurbishment. Even NASA's Space Shuttle, though reusable, required extensive post-flight servicing and refurbishment.
The cost efficiency of Starship is remarkable. Estimates suggest it could deliver up to 100 tonnes of cargo to Mars for a mere $50 million. In contrast, the retired Space Shuttle, with only a fraction of Starship's payload capacity and limited to low Earth orbit, cost approximately $1.5 billion per launch. This significant reduction in costs signifies a transformative shift in space travel accessibility and affordability.
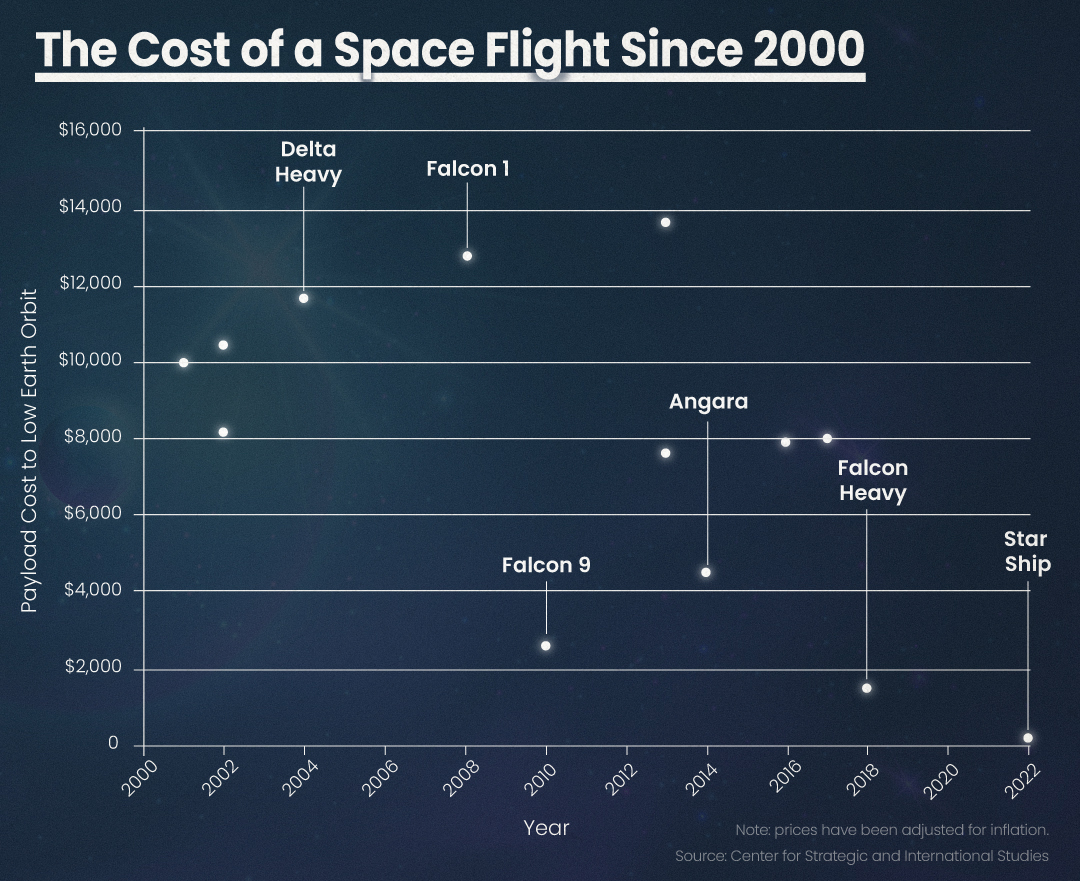
How does this benefit science?
Space exploration has long been hindered by the challenge of launching heavy payloads, making it both costly and impractical. However, the advent of Starship, with its remarkable capacity and cost-effectiveness, presents a paradigm shift in the field. This article explores how Starship's capabilities benefit scientific endeavors, ranging from launching larger space telescopes to enabling ambitious missions to the Moon and Mars.
-
Enhanced Payload Capacity
1. Larger Space Telescopes
-
Starship's ability to carry heavy payloads opens avenues for launching larger space telescopes.
-
These telescopes can utilize cheaper but heavier materials, enhancing their efficiency and capabilities.
2. Advanced Equipment for Planetary Exploration
-
Starship facilitates the deployment of bigger equipment on future Moon and Mars missions.
-
Examples include full-sized drilling rigs capable of penetrating up to a kilometer below the surface.
Unprecedented Scientific Access
1. Exploration of Planetary Interiors
-
The increased payload capacity enables scientists to explore the interiors of the Moon and Mars.
-
Access to these regions, believed to harbor valuable resources, can unlock crucial insights into planetary formation and evolution.
2. Sample Return Missions
-
Starship's capability to return to Earth enables the retrieval of substantial samples from the Moon and other celestial bodies.
-
These samples hold the potential to unravel mysteries about the solar system's history and the origins of life.
Integral Role in NASA's Artemis Program
1. Moon Exploration
-
Starship serves as a cornerstone of NASA's Artemis program, designed to return astronauts to the Moon by 2030.
-
Its capacity to transport large payloads facilitates the establishment of sustainable lunar exploration missions.
2. Mars Exploration
-
Beyond the Moon, Starship is poised to play a crucial role in NASA's ambitions to send astronauts to Mars.
-
With its advanced capabilities, Starship paves the way for humanity's endeavors to explore and potentially colonize the Red Planet.
What are the challenges?
Safety and Reliability
-
SpaceX must demonstrate that the Starship is safe and reliable before realizing its promised benefits.
-
Historically, ensuring safety and reliability while keeping costs low has been a significant challenge for space flight programs.
Cost Management
-
Keeping costs low is crucial for SpaceX's Starship program to fulfill its promises.
-
The Space Shuttle program faced criticism for its reusable shuttles being more expensive than expendable rockets.
Progress and Development
-
Despite rapid development, progress with the Starship has been slower than anticipated.
-
The pace of development has raised concerns about safety and worker well-being.
Worker Safety
-
Reuters investigation revealed concerns about worker safety in SpaceX's facilities in Texas and California.
-
Over 600 workplace injuries were documented, with employees attributing them to the push for rapid development.
The recent successful test flight of Starship is a major step forward in SpaceX's ambitious goal of making space travel more affordable and practical. The potential scientific and economic benefits are enormous, but challenges remain. Continued advancements and careful management will be essential to fully realize the vision of a reusable and cost-effective space travel system.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.


























