Space exploration has long been a captivating pursuit, representing the ultimate frontier of human achievement and curiosity. From the first moon landing to the latest Mars missions, the benefits of space exploration are far-reaching and transformative. But it’s not just about distant planets and galaxies—space exploration has a direct, practical impact on Earth. With advancements in technology, space missions are helping us solve pressing problems, advancing scientific knowledge, and even inspiring future generations.

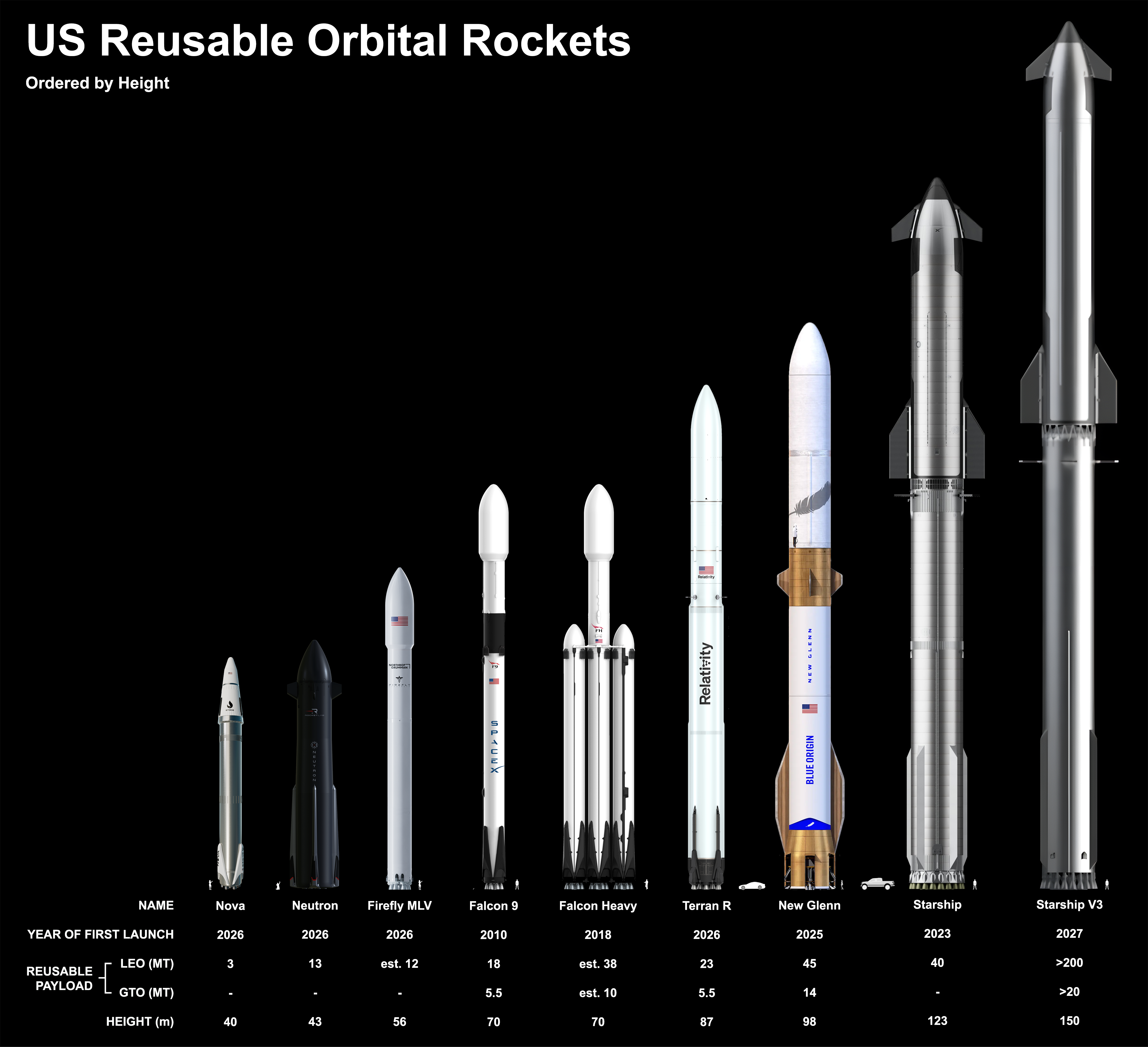
The Era of Reusable Rockets: Making Space More Accessible
One of the most groundbreaking advancements in space technology is the development of reusable rockets. Historically, rockets were single-use, discarded after launching their payload into space, making missions prohibitively expensive. However, innovations in reusable rocket technology are revolutionizing how we approach space exploration by significantly reducing launch costs.
SpaceX and Blue Origin: Pioneering Reusability
SpaceX, with its Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets, has led the charge in reusable rocket technology. The Falcon 9’s first stage can land on a drone ship or ground pad, allowing it to be reused multiple times. This breakthrough has drastically reduced the cost of launching payloads into orbit. SpaceX’s Starship, still under development, is aiming to make both stages of the rocket reusable, bringing down costs even further and enabling missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
Similarly, Blue Origin has developed reusable rockets with its New Shepard, designed for suborbital missions, and New Glenn, intended for orbital missions. These innovations are making space more accessible and paving the way for industries like space tourism, satellite deployment, and interplanetary exploration.
Key Benefits of Reusable Rockets
-
Satellite Deployment: Reusable rockets have made launching satellites more affordable and efficient. This has expanded capabilities for global communications, Earth observation, and weather forecasting, benefiting both public and private sectors.
-
Space Tourism: Companies like Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic are making space tourism a reality, allowing civilians—not just astronauts—to experience space firsthand.
-
Interplanetary Exploration: SpaceX’s fully reusable Starship aims to make interplanetary exploration feasible, with missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond within reach.
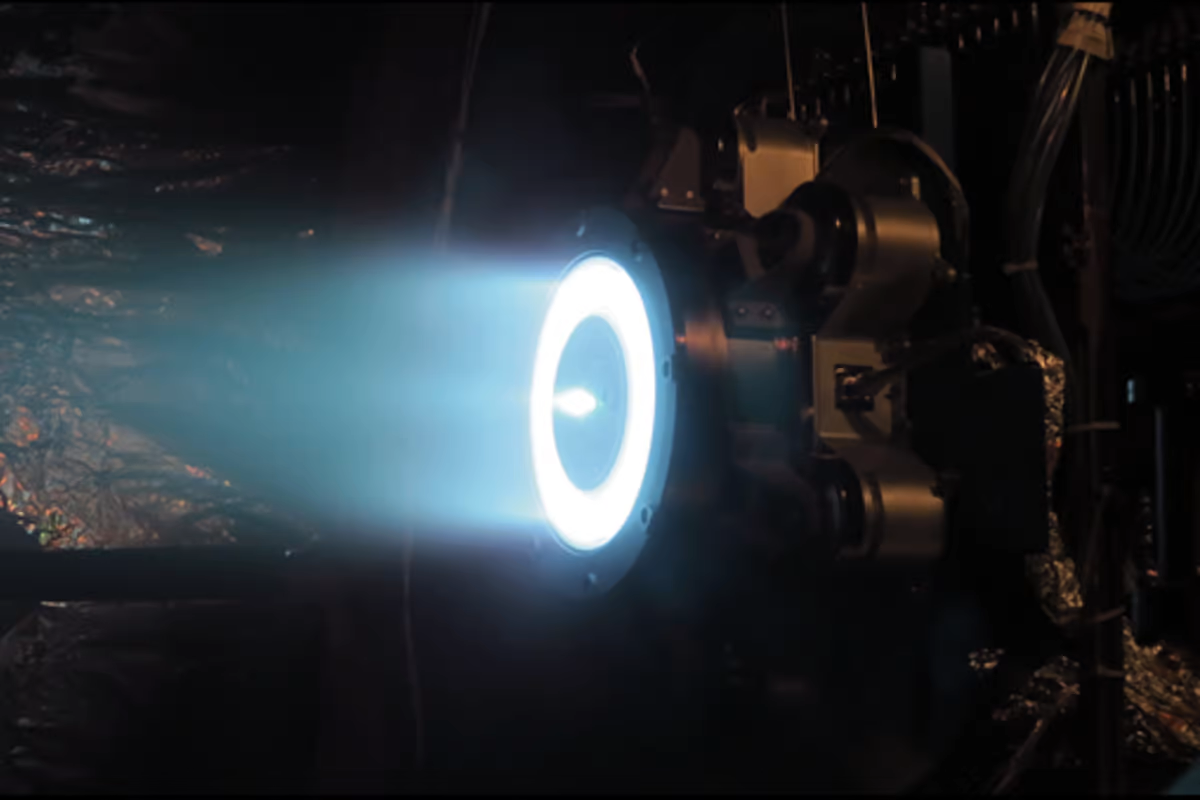
Advanced Propulsion Systems: The Future of Deep-Space Exploration
While reusable rockets have revolutionized how we reach orbit, exploring deeper into space requires even more advanced propulsion systems. Traditional chemical rockets, while powerful, are inefficient for long-distance travel, making them impractical for interplanetary and deep-space missions. New propulsion technologies are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in space exploration.
Ion Propulsion and Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP)
Ion propulsion is one of the most promising technologies for deep-space missions. Unlike chemical rockets, which burn fuel for thrust, ion propulsion uses electric fields to accelerate ions, creating a continuous, fuel-efficient thrust. This allows spacecraft to travel vast distances with minimal fuel, making it ideal for long-duration missions, such as NASA’s Dawn spacecraft, which explored the asteroid belt.
For human missions to Mars, Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP) holds great promise. By using nuclear reactors to superheat hydrogen, NTP provides far greater efficiency than chemical rockets, significantly reducing travel times and minimizing astronaut exposure to harmful radiation.
Solar Sails: A Fuel-Free Solution for Deep-Space Travel
Solar sails, like those demonstrated by The Planetary Society’s LightSail project, offer a revolutionary method of propulsion. By harnessing sunlight, solar sails generate continuous acceleration without the need for fuel. While their thrust is gradual, solar sails could enable lightweight probes to travel far beyond the solar system, opening the door to interstellar exploration.
The Role of Advanced Propulsion
-
Deep-Space Exploration: Ion propulsion is already enabling missions to asteroids and distant planets, with ongoing missions like NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) and Psyche.
-
Crewed Mars Missions: NTP could make human missions to Mars viable by reducing travel times and exposure to radiation.
-
Interstellar Voyages: Solar sails could allow for long-duration, fuel-free missions to the farthest reaches of space.
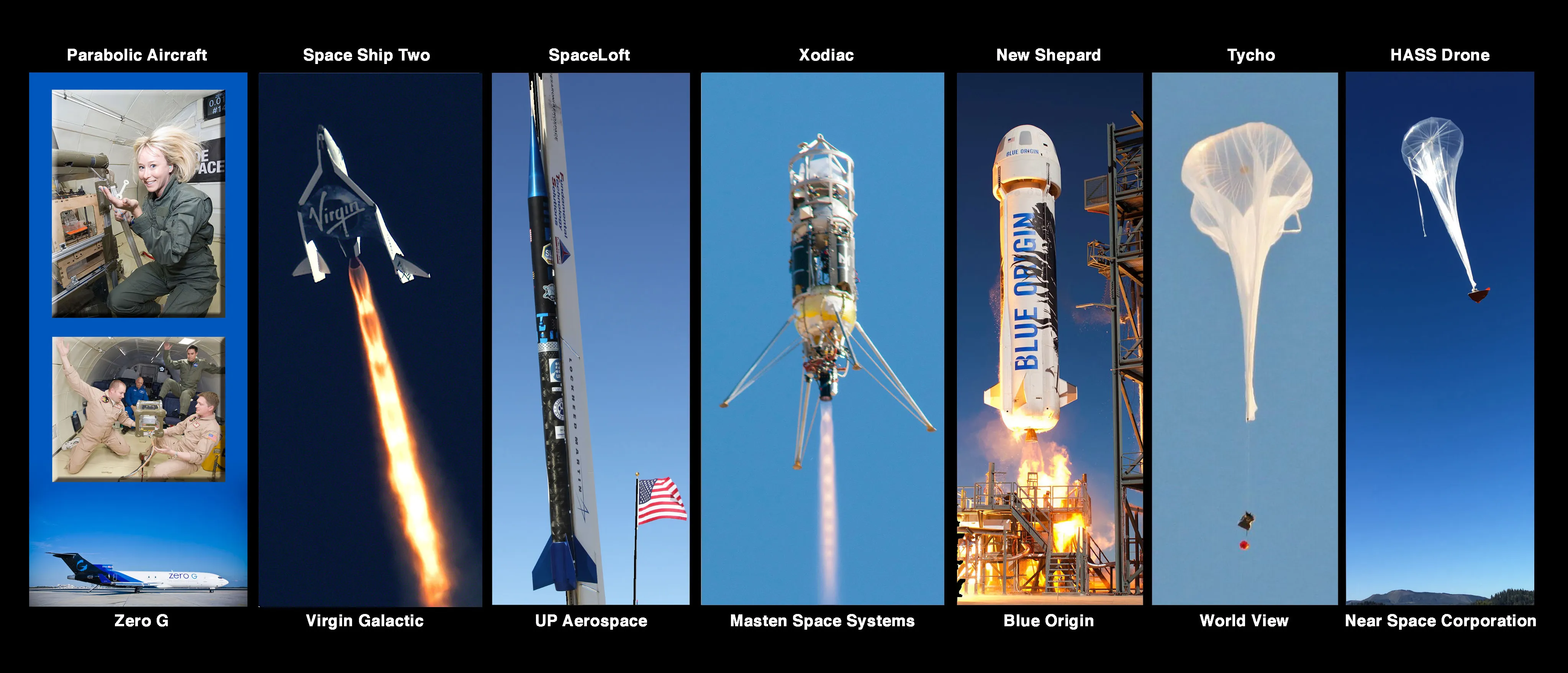
Habitats and Life Support Systems: Ensuring Survival Beyond Earth
As space missions extend beyond Earth’s orbit, ensuring astronauts’ survival becomes increasingly complex. Unlike short missions to the International Space Station (ISS), future lunar or Martian outposts will need to be self-sustaining, operating with minimal external support.
Closed-Loop Life Support Systems
NASA’s Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) aboard the ISS already recycles water and oxygen, reducing reliance on Earth-based supplies. Future missions to the Moon and Mars will require even more advanced life support systems, capable of recycling air, water, and waste.
Inflatable Habitats for Long-Term Living
Inflatable habitats, such as Bigelow’s Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) on the ISS, offer lightweight and expandable living spaces that can be easily transported and set up on other planets. These modules provide a practical solution for building sustainable habitats on the Moon, Mars, or even other moons in the solar system.
Key Life Support Innovations
-
Radiation Protection: New technologies, such as water-based radiation shields and magnetic field generators, are being developed to protect astronauts from harmful cosmic rays and solar flares.
-
Sustainable Lunar and Martian Habitats: Closed-loop life support systems and inflatable habitats will allow astronauts to live and work on the Moon or Mars for extended periods.
_1746526072.jpg)
In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU): Using Space to Survive in Space
In-situ resource utilization (ISRU) represents the next frontier in space sustainability. By using resources found on the Moon, Mars, or asteroids, ISRU minimizes reliance on Earth-based resupply missions.
Applications of ISRU
-
Lunar Bases: Extracting oxygen and water from lunar regolith will help sustain long-term lunar bases, reducing the need for costly supply missions.
-
Mars Colonization: ISRU will enable astronauts to produce water, oxygen, and fuel on Mars, making the red planet a viable location for human settlement.
-
Fuel Stations in Space: Fuel depots on the Moon or Mars could allow spacecraft to refuel, reducing the need to launch supplies from Earth.

Space Exploration and Technology Innovations
The benefits of space exploration also extend to technological advancements that have transformed everyday life. Space missions have driven the development of technologies that were once only available to astronauts but are now an integral part of modern society. Innovations such as GPS, satellite communication, medical imaging, and solar panels were all first developed for space exploration before making their way into widespread use on Earth.
Some notable examples of space spin-off technologies include:
-
GPS and Satellite Communications: Originally developed for military and space purposes, GPS technology is now an everyday tool for navigation, mapping, and communication.
-
Medical Imaging (MRI scans): Techniques developed for observing the human body in space have led to advancements in medical imaging, particularly MRI scans, which are crucial for diagnosing various conditions.
-
Robotic Surgery: Technologies developed to assist astronauts in space have improved medical precision on Earth, allowing for robotic surgeries with minimal invasiveness.
-
Solar Panels: Solar power, essential for generating energy on spacecraft, has become a key renewable energy source on Earth.
-
Water Purification Systems: Innovations from space research have contributed to water purification technologies, ensuring clean water access even in remote areas.
The Incredible Benefits of Space Exploration: Why We Should Reach for the Stars
Space exploration isn’t just about exploring the cosmos—it’s also about ensuring the survival of humanity. Monitoring space threats, such as asteroid impacts and solar flares, is a critical part of space research. Programs designed to track Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) help prevent potential catastrophes by identifying and redirecting dangerous asteroids. Additionally, space colonization is becoming an increasingly important consideration. By researching life on other planets, scientists are developing the technologies and strategies necessary for establishing sustainable colonies on Mars, the Moon, or other celestial bodies. These ventures not only offer humanity a backup plan in case of global crises but also provide opportunities for resource extraction and the expansion of human civilization beyond Earth.
Through space exploration, we gain knowledge that can be used to ensure the long-term survival of humanity, safeguarding our species from both space-related threats and Earth’s resource limitations.
- Scientific Advancements
Space exploration has expanded our understanding of the universe. Telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revolutionized our ability to observe distant galaxies, uncovering critical information about the origins of the universe and the potential for life beyond Earth. Missions to Mars, Europa, and beyond continue to uncover new insights into planetary systems and the possibility of extraterrestrial life.
- Economic Growth
Space exploration fuels job creation and economic growth. The rise of private space companies, such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic, has spurred the growth of high-tech industries, creating thousands of jobs and driving innovation in engineering, robotics, and aerospace. Additionally, the emerging space tourism industry holds the potential to generate billions of dollars in revenue.
- Environmental Benefits
Space exploration contributes to environmental protection by providing crucial data on climate change, deforestation, and pollution. Satellites play a key role in monitoring global warming and helping scientists track environmental changes, such as rising sea levels and melting ice caps.
- Human Survival
By studying space threats like asteroid impacts and solar flares, space exploration is helping safeguard humanity. The research and technology developed for space missions are also laying the groundwork for human colonization of other planets, providing a potential backup plan for humanity’s survival.
- Education and Inspiration
Space exploration plays a critical role in inspiring future generations. The benefits of space exploration extend to education by fostering an interest in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). Space missions like the Apollo Moon landings and the ongoing exploration of Mars spark the imaginations of students worldwide, encouraging them to pursue careers in these essential fields.
Furthermore, international collaborations, such as the International Space Station (ISS), demonstrate how space exploration can foster global cooperation, promoting peace and shared knowledge across borders. The technological advancements and scientific discoveries resulting from space missions not only contribute to our understanding of the universe but also fuel human curiosity and creativity.
Through space exploration, young minds are encouraged to reach for the stars, embodying the true benefits of space exploration—the inspiration to dream bigger and aim higher.
Reaching for the Stars
The benefits of space exploration are vast and wide-reaching, from scientific breakthroughs to technological innovations, economic growth, environmental conservation, and ensuring humanity’s survival. By continuing to explore space, we not only satisfy our curiosity but also improve life on Earth, create new opportunities, and inspire future generations to reach for the stars.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.


























