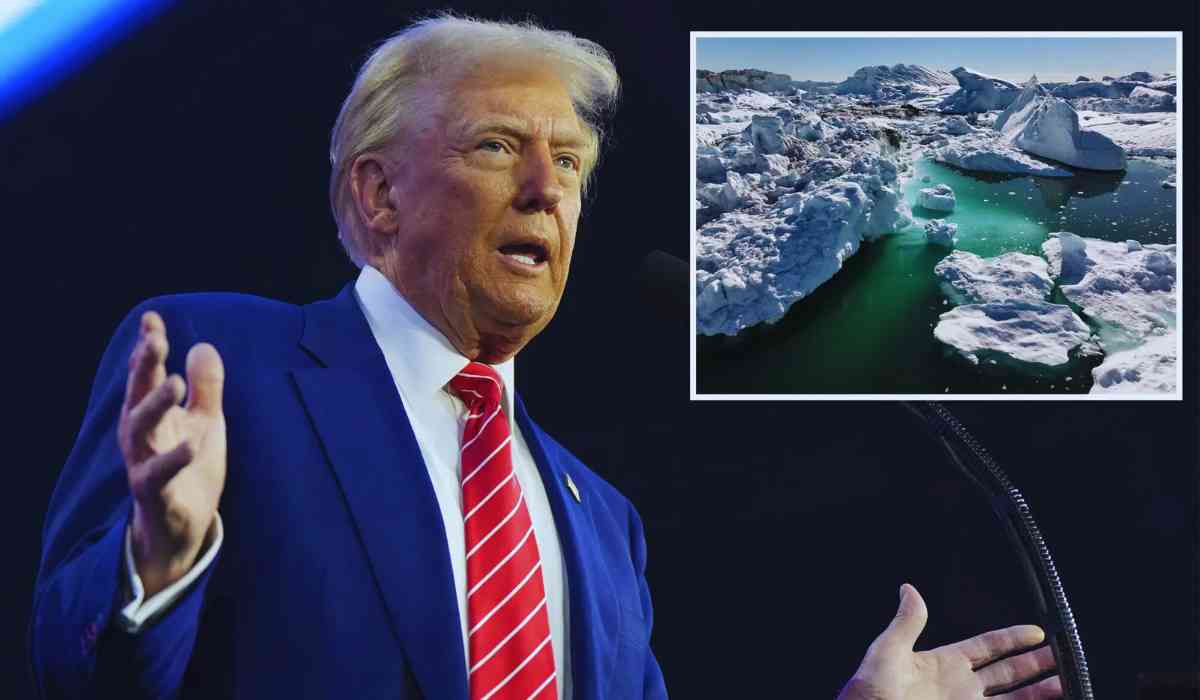
Donald Trump’s aspiration to acquire Greenland has resurfaced, prompting discussions about the island's potential value and its geopolitical significance. As of January 15, 2025, this topic remains relevant, especially in light of recent analyses estimating the cost of Greenland could range from $12.5 billion to $77 billion. This valuation comes from David Barker, a real estate developer and former economist at the New York Federal Reserve, who based his estimates on historical transactions involving the US Virgin Islands and Alaska, adjusted for inflation and economic growth.
Greenland's Strategic Importance
Greenland is not only rich in natural resources but also holds a vital strategic position in the North Atlantic. The island is home to significant reserves of minerals, oil, and natural gas, although these resources are largely untapped due to underdeveloped infrastructure. Currently, Greenland's economy heavily relies on fishing, which constitutes over 95% of its exports, alongside substantial annual subsidies from Denmark that cover half of its public budget.
The US maintains a military presence in Greenland through the Pituffik air base, established under a 1951 agreement with Denmark. This base is critical for US defense operations in the region. Historically, the US has shown interest in acquiring Greenland; a notable attempt occurred during the Cold War when an offer of $100 million in gold was made in 1946 but ultimately declined by Denmark.
Political Context
Trump's renewed interest in Greenland echoes his previous proposal in 2019, which was met with firm rejection from both Greenland and Denmark. Greenland's Prime Minister Mute Egede has been vocal about the island's right to self-determination, asserting that "Greenland is not for sale" and emphasizing that its future should be decided by its people.
Denmark's Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen also dismissed Trump’s acquisition proposals as "absurd," reaffirming that any decisions regarding Greenland's future must involve its residents.
Future Prospects
Should Greenland pursue independence from Denmark, it could consider entering a "free association" with the United States. This arrangement would potentially replace Danish subsidies with US support while granting military rights to the US.
However, experts caution that many Greenlanders prioritize their autonomy and welfare over being controlled by another foreign power.As discussions continue regarding the viability of Trump's ambitions and Greenland's political landscape, it remains clear that any future negotiations will hinge on the island's desire for self-governance and its strategic importance in global geopolitics.
What are the main reasons Greenland rejected Trump's offer?
Greenland's rejection of Donald Trump's offer to purchase the island can be attributed to several key factors:
1. Self-Determination and Autonomy
Greenland has been pursuing greater independence from Denmark, having achieved home rule in 1979 and expanded its autonomy further in 2008. The island's government, led by Prime Minister Múte Egede, emphasizes that any decisions regarding its future must be made by the Greenlandic people themselves. Egede has stated that "Greenland belongs to the Greenlanders," reinforcing the sentiment that the island is not a commodity for sale but a territory with its own aspirations and identity.
2. Denmark's Firm Stance
Danish Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen labeled Trump's interest as "absurd," firmly rejecting the notion of selling Greenland. Denmark, as a NATO ally of the United States, views Greenland as an integral part of its territory and is unlikely to relinquish control over it. Frederiksen has highlighted the importance of respecting Greenland's right to self-determination, indicating that any potential changes must involve the island's population..
3. Historical Context and Colonial Legacy
The historical context of colonialism plays a significant role in Greenland's rejection of Trump's offer. The island's predominantly Inuit population has experienced a long history of colonial rule, leading to a strong desire for self-governance and independence. Recent discussions around historical injustices have further fueled this sentiment, making the prospect of being sold or controlled by another nation particularly unappealing.
4. Economic Considerations
While Greenland possesses valuable natural resources, including minerals and rare earth elements, the island currently relies heavily on financial support from Denmark, receiving approximately $500 million annually. Many Greenlanders are wary of losing this support and becoming economically vulnerable if they were to align with the U.S. under Trump's vision. The potential for economic instability makes full independence or affiliation with another country a complex issue for many residents .
These factors collectively illustrate why Greenland has firmly rejected Trump's proposal, emphasizing their commitment to self-determination and a desire to shape their own future without external imposition.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
*The views expressed are personal to the author and do not reflect the platform's opinion of the same.
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.