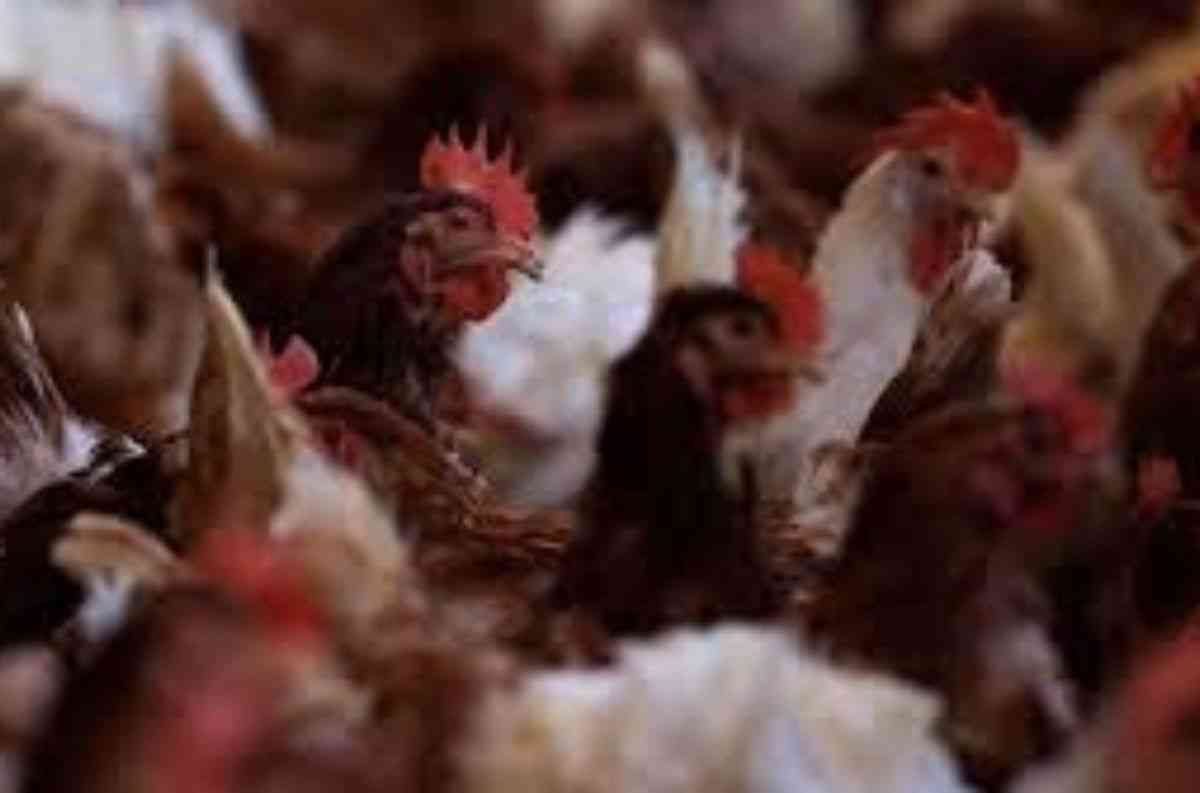
In a tragic development, the United States has recorded its first human death from the H5N1 bird flu. A Louisiana resident, over 65 years old with underlying health issues, succumbed to the illness after exposure to a backyard flock and wild birds. While authorities confirmed no spread to others, experts warn this alarming milestone highlights the virus's evolving threat. With a 50% global fatality rate, H5N1 remains a severe concern, demanding urgent precautions and heightened awareness.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) expressed its condolences while reinforcing the rarity of human deaths. The CDC stated that this is the first H5N1-related death in the U.S. among the 66 confirmed cases since 2024. It is a reminder to take preventive measures against this virus spread. Globally, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported over 950 cases of H5N1 in humans.
Rising Concerns and Human Risks
Bird flu viruses, such as H5N1, primarily affect birds and occasionally transfer to humans. In this case, exposure to birds is the primary source of infection. Also, the experts confirm that human-to-human spread is not possible from the evidence of this Louisiana patient. CDC states that the general public’s risk is low but the persons who are exposed to birds- such as poultry workers and farmers, are at risk of this infection.
Since the virus was first identified in 1996, outbreaks have been more frequent, especially in the past four years, affecting over 300 million birds worldwide. Beyond agriculture, infections are found to be in endangered species like California condors, posing a risk to wildlife.
The U.S. Response and Ongoing Research
To counter bird flu, the U.S. government is taking necessary actions by allocating $306 million for research and better monitoring of the virus. These are efforts to develop vaccines and track any changes in the virus that could help it spread more easily between people. The CDC is focused on preventing any mutations that could make treatments less effective.
Epidemiologists like Dr. Jennifer Nuzzo emphasize the virus's lethal potential. "The unchecked spread of H5N1 is alarming," she told AFP. "This death is a reminder of the importance of timely action to combat bird flu outbreaks."
Low General Risk
The Louisiana Department of Health reported that the deceased had contact with both backyard poultry and wild birds. With no identified cases of human-to-human transmission in either the U.S. or globally, bird flu symptoms like fever, cough, and in severe occurrences, respiratory distress, remain tied to direct animal contact. The CDC advises individuals working in high-risk environments to wear protective equipment and follow strict hygiene measures.
Moreover, outbreaks and transmission are fueling economic and livelihood strains across farm-reliant countries. In addition, virologists warn that bird flu mutations could increase pandemic risks. The CDC continues its "One Health" approach, a collaboration between public health, agriculture, and environmental experts.
Types of Bird Flu
Bird flu, or avian influenza, refers to influenza A viruses, which often infect birds but can also spread to other animals, including humans Here are some key types:
- H5N1: The main type causing severe cases and deaths, with high fatality rates.
- H5N2: Recently found in Mexico and linked to human deaths and poultry outbreaks.
- H5N6: Occasionally causes serious illness in humans.
- H5N8: Mainly affects birds, with few cases in humans.
- H7N9: Mainly seen in Asia with a few human cases.
- H9N2: A more common strain that usually causes mild illness in humans, with cases reported in India.
Global Bird Flu Situation
Bird flu is a serious problem around the world, especially in places like Asia and Africa where the disease is still causing deaths. Experts stress the need for urgent assessments in farming countries where people depend on poultry for their food and livelihood.
Globally, here’s an overview of bird flu cases:
- United States: 66 cases since 2024, with 1 death in Louisiana.
- Mexico: One death connected to H5N2, amidst poultry outbreaks.
- China and Vietnam: Report the majority of global H5N1 cases, facing significant challenges.
- India: Recently confirmed another case of H9N2, adding to the list.
- Canada: Has identified some isolated cases, with no deaths yet.
- Other Regions: Occasional infections have also been reported in places like Australia and Cambodia, underscoring the virus's widespread presence.
The UN and WHO stress preventive measures to mitigate the virus, calling for intensified farm immunizations and promoting vaccination among farm workers. However, "low-to-moderate" risks to humans underline the need for careful surveillance globally.
Outlook and Lessons
As we look at this Louisiana case, it gives us simple lessons. With rare but lethal human cases, the United States must remain focused on biosecurity. While this tragedy doesn’t signify an immediate pandemic threat, it reveals gaps to take the necessary awareness.
From wearing protective equipment while working with poultry to washing hands after any exposure to birds, simple actions could reduce infection risks significantly. The case also reminds us of the importance of continuous research into vaccines tailored to this strain and clear communication to the public about potential emerging health threats.
Bird flu remains an evolving challenge, but coordinated global efforts and local measures can help reduce its impacts.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
The views expressed are personal to the author and do not reflect the platform's opinion of the same.
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.
Author's Bio
Ashwini Devi S is a seasoned content writer having experience in creative content, blogs, SEO-optimised articles, and product descriptions. She has written website content for an interior design brand, curated content for a boutique jewelry brand, and has written eBook too. Her eBooklet is Modern Parenting available on amazon kindle.