In the fast-evolving digital world, innovation isn’t limited to startups or major tech giants. Cybercriminals, too, are constantly innovating—finding new vulnerabilities, exploiting technological gaps, and breaching defenses with increasingly complex attacks. To stay ahead, businesses must adopt advanced cybersecurity solutions that not only detect but proactively respond to emerging threats.
The urgency of this task became more evident during the COVID-19 pandemic, which accelerated digital transformation and remote work adoption. This transition, while necessary, expanded the attack surface for hackers and exposed vulnerabilities that traditional defenses couldn’t manage effectively.
As cyberattacks surge to record levels and threat actors grow more sophisticated, the global cybersecurity market is poised to reach a staggering $1.5 trillion. Companies across industries are investing heavily in advanced defense mechanisms to safeguard their data, systems, and workforce.

1. AI-Powered Cybersecurity Platforms
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing cybersecurity with its ability to detect and neutralize threats autonomously. By leveraging machine learning, AI-based platforms can analyze real-time data, track patterns, and adapt to new threats without human intervention.
Key Features:
-
Machine learning for continuous learning and adaptation
-
Real-time anomaly detection and threat response
-
Deep learning to monitor logs, transactions, and network traffic
-
Unsupervised learning to uncover unknown vulnerabilities
Key Benefits:
-
24/7 threat detection without manual oversight
-
Rapid identification of novel attack patterns
-
Reduced burden on IT security teams
-
Comprehensive digital infrastructure protection
2. Behavioral Analytics
Behavioral analytics is redefining cybersecurity by focusing on user behavior patterns. By analyzing daily user interactions, systems establish a behavioral baseline to detect deviations that could indicate security breaches.
Key Features:
-
Continuous monitoring of user actions
-
Detection of anomalies in data usage and access behavior
-
Integration with endpoint security and SIEM tools
Key Benefits:
-
Early detection of insider threats
-
Stronger identity and access control
-
Enhanced visibility into user activity
-
Reduced false positives in threat detection
3. Blockchain Technology
Originally designed for cryptocurrency, blockchain has become a powerful cybersecurity tool. Its decentralized and immutable ledger makes it nearly impossible to alter transaction history, ensuring data integrity and transparency.
Key Features:
-
Distributed ledger technology
-
Cryptographically secure and tamper-proof records
-
Timestamped and digitally signed transactions
-
Elimination of centralized authentication systems
Key Benefits:
-
Tamper-proof data records
-
Elimination of password-based vulnerabilities
-
Increased transparency and traceability
-
Resilient against fraud and data breaches
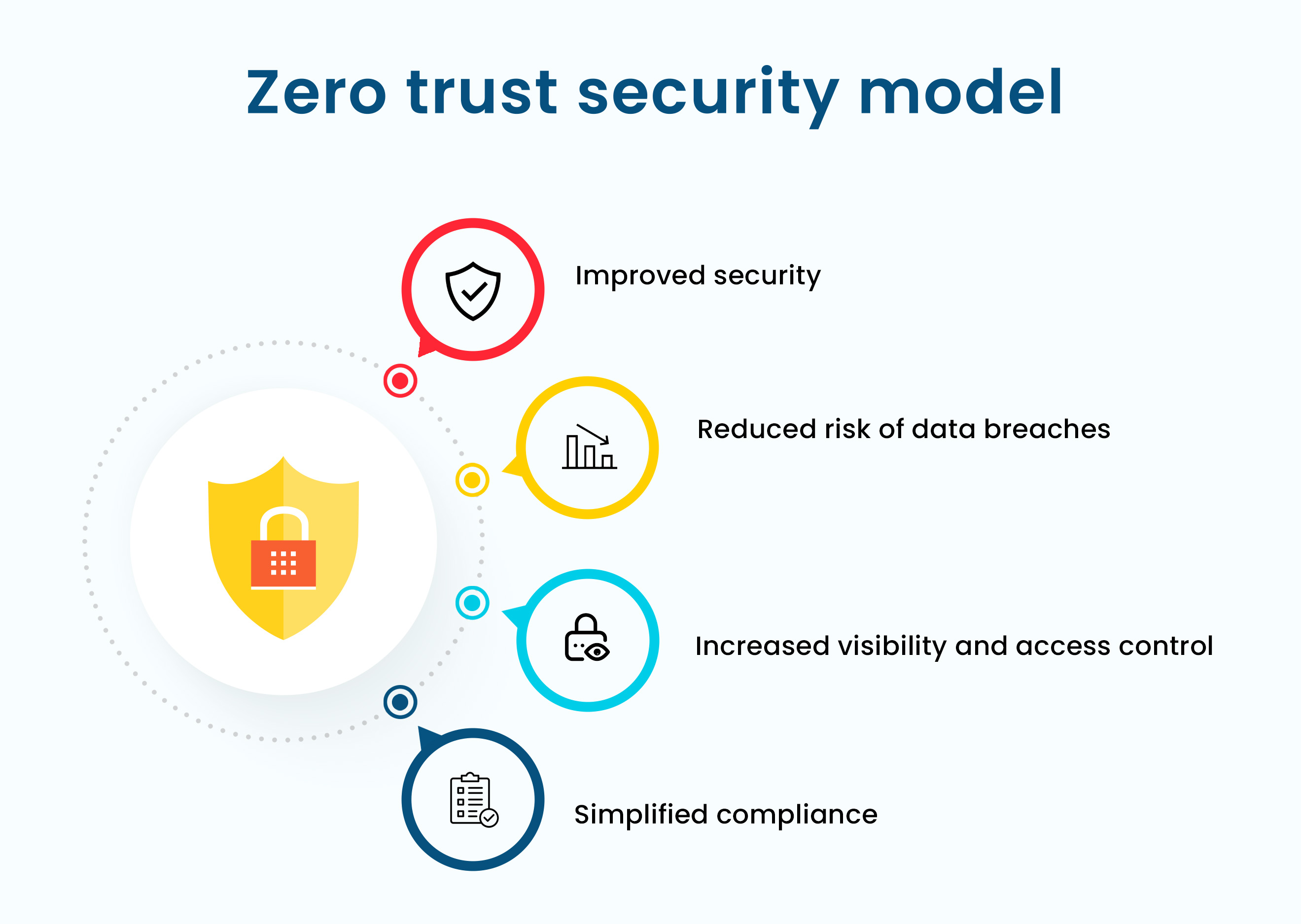
4. Zero Trust Model & Continuous Authentication
The Zero Trust model assumes that every user, device, and system—internal or external—must be verified before gaining access. This approach minimizes the risk of internal breaches and eliminates blind trust in any network component.
Key Features:
-
Continuous user validation
-
Micro-segmentation of data and assets
-
Biometric and multifactor authentication
-
Real-time threat detection and response
Key Benefits:
-
Drastically reduced attack surface
-
Equal protection from internal and external threats
-
Improved compliance and governance
-
Frictionless user authentication experiences
5. Hardware Authentication
Hardware authentication reinforces security by requiring a physical device—such as a token or security key—for user login, often used alongside a password or biometric verification.
Key Features:
-
Temporary cryptographic codes
-
Physical tokens or USB devices
-
Embedded authenticators and secure elements
-
Integration with 2FA and MFA systems
Key Benefits:
-
Strong defense against phishing attacks
-
Secure access control for sensitive systems
-
Enhanced user identity verification
-
Reduced dependency on passwords
6. Cloud-Based Biometric Solutions (Biometrics-as-a-Service - BaaS)
Cloud-based biometrics offers scalable, secure authentication without requiring large IT investments. These services are especially beneficial for small to medium enterprises seeking enterprise-grade security.
Key Features:
-
Fingerprint, facial, and voice recognition in the cloud
-
Seamless integration with cloud apps and devices
-
Centralized biometric data management
-
Pay-as-you-go SaaS model
Key Benefits:
-
Cost-effective biometric implementation
-
High scalability across user bases
-
Secure and frictionless user experience
-
Reduced infrastructure burden
7. Liveness Detection
Liveness detection ensures that biometric inputs—like a face or voice—are from real, living users and not spoofed photos or recordings. This technology is essential in preventing presentation attacks on biometric systems.
Key Features:
-
Active and passive liveness detection
-
AI-powered spoof detection algorithms
-
Integration with facial recognition and voice systems
-
No user interaction required for passive systems
Key Benefits:
-
Prevention of fake biometric attacks
-
Strengthened biometric system security
-
Enhanced user trust and privacy
-
Real-time spoof detection capabilities
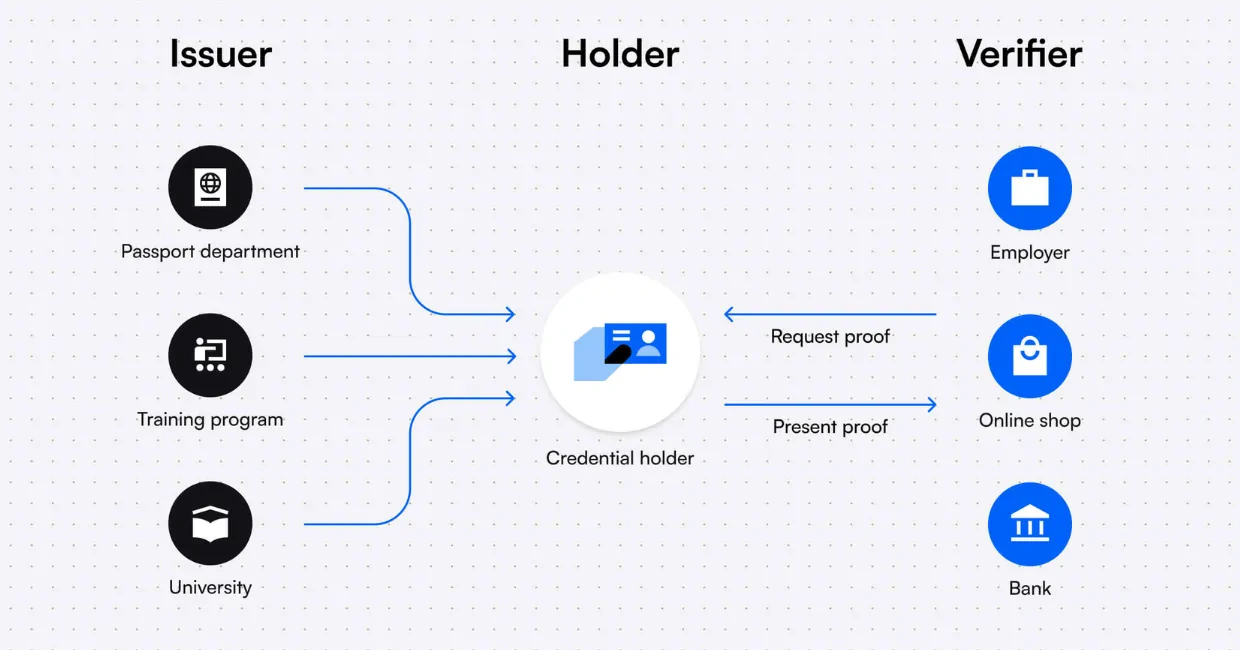
8. Decentralized Authentication
This innovation removes the need for a central authority in verifying identities. Instead, users maintain control of their credentials via decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and blockchain-backed identity trust fabrics.
Key Features:
-
User-centric identity systems
-
Blockchain-based identity verification
-
No centralized data storage
-
Crypto-biometrics for secure access
Key Benefits:
-
Improved privacy and user control
-
Reduced risk of centralized data breaches
-
Compliance-friendly authentication
-
Elimination of single points of failure
9. Deception Technology
Deception technology uses traps and decoys to detect and neutralize attackers early in the intrusion cycle. It mimics real systems to trick attackers into revealing their presence.
Key Features:
-
Fake systems, credentials, and data
-
Real-time threat alerts
-
Behavioral analytics to study attacker tactics
-
Integration with incident response tools
Key Benefits:
-
Early detection of advanced threats
-
Real-time incident containment
-
Reduced risk of data theft
-
Proactive insight into attacker behavior
10. Cybersecurity Mesh Platforms
Cybersecurity mesh provides a unified security structure across a distributed network, ensuring consistent policy enforcement and visibility across all digital touchpoints.
Key Features:
-
Modular and API-driven security layers
-
Integration with cloud and IoT systems
-
Automated threat isolation and response
-
Unified access management
Key Benefits:
-
Seamless protection across cloud and on-prem environments
-
Reduced attack surfaces and security gaps
-
Real-time coordination of defenses
-
Scalable, resilient security architecture
11. Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
MDR services offer organizations 24/7 expert monitoring, threat detection, and response without needing an in-house cybersecurity team.
Key Features:
-
24/7 threat monitoring
-
Access to skilled security analysts
-
Use of SIEM, EDR, and deception technologies
-
Comprehensive response playbooks
Key Benefits:
-
Enterprise-grade protection for all business sizes
-
Fast, effective incident response
-
Reduced investment in internal cybersecurity teams
-
Improved regulatory compliance
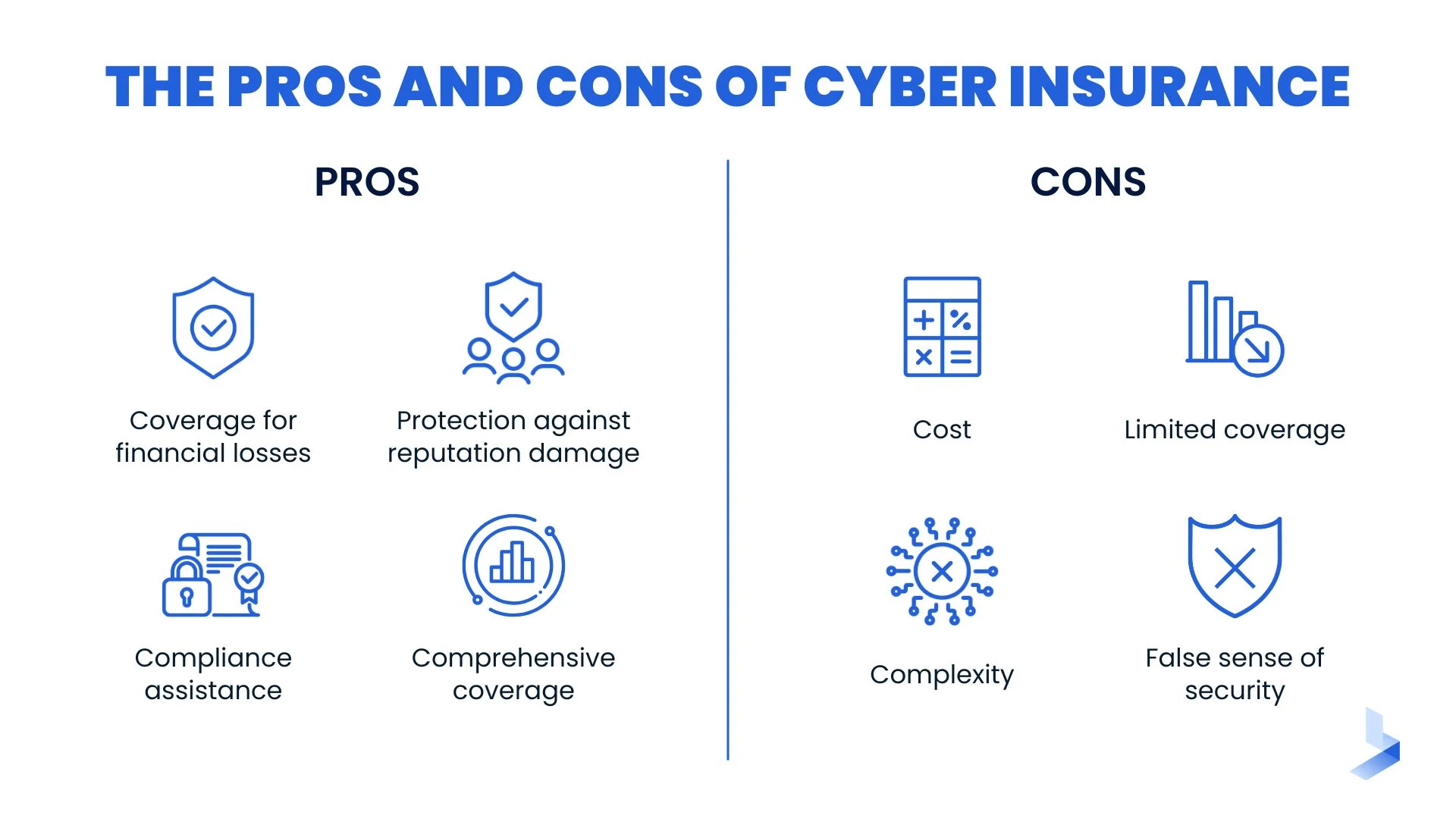
12. Cyber Insurance
Even the best cybersecurity defenses can’t guarantee zero incidents. Cyber insurance offers financial protection and crisis management support in the event of a breach.
Key Features:
-
Coverage for data breaches, business interruption, and lawsuits
-
Support for PR and legal management
-
Customizable policy options
-
Compliance-driven underwriting
Key Benefits:
-
Reduced financial impact from cyber incidents
-
Confidence in risk management planning
-
Enhanced stakeholder trust
-
Peace of mind for business continuity
Final Thoughts: Cybersecurity Innovation as a Business Imperative
Cybersecurity is no longer optional—it’s foundational to every modern business. While cybercriminals continue to innovate, these 12 technological advancements empower businesses to stay one step ahead.
Investing in these innovations means building a secure, resilient infrastructure that supports growth, protects stakeholders, and ensures continuity even amidst the most complex threats.
Whether you implement a few or all of these technologies, even incremental adoption can significantly reduce your cyber risk. Combine proactive solutions with strong policies and cyber insurance, and your organization becomes far more secure in an increasingly digital world.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.






















