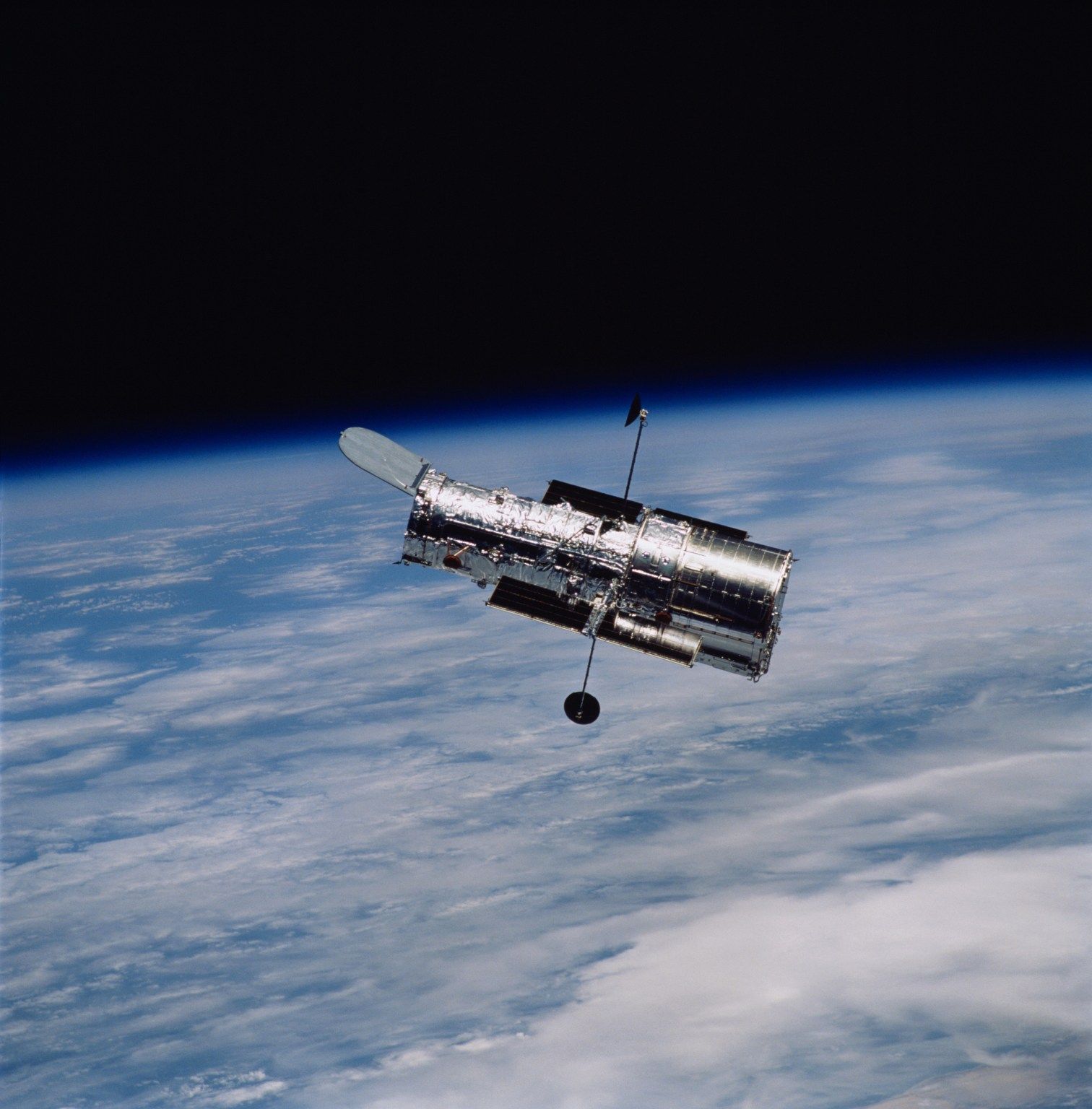
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was the pioneering optical observatory launched into Earth's orbit. The Earth's atmosphere interferes with the observations of celestial objects from the ground by either absorbing or distorting the incoming light rays. In contrast, a telescope positioned in outer space remains unaffected by the atmosphere and captures images with significantly enhanced brightness, sharpness, and detail as compared to ground-based telescopes equipped with similar optics.
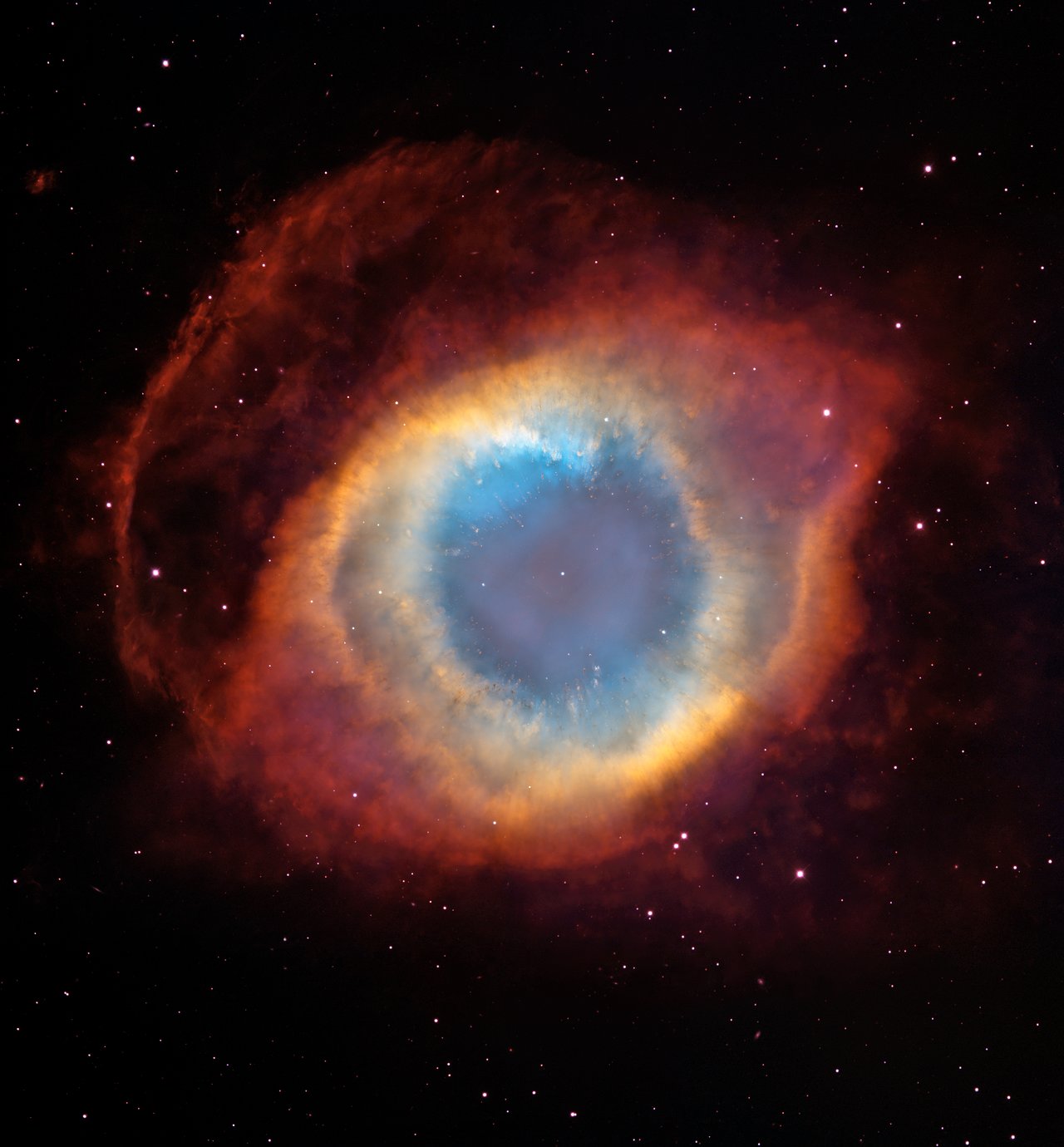
In its thirty years of operation, The Hubble Space Telescope has changed the perspective of how we visualise the cosmos. Based on the data given by the telescope and the beautifully captured digital images, the scientific knowledge of our solar system has been vast.
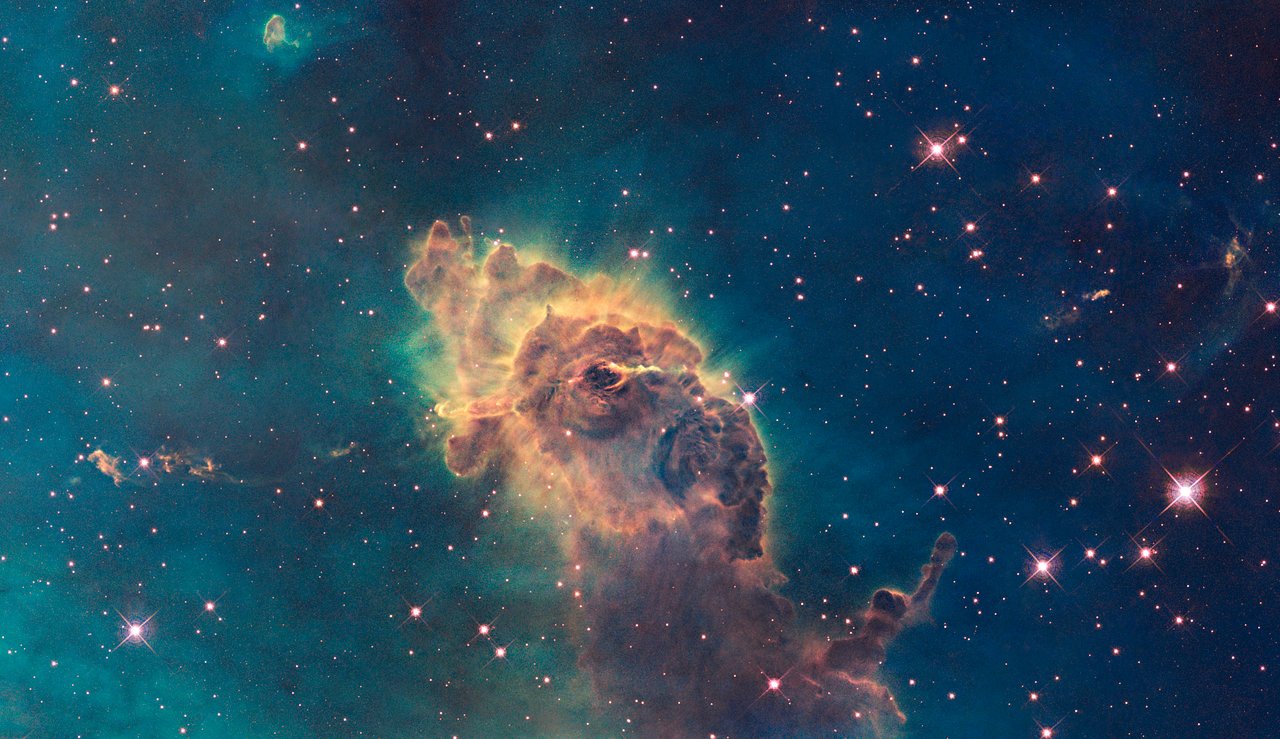

The 1995 portrayal of the Eagle Nebula played a crucial role in restoring the Hubble Space Telescope's reputation following its initial focusing issues. This image, unveiled a few months after astronauts had repaired the telescope, publicly demonstrated the visual potential of Hubble's imagery. The enthusiastic response from the public encouraged the creation of more Hubble images. Specifically, it served as an inspiration for a team of astronomers and image experts at the Space Telescope Science Institute, a research facility in Baltimore, Maryland responsible for managing the telescope, leading to the formation of the Hubble Heritage Project. This initiative embarked on releasing captivating images on a nearly monthly basis from October 1998 to May 2016.

These stunning images were unveiled in honor of Jupiter's opposition to the Sun when observed from Earth. The Hubble Telescope captures images in the optical light spectrum, enabling it to perceive details beyond the range of human vision. By utilizing various wavelengths, scientists can discern diverse characteristics of celestial objects.
Hubble's observation of Jupiter facilitates the study of its tumultuous atmosphere, specifically focusing on the massive storm known as The Great Red Spot. “While the storm appears red to the naked eye, this ultraviolet image portrays it as darker because particles in the high-altitude haze absorb light at these specific wavelengths”, as explained by NASA.” The reddish and undulating polar hazes are slightly less effective at absorbing this light, possibly due to variations in particle size, composition, or altitude”.
In the end it can be said that Hubble Telescope’s impact extends beyond scientific discoveries. Its observations of nebulae, planets, galaxies, and star fields have influenced our perception of these celestial entities and our connection to them, making it commonplace to imagine our universe in vivid colours and exceptional detail.
© Copyright 2023. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.








