Everyone is talking about "permaculture" these days, and for good reason. Global interest in green and healthy farming is growing. People who practice permaculture try to make their yards work like the closed-loop processes that happen in nature. This article explains how learning about the main ideas and methods of permaculture can change how we live on the land.
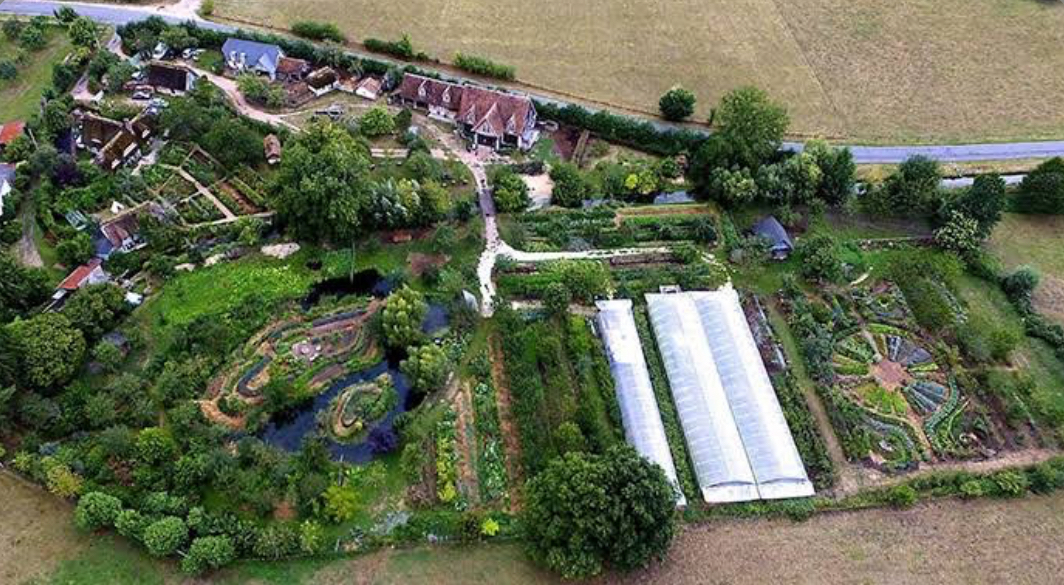

An Overview of a Holistic Approach
There is more to permaculture than just growing food. This way of thinking stresses working with nature instead of against it. Similar to natural ecosystems, it brings together resources, people, land, and the environment in a way that works well together. Permaculture is a planning science that can be used in spaces of all sizes, from small balconies in cities to large farms.

People think of Bill Mollison as the "father" of permaculture. He established the basic rules for this practice:
- Earth Care: Using environmentally friendly methods to protect the planet's processes that keep life going.
- People care: means making sure that people's wants are met so they can live a healthy, happy life.
- A fair share : means taking only what we need and giving the rest to the group, which includes other species.
These ethics underpin the twelve permaculture principles, a set of guidelines for designing resilient and productive systems. Some key principles include:
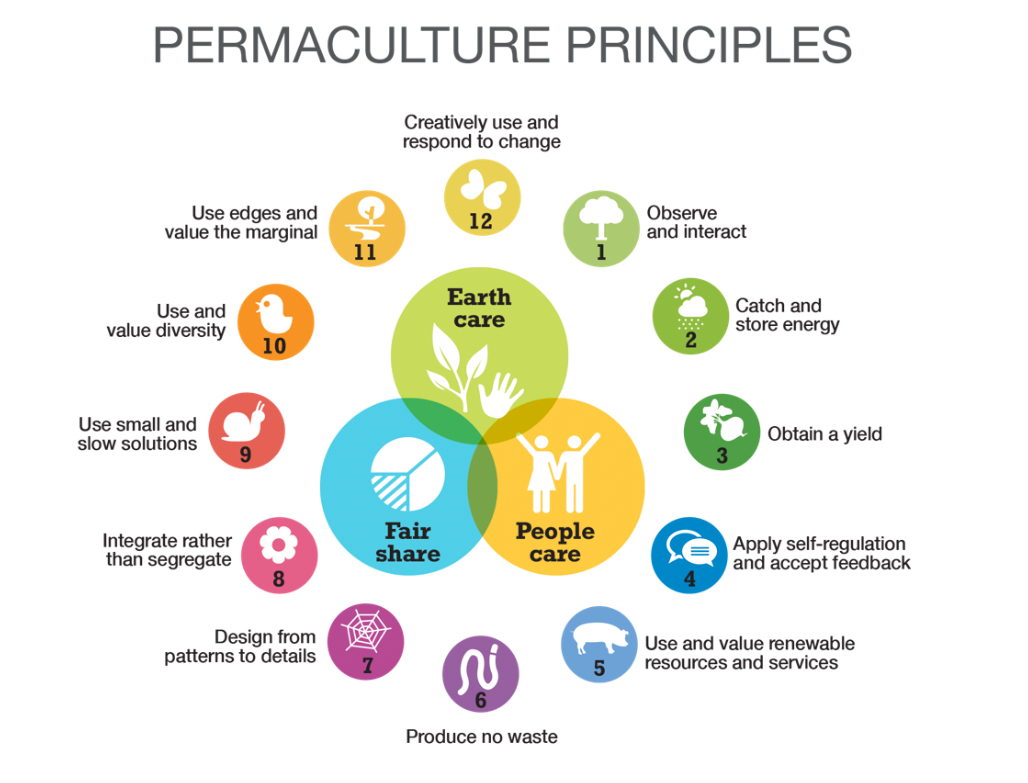
-
Watch and interact: Before making changes, carefully study the land and how it works naturally.
-
Make No Waste: Plan systems to use the outputs of one part as inputs for another, minimizing waste.
-
Gather and store energy: For long-term effects, use renewable resources such as sunlight and rainwater.
-
Integrate instead of segregate: Get different parts of the system to work together in a way that benefits everyone.
-
Purpose and value Diversity: To make environments more stable and resilient, copy the variety that exists in nature.
The Benefits of Sustainable Permaculture

In many ways, permaculture is beneficial for farmers, the earth, and society as a whole.
-
Cheaper costs: Because permaculture methods often don't need as many outside inputs like pesticides and fertilisers, the cost of production is cheaper.
- Less Waste: Permaculture reduces waste and promotes resource protection by closing the loop on resource use.
-
Water Efficiency: Collecting rainwater and using water-efficient gardening methods are ways to protect our limited water supplies.
-
More self-sufficiency: permaculture gives farms the tools they need to grow more types of food, which means they depend less on food from other countries.
-
Increased Biodiversity: Permaculture creates diverse ecosystems that draw beneficial insects, pollinators, and soil microbes. This makes the environment healthier.
-
Pollution: The use of natural processes instead of chemicals reduces pollution. These changes clean up the land, water, and air.
-
Low-Maintenance Systems: Permaculture designs often work on their own, so they need less help from people to be productive in the long run.

Examples of Common Practices for Putting Permaculture into Action
Certain permaculture methods are applicable in specific situations, while others are not. The following is a list of common activities people engage in:
-
Water management strategies include collecting rainwater, installing swales, and using greywater devices.
-
Environmentally friendly building: building with nearby and easily renewable materials makes buildings that last and use little energy.
-
As you plant trees, shrubs, and crops together in agroforestry, you make systems that are more diverse, useful, and good for the environment.
-
Grow different kinds of plants together to get better yields, keep pests away, and draw good bugs. We refer to this as intercropping and companion planting.
-
Turning organic waste into nutrient-rich compost and mulching: Both composting and mulching are good ways to support healthy soil.
-
Soil structure is protected, and healthy microorganisms thrive in no-till or reduced-till farming because the soil is disturbed as little as possible.
-
The goal of designed gardens like permaculture gardens is to get the most out of their space by combining different things like flowers, herbs, veggies, and fruit trees.

Conclusion: A Sustainable Future with Permaculture
As we work towards a more healthy future, permaculture becomes more appealing. To make farming systems that are productive, long-lasting, and good for future generations, permaculture ideals tell us to work with nature instead of against it. The all-around view of permaculture is helpful for creating a more sustainable future as we work to make the world healthier and ensure everyone has enough food.
Image Source: Multiple Agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.






















