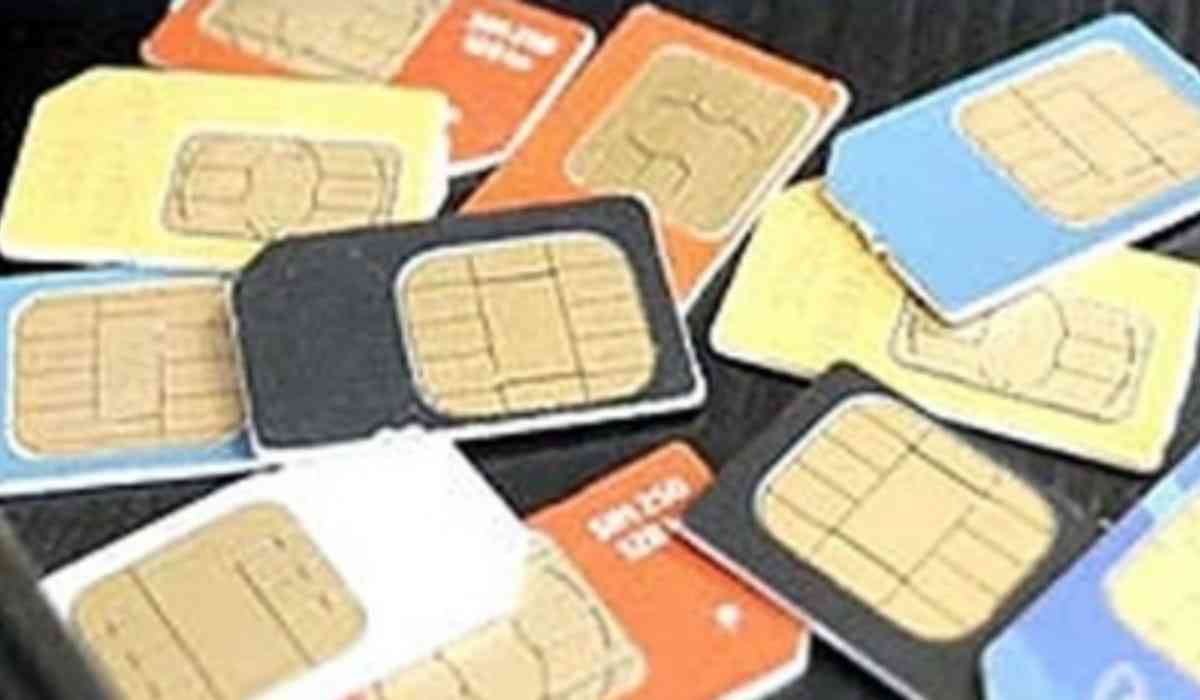
A new section of the Telecommunications Bill 2023 was introduced in the Lok Sabha on December 18 and requires telecom firms (telcos) to get biometric identification before providing SIM cards to customers.
According to the proposed legislation, "Any authorized entity that provides telecommunication services that the Central Government may notify it to must use verifiable biometric-based identification to identify the person to whom it provides telecommunication services."

The bill, which was introduced in Parliament on December 18 by Telecom Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw, does not include over-the-top (OTT) services such as online messaging, e-commerce, and payments under the definition of telecommunication services.This follows a significant outcry from internet firms and civic society last year when an earlier draft of the bill brought OTT services under its jurisdiction.
The primary goal of the bill's numerous amendments to the telecom licensing and spectrum allocation system is to streamline business processes in the rapidly expanding telecom industry.
BENIFIT OF BIOMETRIC IDENTIFICATION FOR NEW SIM CARD
Additionally, it has made it mandatory to obtain customers' prior authorization before sending them advertisements and promotional messages for products, services, or financial investment solicitations.
It further specifies that an authorized provider of telecommunication services must set up an online portal via which consumers can file complaints about the telecommunication service and have those complaints resolved.
It further specifies that an authorized provider of telecommunication services must set up an online portal via which consumers can file complaints about the telecommunication service and have those complaints resolved.
MORE ABOUT TELECOME BILL 2023
On December 18, 2023, the Telecommunications Bill, 2023 was presented in the Lok Sabha. It aims to control telecommunication-related activity. The Indian Telegraph Act of 1885, the Telegraph Wires (Unlawful Possession) Act of 1950, and the Indian Wireless Telegraphy Act of 1933 are all repealed by it. The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Act, 1997 is also amended by it.
The bill gives the government the authority to forbid or stop the use of telecom equipment from nations or individuals who may be notified in the event of a national security emergency. Telecom equipment must only be purchased from reliable vendors. The bill suggests obtaining prior approval before sending out any promotional or advertising messages in order to safeguard telecom customers.
IMAGE SOURCE-X
Ⓒ Copyright 2023. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.