Ever felt like you're melting faster than an ice cream cone on a sunny day? Welcome to the wild world of heat stroke!

What is Heatstroke?
Heatstroke is a critical condition caused by excessive heat exposure, where the body fails to regulate its temperature through sweat production. With core temperatures reaching up to 40 degrees Celsius, it becomes life-threatening. This imbalance disrupts essential salts like sodium and potassium, leading to organ dysfunction and a range of symptoms. Heatstroke is also known as hyperthermia or heat illness and can stem from milder heat-related issues like exhaustion, fainting, or cramping.

Types of Heatstroke
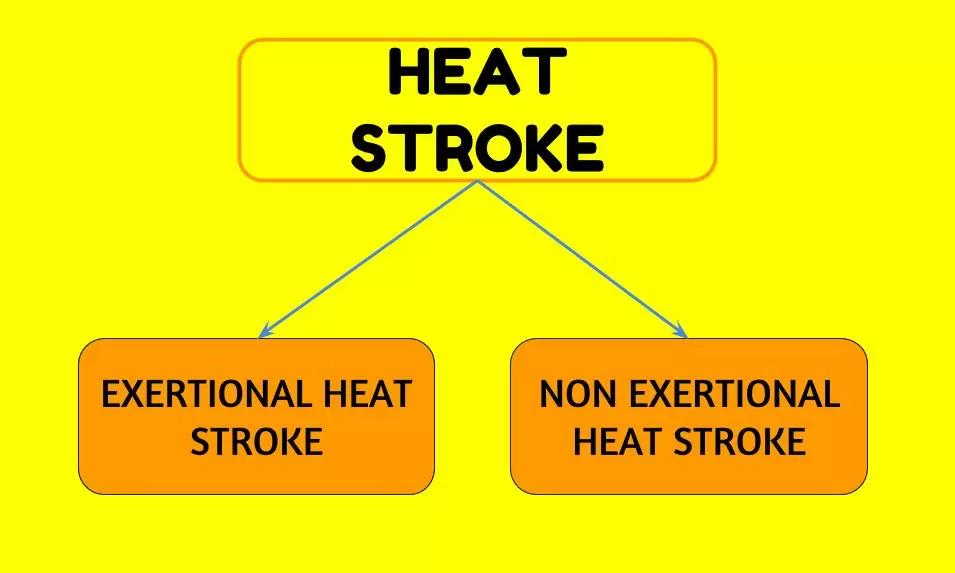
Heat stroke comes in two primary forms:
-
Exertional Heat Stroke (EHS)
EHS happens when individuals overheat during intense physical activity in hot or humid environments. It commonly affects athletes, soldiers, and outdoor laborers who fail to take sufficient breaks or stay hydrated. EHS can emerge within a few hours.
-
Nonexertional (Classic) Heat Stroke (NEHS)
NEHS occurs when individuals endure prolonged exposure to hot, humid conditions, particularly during heatwaves. This type primarily impacts older adults, individuals with chronic ailments, and infants who struggle to regulate their body temperature. NEHS typically develops over several days.
How serious can it be?
-
Heat Stroke Severity: Heat stroke poses a serious threat, potentially leading to fatality or organ damage, particularly affecting the brain.
-
Brain Impact: Heat stroke can cause cognitive impairment, drowsiness, and in severe cases, coma, by affecting brain function.
-
Organ Damage: Kidney and liver damage are common consequences of heat stroke, ultimately leading to organ failure and death.
-
Cell Instability: Elevated body temperatures destabilize cells, impacting the central nervous system, brain, and organs.
-
Brain Shutdown: Heat-induced swelling causes the brain to shut down, disrupting communication with organs.
-
Inflammation Effects: Inflammation from extreme temperatures disrupts nerve and brain function, releasing harmful cytotoxins.
-
Intestinal Permeability: Increased cytokine release due to heat can raise gut permeability, releasing substances that are normally contained.
-
Blood Vessel Response: Heat causes blood vessels to dilate excessively, potentially leading to scenarios akin to septic shock.
-
Clotting Risk: Excessive heat can induce blood clotting, impeding oxygen and nutrient transport vital for organ function.
-
Consequences: Heat stroke can result in unconsciousness, coma, convulsions, and eventually organ failure and death, as tragically seen in some cases.
Symptoms of heatstroke
Heatstroke can occur suddenly, but warning signs often precede it. Adults over 65, infants, and individuals engaging in outdoor activities in hot, humid conditions are particularly at risk. While certain groups are more susceptible, anyone can experience heatstroke, necessitating awareness of symptoms. Elderly individuals, children, and those with existing health conditions require special attention due to increased susceptibility to heat-related complications.
Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention:
-
Fainting
-
Lightheadedness
-
Red, hot, and dry skin
-
Seizures
-
Unconsciousness
-
Absence of Sweating Despite High Body Temperature
-
High Fever (Hot Skin)
-
Excessive or Absent Sweating (Anhidrosis)
-
Muscle Cramps
-
Rapid Pulse and Heart Rate
-
Low Blood Pressure
-
Rapid Breathing
-
Loss of Balance
-
Disorientation
-
Irrational or Erratic Behavior
-
Dizziness
-
Headache
-
Nausea and Vomiting
-
Dehydration (Dry Mouth and Intense Thirst)
-
Low Urine Output or Dark Urine
-
Physical Collapse
-
Coma

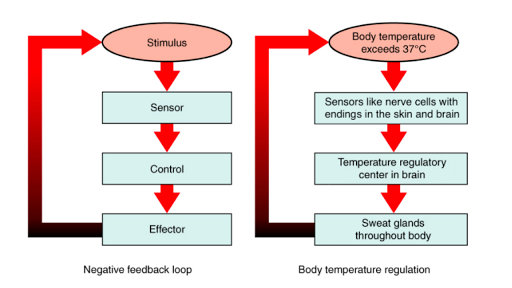
The body’s cooling system
Maintaining a body temperature of 37 degrees Celsius is crucial for optimal bodily functions. Our bodies employ various homeostatic mechanisms like shivering and sweating to either generate or release heat. To cool down, humans rely on several methods including conduction, convection, evaporation, and radiation.
Conduction occurs through direct contact with cooler objects, such as touching ice water. Convection, contributing to approximately 10 percent of heat loss, involves heat transferring to the surrounding air or water, often aided by methods like using a fan or taking a cold shower. Evaporation accounts for roughly 35 percent of heat loss, while radiation, comprising about 65 percent, transfers heat away from the body in the form of electromagnetic waves.
However, when ambient temperatures surpass 35 degrees Celsius, radiation becomes less effective. Various factors like clothing, hydration levels, humidity, and acclimatization can influence the efficiency of these heat-regulating mechanisms.
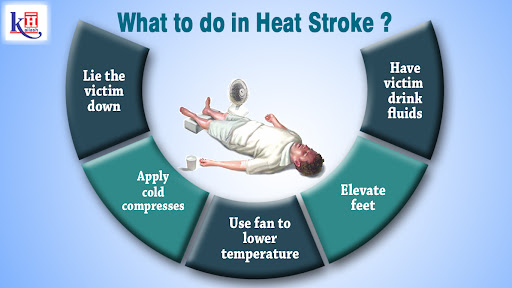
First aid for heatstroke
When facing symptoms of heatstroke, it's crucial to take immediate steps to lower body temperature while awaiting professional medical assistance.
Here's what you can do:
-
Find relief from the heat by moving to an air-conditioned space or a shaded area.
-
Remove any excess clothing to help facilitate cooling.
-
Consider immersing the body in a cold-water bath or ice bath to rapidly lower temperature.
-
If a cold-water bath isn't feasible, apply cold compresses to key areas such as the groin, back of the neck, forehead, and armpits.
-
If conscious and able to tolerate fluids, drink cool or cold water or suck on ice chips to aid hydration and cooling.
-
Remember, seeking medical evaluation and treatment is imperative, even if symptoms improve after these initial measures.
Prevention from heatstroke
-
To minimize heat-related risks, it's recommended to refrain from outdoor activities between midday and 3 pm.
-
During this period, avoid engaging in strenuous exercises or activities.
-
Ensure adequate hydration even if you don't feel thirsty by regularly consuming water. Additionally, opt for hydrating beverages like lassi, buttermilk, lemon water, or ORS to maintain electrolyte balance.
-
Steer clear of drinks like tea, coffee, alcohol, and carbonated beverages, as they can exacerbate dehydration.
-
Wear appropriate attire such as shoes, an umbrella, goggles, and loose-fitting cotton clothes in lighter shades.
-
Apply sunscreen with a minimum SPF of 30 to shield your skin from harmful UV rays.
-
Keep your body temperature regulated by taking cold showers and using damp cloths.

Heatwave impact on Indian Economy
The scorching heatwaves sweeping across India aren't just a matter of discomfort; they're inflicting profound wounds on the nation's economy. Beyond the visible toll on individuals, from diminished productivity to stalled construction projects, strained power grids, and farmers grappling with poverty, lies a deeper economic narrative of distress. As temperatures soar, so do the economic challenges. The burning question: what exactly is the toll of these heatwaves on India's economy, and what shadows might they cast on its future?
Workforce Productivity
-
Heatwave Impact on Workforce Productivity:
-
During heatwaves, people's productivity declines due to high temperatures, especially at night.
-
Urban areas suffer more due to the urban heat island effect, making cities significantly hotter than their surroundings.
-
-
Devastating Effects in India:
-
In India, where 45.76% of the workforce is in agriculture and 83% work in the unorganised sector, heatwaves pose severe challenges.
-
Low-income households, lacking adequate water and cooling resources, face heightened risks.
-
Outdoor workers, the elderly, and children are particularly vulnerable to heat-related illnesses.
-
-
Health Risks and Mortality:
-
Heatwaves increase the risk of heat exhaustion and heatstroke, contributing to a significant number of fatalities.
-
The World Health Organization reports over 166,000 deaths attributed to heatwaves between 1998 and 2017.
-
-
Economic Impact:
-
Construction activities halt during extreme heat, affecting GDP growth.
-
A 2023 Cambridge study highlighted a potential 15% loss in outdoor working capacity due to extreme heat, impacting around 480 million people.
-
By 2050, this could result in a 2.8% GDP loss, particularly affecting heat-exposed sectors like agriculture, mining, construction, and manufacturing.
-
On farmers, vegetable prices and inflation
-
Impact of Heatwaves on Water Reservoirs:
-
Severe heatwaves are straining power grids and leading to a significant decrease in water levels in major reservoirs across India.
-
Water storage in 150 key reservoirs has hit its lowest point in five years, exacerbating drought-like conditions in various regions.
-
Currently, water levels stand at only 35% of their storage capacity, with a notable 17% decrease compared to the same period last year.
-
Particularly in South India, 42 reservoirs are operating at a mere 23% of their capacity, intensifying water scarcity.
-
-
Consequences for Farming and Vegetable Prices:
-
The dwindling water reservoir levels pose multifaceted challenges for agricultural activities.
-
Farmers face difficulties accessing water for both drinking and irrigation purposes, impacting crop cultivation and livestock fodder production.
-
Furthermore, heatwaves adversely affect horticulture, exacerbating the already strained situation.
-
The ripple effect extends to vegetable prices, potentially triggering inflationary pressures within the economy.
-
Analysts, including Vivek Kumar from QuantEco, anticipate a surge in vegetable prices within a month, attributing it to the ongoing heatwave.
-
-
Concerns Raised by Financial Institutions:
-
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has expressed apprehensions regarding the potential inflationary impact of rising food prices due to the prevailing weather conditions.
-
There is a growing concern that prolonged heatwaves could impede the process of disinflation and sustain elevated vegetable prices, necessitating careful monitoring and potential adjustments in monetary policy.
-

On Agriculture and Healthcare
-
Agricultural Impoverishment:
-
Farmers in regions experiencing heightened weather extremes are facing increased financial strain.
-
The escalating frequency of heatwaves contributes to declining agricultural productivity, exacerbating poverty among farmers.
-
-
Strain on Healthcare System:
-
India's healthcare infrastructure faces significant strain during heatwaves.
-
Conditions like heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and related illnesses pose life-threatening risks.
-
Hospitals often experience a surge in patient admissions, overwhelming medical resources and personnel.
-

On the Electricity Grid
-
Increased Power Demand:
-
India anticipates a surge in power demand, potentially reaching 260 GW during the upcoming summer.
-
Peak demand reached a record high of 243 GW in the preceding September, indicating a continual upward trend.
-
-
Preparedness Meetings:
-
Union power ministry officials are conducting review meetings in collaboration with other relevant ministries and power companies.
-
These discussions aim to strategize and prepare for the potential challenges posed by extreme heatwaves.
-
-
Consequences of Power Shortages:
-
Inadequate power supply could necessitate electricity cuts in various regions of the country.
-
Such interruptions not only disrupt daily life but also hamper industrial productivity.
-
-
Economic Impact:
-
Studies reveal significant economic losses, with India facing annual food losses amounting to $13 billion.
-
Only a small fraction (four percent) of perishable produce benefits from cold chain facilities, exacerbating food wastage issues.
-

On businesses
-
Business Opportunities Amidst Changing Trends:
-
While certain sectors face challenges, opportunities arise for others.
-
Specific businesses, such as those in the AC and refrigerator manufacturing industry, stand to gain substantially.
-
-
Potential Growth in AC Market:
-
Projections suggest a significant upsurge in sales for AC manufacturers, estimated to exceed 1.15 crore units in the current year.
-
Factors contributing to this growth include a forecasted hot summer and a rise in disposable income among consumers.
-
-
Optimistic Outlook for Top Brands:
-
Leading brands like Daikin, Panasonic, LG Electronics, Blue Star, Godrej Appliances, and Lloyd anticipate a 25% increase in sales.
-
The surge in demand is expected to be particularly pronounced in Tier-III towns and smaller markets.
-
-
Impact on Employment:
-
The expansion of the cooling products market is poised to generate employment opportunities across various sectors.
-
Increased demand typically translates to a higher need for workers in manufacturing, retail, installation, and after-sales services.
-

Future impact
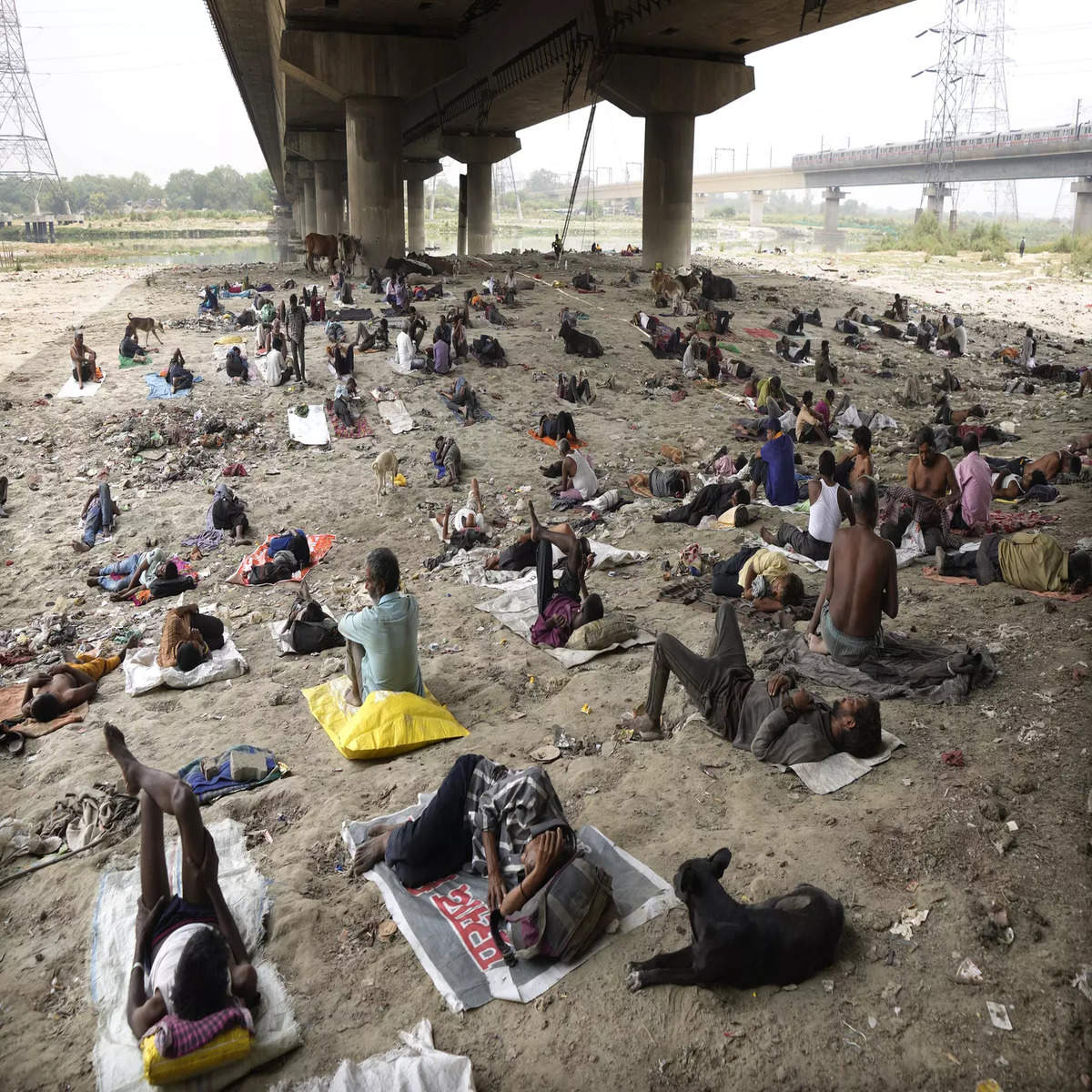
In the looming future, dire consequences await. By 2030, India might shoulder a staggering 34 million of the predicted 80 million global job cuts due to declining productivity from heat stress, as per a World Bank report. With a whopping 75 percent of Indian workers battling heat-induced stress, the nation could face a GDP loss of up to 4.5 percent (equivalent to roughly $150-250 billion) by the decade's end, states a McKinsey Global Institute report.
Experts caution that India must brace itself for the impact. While strides have been made in heat mitigation, including recognizing heatwaves in disaster relief plans, there's a pressing need to expedite implementation. Ramit Debnath from the University of Cambridge emphasizes the importance of optimizing existing plans, stressing that although India's adaptation measures are robust on paper, their execution will be the key determinant of success.
And remember, when it comes to battling heatstroke, prevention is cooler than a cucumber in an ice bath! Stay chill, literally and figuratively!
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.






















