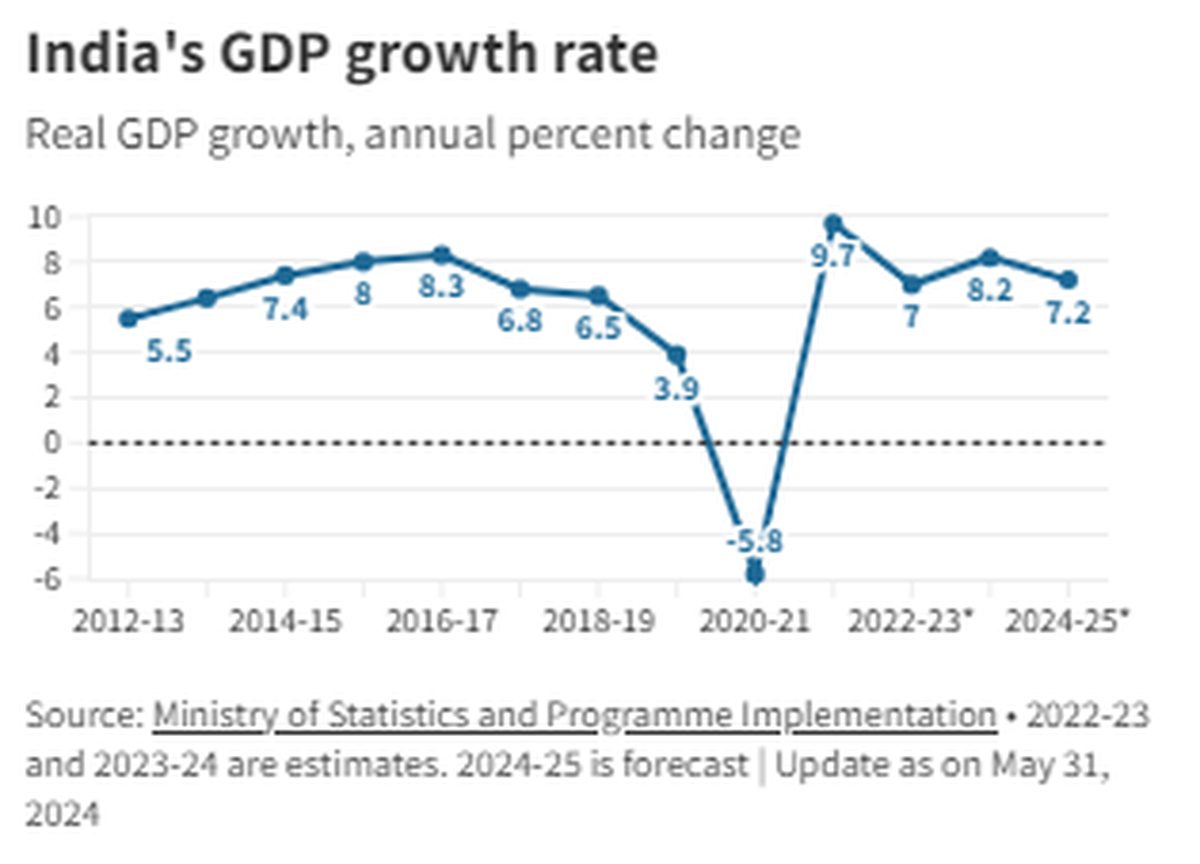
On July 24, 2024, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Economic Survey for the fiscal year 2023-24 in Parliament. This survey sets the groundwork for the Union Budget 2024-25, which was unveiled in the Lok Sabha on July 23, 2024. The Economic Survey offers an optimistic view of India's growth prospects and macroeconomic conditions. It projects a GDP growth rate of 6.5-7 percent for FY25 and anticipates a decrease in inflation to 4.5 percent. However, the survey also highlights several pressing issues related to the youth of the country.
The Economic Survey 2023-24 delves into various factors influencing India’s economic landscape, particularly focusing on the health and habits of the younger population. The survey underscores that while India's growth trajectory appears robust, certain factors could undermine its economic potential if not addressed.

-
Impact on Economic Potential
The survey identifies social media, excessive screen time, and unhealthy food habits as significant threats to India's economic potential. It emphasizes that for the working-age population to be effectively employed and contribute to the economy, they must maintain good health and acquire relevant skills. The survey highlights the detrimental effects of modern lifestyle choices, noting that these factors can compromise public health, reduce productivity, and ultimately diminish India's economic growth.
-
Private Sector's Role
The private sector is noted for its role in perpetuating these 'toxic habits'. The survey criticizes the sector’s contribution to unhealthy trends, including the proliferation of social media and sedentary lifestyles, which are seen as short-sighted and potentially harmful to public health and productivity.

-
Unhealthy Food Habits
According to the survey, the dietary habits of Indians are shifting towards less healthy and environmentally unsustainable practices. It argues that traditional Indian diets, which have historically promoted health and environmental harmony, offer valuable lessons for modern eating habits. Embracing these traditional practices could be beneficial not only for public health but also for Indian businesses looking to capture global market opportunities.
-
Rising Obesity Rates
Obesity is increasingly recognized as a serious health concern in India. The Economic Survey cites data indicating a troubling rise in obesity rates among adults and children. Estimates suggest that the adult obesity rate has more than tripled, with the rate of increase in children being among the steepest globally, behind only Vietnam and Namibia.
-
Adult Obesity Trends: According to the National Family Health Survey 5 (NFHS-5), the obesity rate among Indian men aged 18-69 has risen from 18.9% in NFHS-4 to 22.9% in NFHS-5. For women, the rate has increased from 20.6% to 24.0% over the same period.
-
Health Implications: The Indian Council for Medical Research's latest Dietary Guidelines reveal that unhealthy diets account for 56.4% of India's total disease burden. The shift towards processed foods high in sugars and fats, combined with decreased physical activity and limited access to diverse foods, exacerbates issues like micronutrient deficiencies and obesity.

The Economic Survey 2024, presented by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, provides a detailed analysis of the employment landscape in India. It outlines the current job market, including the impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI), gig work, and climate change. The survey also discusses future job creation needs and highlights potential areas for growth.
-
Current Employment Landscape
India's workforce stands at approximately 56.5 crore, with employment distributed across various sectors:
-
Agriculture: 45%
-
Manufacturing: 11.4%
-
Services: 28.9%
-
Construction: 13.0%
According to the survey:
-
Self-Employed Workers: 57.3%
-
Unpaid Workers in Household Enterprises: 18.3%
-
Casual Labour: 21.8%
-
Regular Wage/Salaried Workers: 20.9%
A notable trend is the increasing shift of female workers towards self-employment, contrasting with the stability of male employment patterns. This shift is largely driven by rural women entering agriculture and related activities, contributing to a significant rise in female labor force participation over the past six years.
-
Employment Trends and Recovery
The survey highlights that India's employment landscape has undergone significant changes in the last decade, driven by economic reforms, technological advancements, and skill development initiatives. Key findings include:
-
Unemployment Rate: The all-India annual unemployment rate has been on a declining trend since the COVID-19 pandemic, with the quarterly urban unemployment rate dropping to 6.7% by March 2024.
-
Youth Unemployment: The unemployment rate among youth (ages 15-29) has decreased from 17.8% in 2017-18 to 10% in 2022-23.
-
Formal Employment: The number of new EPF subscribers aged 18-28 has increased significantly, indicating a positive trend in formal employment.

-
Jobs in different sectors
1. Labour Market Dynamics
The Economic Survey notes several positive developments in the labour market:
-
Female Labour Force Participation: This has risen from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 37% in 2022-23, largely due to increased participation of rural women.
-
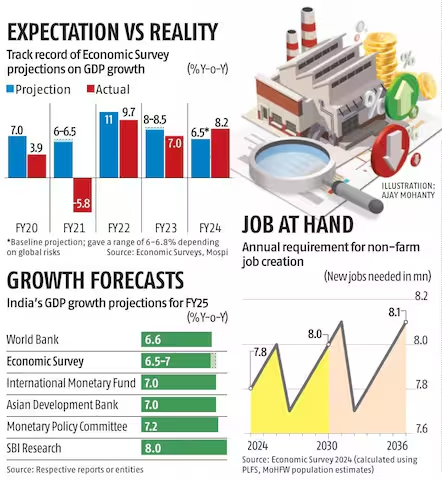
Job Creation Needs: To accommodate a growing population, India needs to generate approximately 78.51 lakh new jobs annually in the non-farm sector.
-
Formal Sector Growth: Net payroll additions under EPFO have more than doubled in the past five years, signaling robust growth in formal employment.
Manufacturing and Wages
-
Manufacturing Sector: The Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) data for 2020-21 and 2021-22 indicates that the manufacturing sector has shown resilience, with employment surpassing pre-pandemic levels.
-
Wage Growth: Wages per worker in rural areas have grown at a 6.9% CAGR from FY15 to FY22, compared to a 6.1% CAGR in urban areas. This growth in wages, coupled with higher wages in rural areas, is expected to stimulate demand in the countryside.
Organised Sector Developments
-
Factory Size Trends: In 2021-22, smaller factories (employing less than 100 people) made up 79.2% of all factories but accounted for only 22.1% of total employment. There is a growing trend towards larger factories, with those employing more than 100 workers increasing by 11.8% from FY18 to FY22.
-
EPFO Payroll Data: The organised sector has seen a consistent year-on-year increase in payroll additions, more than doubling from 61.1 lakh in FY19 to 131.5 lakh in FY24, aided by the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY). The EPFO membership grew by 8.4% CAGR from FY15 to FY24.
2. The Rise of the Gig Economy
Recent surveys reveal a global shift in employment trends, leading to a notable rise in the gig economy. This sector includes freelancers, online platform workers, self-employed individuals, on-call workers, and creative tech talent.
In India, several factors have contributed to the growth of the gig economy:
-
Tech-Enabled Platforms: The proliferation of digital platforms has facilitated easier access to gig work.
-
Internet Access: Improved internet connectivity, bolstered by advances in digital public infrastructure, has expanded opportunities.
-
Flexible Work Demand: There is a growing demand for flexible work arrangements.
-
Focus on Skills: Emphasis on skill development supports the rise of gig roles.
According to NITI Aayog’s estimates based on national labor force survey data, there were approximately 7.7 million workers engaged in the gig economy during 2020–21. This number represents 2.6% of the non-agricultural workforce and 1.5% of the total workforce in India.
The persistent demand for gig services and job flexibility is fostering job creation in tier-2 and tier-3 cities. It also offers part-time work opportunities for students and serves as a buffer during periods of temporary unemployment. Workers often transition to higher-paying jobs after gaining experience on these platforms (NCAER 2023).

3. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence
The survey underscores the growing prevalence of artificial intelligence (AI) across various economic activities. As AI continues to advance, it is crucial to align technological choices with collective welfare. Employers need to strike a balance between technology deployment and labor.
-
Sectors Most Affected by AI
Based on additional research and the Economic Survey 2023-24, the impact of AI varies across different sectors:
-
Manufacturing Sector: AI's impact on manufacturing is limited as industrial robots are less flexible and cost-effective compared to human labor.
-
Inventory and Supply Chain Management: AI in these areas is more likely to complement rather than replace human workers.
-
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO): The BPO sector is at significant risk due to generative AI technologies that automate routine cognitive tasks, potentially leading to substantial job reductions over the next decade.
-
Healthcare, Weather, and Education: AI can enhance these sectors by identifying health risks from digital health data, predicting weather patterns, and aiding educators in grading and translation.
-
Services Sector: Widespread AI adoption in the services sector could substantially reshape or even replace existing jobs.
4. MSME and Skill Development
The increase in candidates participating in government-led skill development programs highlights the focus on 'Skill India.' However, job creation is hindered by regulatory challenges such as land use restrictions, building codes, and limitations on women's employment in certain sectors and hours. Addressing these barriers is crucial for boosting employment and increasing women's labor force participation.
-
Policy Focus Areas
The survey identifies several key policy areas for short to medium-term attention:
-
Job and Skill Creation: Enhance efforts to generate and match job opportunities with skill sets.
-
Agriculture Sector: Unlock the full potential of agriculture by removing policy impediments.
-
MSME Support: Address challenges faced by micro, small, and medium enterprises.
-
Green Transition: Manage the transition to a sustainable economy.
-
China Relations: Navigate challenges related to China.
-
Corporate Bond Market: Deepen and develop the corporate bond market.
-
Inequality and Health: Address economic inequality and improve health outcomes for the youth.
The document highlights a growth strategy for 'Amrit Kaal,' focusing on:
-
Private Investment: Foster private sector investment.
-
MSME Expansion: Prioritize the growth of MSMEs.
-
Agriculture Potential: Recognize and enhance agriculture's role in future growth.
-
Green Transition Financing: Secure financing for sustainable development.
-
Education-Employment Gap: Bridge the gap between education and employment.
-
State Capacity: Build and enhance state capacity to sustain progress.
The survey suggests that with sustained structural reforms, the Indian economy could potentially grow at a rate of over 7% in the medium term, contingent on collaboration between the Union Government, State Governments, and the private sector.
5. Agro-Processing as a Rural Employment Opportunity
Agriculture and related industries remain vital to the rural economy. Enhancing productivity in this sector is crucial for job creation. Agro-processing offers a pathway to accelerate crop diversification, especially in regions like Punjab and Haryana, where paddy cultivation faces challenges due to groundwater scarcity.
-
Rural Job Demand and MGNREGS
Data from the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) indicates significant demand for low-skill rural jobs, particularly among women, who make up more than half of the MGNREGS workforce. There is considerable potential for transitioning MGNREGS labor to more productive and financially sustainable ventures.
Read the complete PDF here: Economic Survey 2023-24
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.




















