From our homes and offices to hospitals and schools, buildings shape the very fabric of our lives. But beyond offering shelter and function, buildings also play a significant role in the climate crisis—contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, and pollution. As environmental awareness rises and the global push for sustainability intensifies, the architecture and construction industries are experiencing a profound transformation.
Green buildings in 2025 are not just a trend—they are a movement. Fueled by climate imperatives, ESG mandates, and growing consumer demand, green construction has evolved from an eco-conscious niche into an industry-defining standard.

What is Green Building?
Despite what the name may suggest, a green building isn’t defined by its color—it’s about its ecological footprint. Green buildings are designed, constructed, and operated to minimize environmental impact and improve occupant well-being. These structures incorporate sustainable practices from site selection to post-occupancy operations.
Key principles of green buildings include:
-
Development Site Optimization: Prioritize previously developed land to preserve natural habitats.
-
Resource Efficiency: Incorporate low-flow fixtures, greywater systems, and energy-efficient lighting.
-
Toxicity Reduction: Eliminate hazardous materials to improve indoor air quality.
-
Waste Minimization: Use recyclable, biodegradable, and reclaimed materials.
-
Smart Integration: Employ IoT and AI to optimize building operations.
By integrating renewable energy sources, advanced water systems, and biophilic elements, green buildings provide a holistic response to today’s sustainability challenges.

Top Green Building Trends Shaping 2025
Here are the most transformative trends redefining green architecture in 2025:
1. Net-Zero Energy Buildings: Redefining Clean Energy Integration
Net-Zero Energy Buildings (NZEBs) are at the forefront of green construction in 2025. These structures generate as much energy as they consume, reducing dependency on fossil fuels and supporting global decarbonization goals.
Modern NZEBs incorporate cutting-edge technologies such as:
-
Biogas & Waste-to-Energy Systems: Transforming organic waste into clean, usable energy.
-
Custom Gas Scrubbers: Devices like venturi and packed bed scrubbers eliminate up to 80% of harmful emissions (H₂S, NH₃).
-
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): Integrating reverse osmosis, multi-effect evaporators, and solar drying beds to eliminate liquid waste discharge.
Why It Matters:
-
Cuts energy bills by 30–50%
-
Aligns with ESG reporting goals
-
Enhances self-sufficiency and climate resilience
Even when 100% on-site energy production isn’t feasible, retrofitting with renewables and sustainable materials can offset emissions and drive buildings toward net-zero performance.
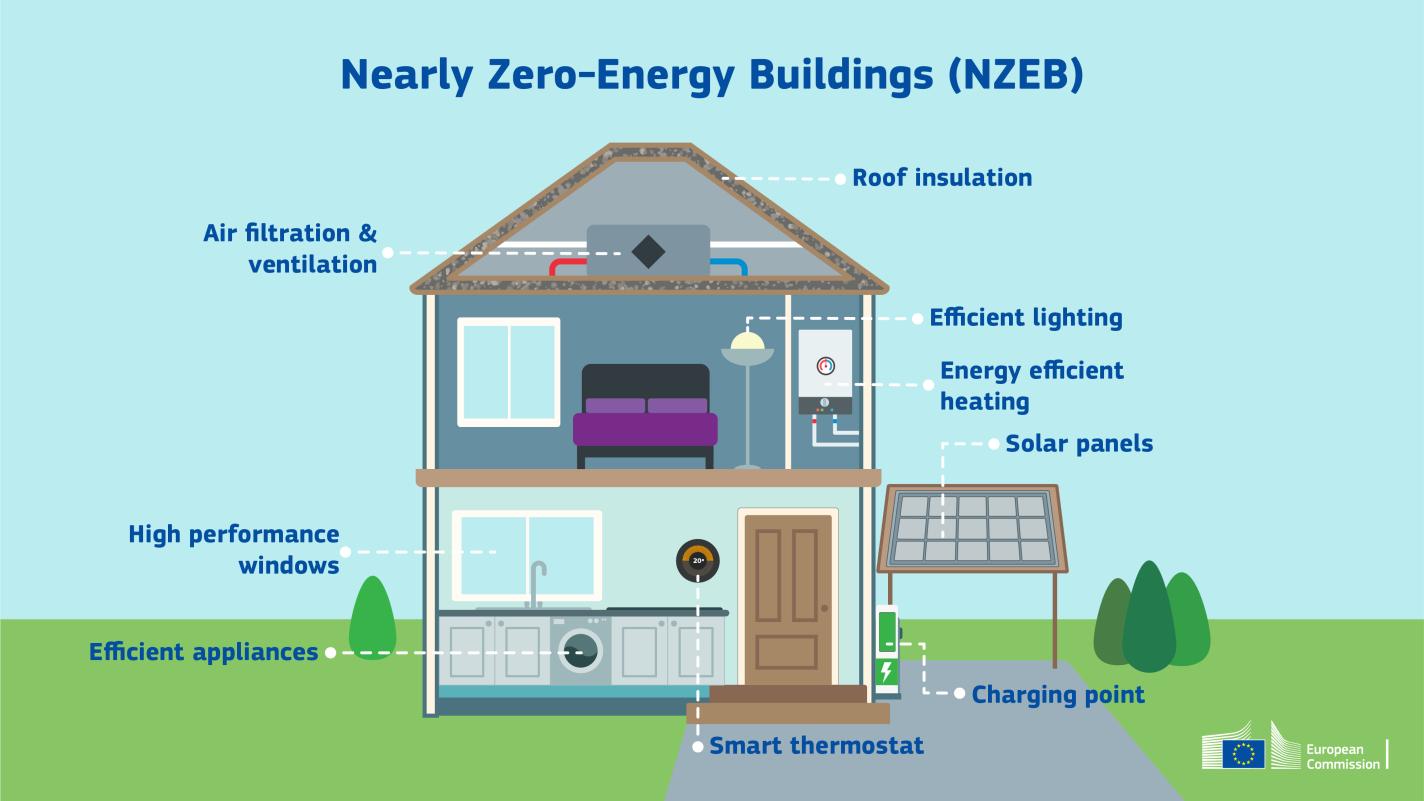
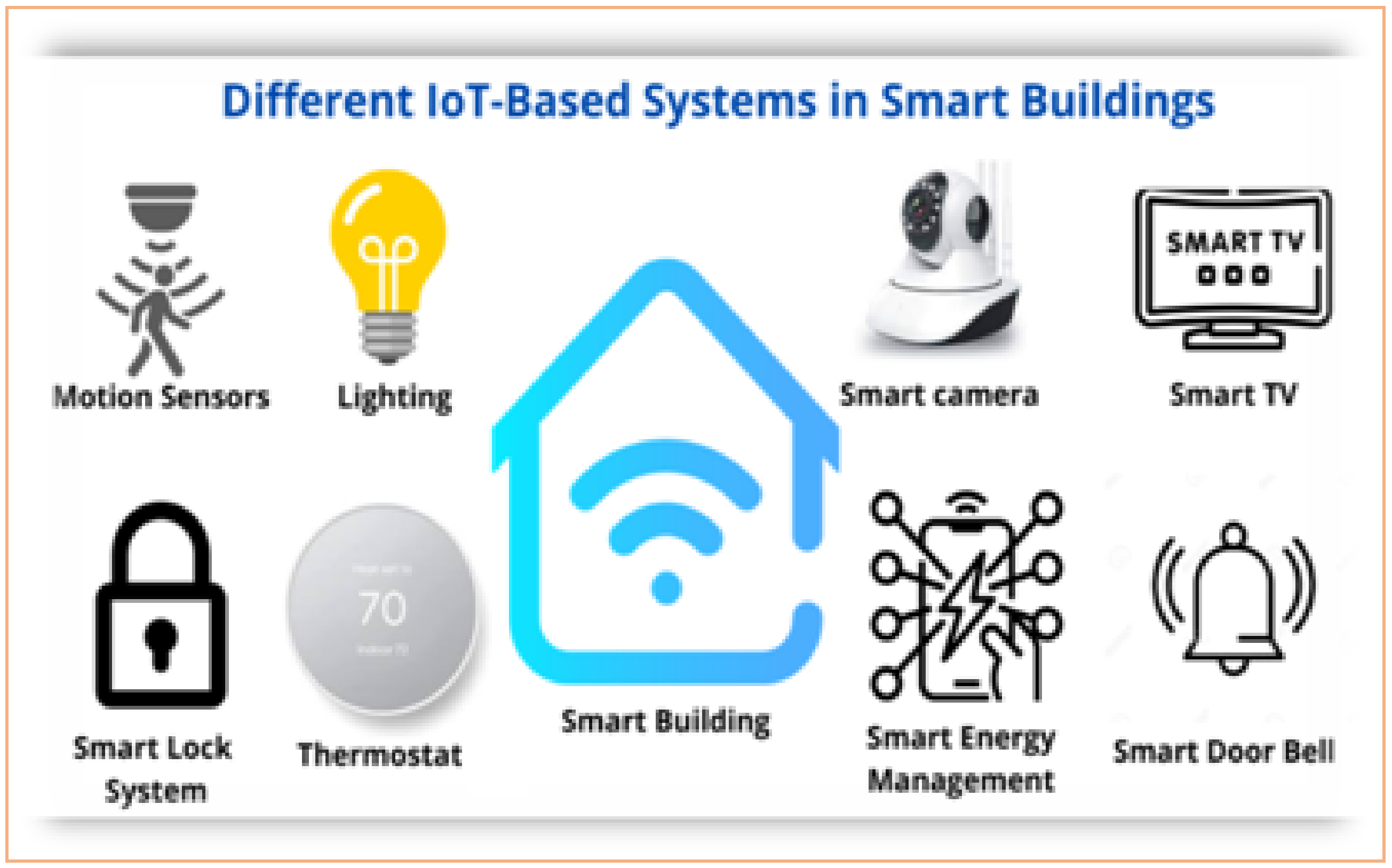
2. Smart Buildings: Merging IoT and AI for Sustainable Efficiency
Smart buildings powered by Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are making sustainability more accessible and cost-effective.
Key Innovations:
-
IoT Sensors: Monitor energy use, water quality (pH, TDS, flow rate), and indoor air conditions in real time.
-
SCADA-Integrated STPs and ETPs: Allow predictive maintenance and remote control, reducing downtime and operational waste.
-
AI Predictive Systems: Identify equipment failures before they happen, minimizing resource waste and unplanned expenses.
-
Smart Grids: Dynamically balance energy loads across buildings and campuses, optimizing for renewable integration.
Benefits:
-
Up to 30% savings on maintenance costs
-
Dramatic reduction in energy and water consumption
-
Seamless integration with circular and net-zero systems
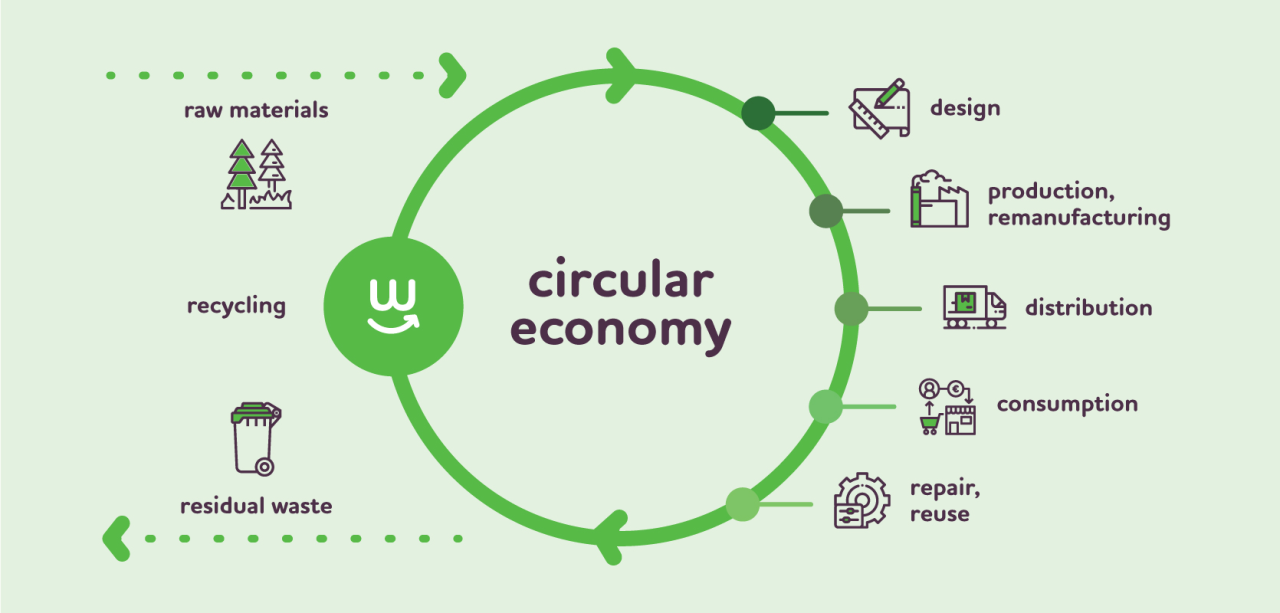
3. Circular Construction: Toward a Zero-Waste Economy
The future of construction is circular. Circular construction means designing buildings—and the entire construction process—to eliminate waste, reuse resources, and lower embodied carbon.
Circular Economy Solutions:
-
Prefabricated STPs & ETPs: These offsite-built systems reduce construction waste by up to 90%.
-
Solid Waste-to-Aggregate Plants: Recycle construction debris into usable materials for roads and buildings.
-
Pyrolysis Plants: Convert non-recyclable plastics into fuel oil, closing the loop on plastic waste.
Why It’s Important:
-
Reduces landfill dependency
-
Accelerates build times
-
Meets certifications like IGBC Green Factory and GEMI Zero Waste
-
Slashes lifecycle costs and carbon footprints
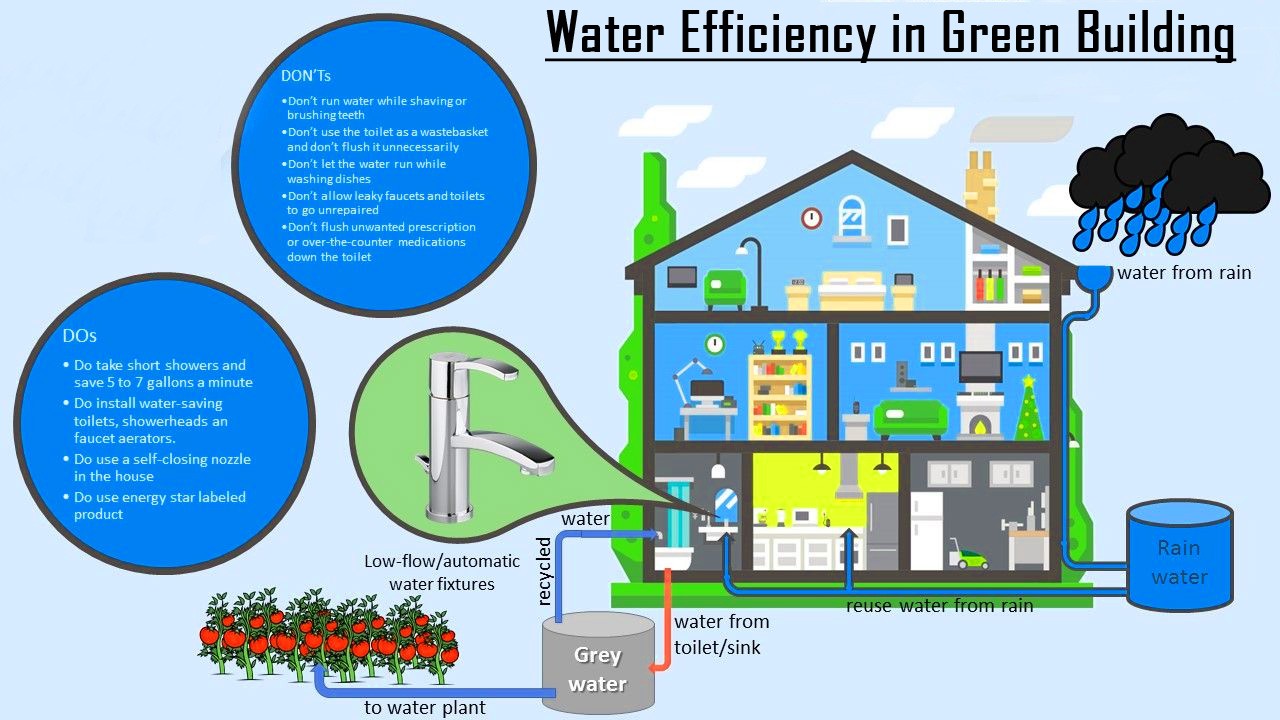
4. Water-Wise Architecture: Smart Water Management for a Thirsty Planet
As water scarcity becomes a critical issue, green buildings in 2025 are equipped with smart water systems that minimize consumption and maximize reuse.
Advanced Water Systems:
-
Rainwater Harvesting: Captures and stores runoff for later use.
-
Dual Plumbing Systems: Separate lines for potable and reclaimed water reduce reliance on fresh supplies.
-
Packaged STPs & ETPs: On-site modular sewage and effluent treatment using MBBR, SBR, and MBR processes make recycling water efficient.
-
RO & UF Systems: Convert wastewater into potable water per WHO standards.
IoT-based Leak Detection and real-time flow tracking help conserve every drop—reducing not just water use but also operating costs and environmental impact.
5. Biophilic and Health-Centric Design: Nature Meets Wellness
Green buildings don’t just protect the environment—they elevate human health and comfort. The biophilic design movement in 2025 integrates nature into everyday living spaces, while health-centric design ensures indoor air quality and non-toxic materials.
Biophilic Elements:
-
Rooftop gardens, vertical green walls, and natural ventilation
-
Architecture inspired by organic shapes, light, and water patterns
Health-Focused Strategies:
-
VOC-Free Materials: Paints, furniture, and adhesives that don’t off-gas harmful toxins
-
Advanced Air Purification: Gas scrubbers in HVAC systems eliminate pollutants
-
Daylight Optimization: Natural light reduces energy use and boosts productivity
Benefits:
-
Reduces stress and enhances mood
-
Improves indoor air quality
-
Increases productivity and satisfaction in commercial settings
Together, these approaches make buildings not only greener—but also happier, healthier places to live and work.

6. Sustainable Materials and Construction Practices
2025 is witnessing a materials revolution. Architects and builders are swapping traditional, high-impact materials with sustainable alternatives that are durable, renewable, and sometimes even self-repairing.
Hot Materials of 2025:
-
Recycled and Reclaimed Resources: Salvaged wood, steel, and glass reduce demand for virgin materials.
-
Self-Healing Concrete: Fills its own cracks with reactive agents, extending longevity.
-
Biodegradable Innovations: Materials like compressed bamboo, mycelium insulation, and biodegradable plastics reduce waste post-demolition.
-
Low-VOC Paints and Sealants: Improve indoor air quality and support occupant health.
-
Low-VOC Paints and Adhesives: Improve indoor air quality and reduce health risks.
Practices to Embrace:
-
Source materials locally to cut carbon emissions
-
Use prefabrication to reduce construction waste
-
Integrate renewable energy into construction operations
7. Green Building Certifications and Regulations
With sustainability now central to urban development, green certifications are evolving to keep up with 2025’s demands.
Updated Certifications:
-
LEED v5 (U.S.): Now includes decarbonization, climate resilience, equity, and lifecycle sustainability.
-
BREEAM v7 (UK/EU): Expands its focus to water conservation and green transport infrastructure.
Why Certify?
-
Boosts property value
-
Ensures long-term performance standards
-
Appeals to eco-conscious tenants and investors
From tenant health to resource conservation, certification ensures your building performs well today and tomorrow.
The Future of Green Buildings: A Sustainable, Smart, and Human-Centric Blueprint
Green buildings in 2025 are more than environmentally responsible—they are technologically advanced, economically smart, and human-centric. Whether you’re constructing new facilities or retrofitting old ones, embracing sustainable practices is no longer optional—it’s essential.
By adopting these seven trends—net-zero design, smart technologies, circular construction, sustainable materials, water-wise systems, biophilic design, and green certifications—developers and architects are helping reshape our built environment into one that’s in harmony with the planet.
Explore green building solutions today, and help lead the way toward a more resilient, healthy, and sustainable tomorrow.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.





















