In a dramatic turn of events, WhatsApp, along with its parent company Meta, has issued a bold ultimatum, declaring its intention to cease operations in India if compelled to compromise its end-to-end encryption and disclose user data to the government. This showdown unfolded during a hearing at the Delhi High Court, where WhatsApp and Meta challenged India's 2021 IT rules, specifically objecting to the requirement to identify the initial source of information.
Tejas Karia, representing WhatsApp, unequivocally stated, "If we are told to break encryption, then WhatsApp goes." This stance has ignited a debate on the delicate balance between individual privacy rights and national security, given WhatsApp's enormous user base of 535.8 million monthly active users in India as of 2024.

What are the IT Rules?
-
IT Rules in India:
- Rule 4(2) mandates social media platforms with messaging services to reveal message sender identities upon court or authority orders.
- Disclosure applies to cases involving public order, national security, or serious crimes like rape, explicit content, or child sexual abuse, punishable by a minimum five-year jail term.
- If less intrusive methods can identify the message originator, no such order should be granted.
-
2021 Social Media Platform Guidelines:
- India introduced new social media platform guidelines.
- These guidelines necessitate the appointment of compliance officers and monthly compliance reports.
- Controversially, one provision demanded the identification of message "first originators," sparking privacy concerns and legal challenges
- The controversial provision led to legal challenges and subsequent amendments to the rules.

What is govt’s stance on the issue?
- WhatsApp took legal action against the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, in the Delhi High Court in 2021.
- The rules require instant messaging platforms with over 50 lakh registered users in India to assist in identifying message originators.
- WhatsApp challenged the constitutional validity of these rules, which came into effect on May 26 of that year.
- The company's spokesperson argued that compliance would compromise user privacy by breaking end-to-end encryption, likening it to keeping a fingerprint of every message.
- The government asserts that following these rules would aid in tracing the origin of fake messages, crucial for combating misinformation, particularly during events like the Covid-19 pandemic.
- While WhatsApp prioritizes protecting user privacy, uncertainty looms over other service providers' compliance with the IT rules.
- The main focus centers on the clash between WhatsApp and the government regarding these regulations.

WhatsApp's Statement
- WhatsApp opposes the IT rule, citing concerns over justifiability and potential criminal repercussions for non-compliance.
- The company argues that complying with traceability requirements would compromise its end-to-end encryption, violating users' privacy and free speech rights.
- Advocate Tejas Karia, representing WhatsApp, emphasizes the platform's commitment to privacy through encryption and warns that compelling decryption could lead to service cessation.
- Karia also highlights the significant data storage burden imposed by the rule, as WhatsApp would need to store vast message volumes for extended periods without knowing which would require decryption.
- WhatsApp asserts its dedication to end-to-end encryption as a means of safeguarding message confidentiality and privacy rights.
- It seeks judicial intervention, challenging Rule 4(2) of the intermediary rule as unconstitutional.

The Court's Perspective
- Bench led by Acting Chief Justice Manmohan and Justice Manmeet Pritam Singh Arora emphasized balanced approach respecting privacy rights.
- Government contends tracing message originators crucial for tackling communal violence, citing concerns over WhatsApp and Facebook's data monetization practices.
- Government questions absolute privacy protection claims by WhatsApp and Facebook, highlighting global endeavors to hold Facebook accountable for user data management.

WhatsApp's Past Controversies
WhatsApp has faced allegations concerning data privacy breaches and the proliferation of misinformation on a large scale.
- Spread of Misinformation and Fake News
The platform's ease of sharing and lack of robust fact-checking mechanisms have facilitated the dissemination of misinformation, resulting in real-world violence and social unrest, especially in regions with volatile political climates.
- Privacy Concerns
Despite offering end-to-end encryption for messages, worries persist regarding user data collection, potential government surveillance access, and data-sharing practices with its parent company, Meta (formerly Facebook).
- Hate Speech and Incitement to Violence
Misuse of group chats has contributed to the propagation of hate speech and incitement to violence in some countries, presenting a challenge in balancing freedom of expression with the prevention of harm.
- Cyberbullying and Harassment
The platform's anonymity and communication ease have fostered an environment conducive to cyberbullying and harassment.
- Encryption Debate: Apple vs FBI
In 2016, a dispute arose between Apple and the FBI when the FBI sought Apple's help in unlocking an iPhone linked to one of the San Bernardino shooters. Apple's refusal, citing concerns about compromising user security, ignited a broader debate on balancing national security needs with individual privacy rights. Similar conflicts persist, with law enforcement advocating for access to encrypted data to combat crime and terrorism, while tech firms emphasize the importance of robust encryption for user privacy and security. The issue remains unresolved, fueling ongoing legal and technological discussions on digital privacy and law enforcement practices.

Ongoing Court Proceedings
The court is scheduled to resume hearings for the cases on August 14th.
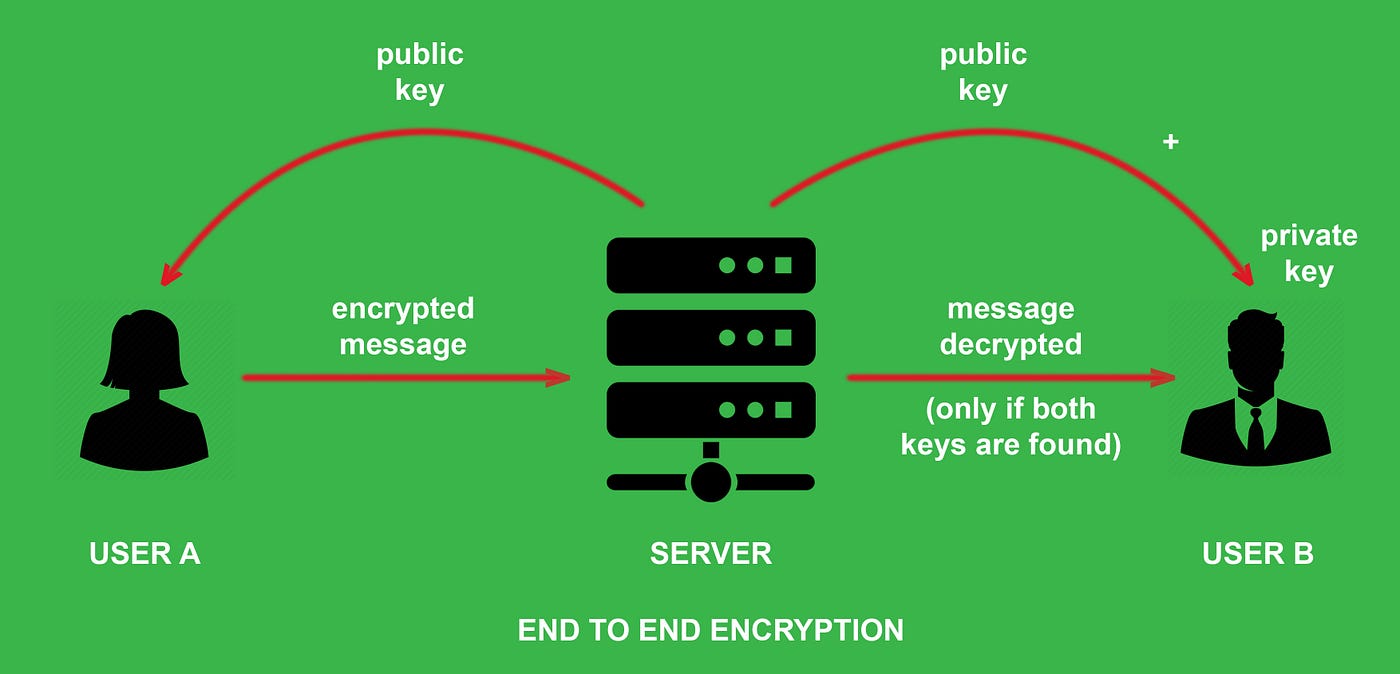
What is End-to-End Encryption?
End-to-end encryption, introduced by WhatsApp in 2016, ensures that only the sender and receiver have access to message content. This encryption process converts messages into unreadable codes, safeguarding them from unauthorized access. Despite other platforms offering similar features, WhatsApp remains highly popular in India, boasting an estimated 400 million users.
The significance of end-to-end encryption is in protecting user privacy and preventing data breaches. WhatsApp’s firm stance on maintaining strong encryption underscores the ongoing global debate between privacy rights and law enforcement needs.
Can WhatsApp Access Your Messages?
- WhatsApp founders Jan Koum and Brian Acton emphasized that neither WhatsApp nor any other party could access messages due to end-to-end encryption.
- End-to-end encryption ensures that only the intended recipient can decrypt and read the messages, enhancing privacy comparable to face-to-face conversations.
- According to WhatsApp's FAQ, end-to-end encryption automatically secures messages, with only the sender and recipient possessing the decryption keys.
- WhatsApp reiterated that it cannot view message content or listen to encrypted calls.
- Encryption and decryption occur solely on the users' devices, ensuring privacy and security.

Why is end-to-end encryption important?
- End-to-end encryption is emphasized by WhatsApp's founders as essential for privacy and security in the digital age.
- Weakening encryption not only risks individual safety but also exposes data to cyber threats.
- Experts warn that compromising encryption could result in widespread surveillance, violating fundamental human rights.
- Mishi Choudhary from the Software Freedom Law Centre states that encryption is crucial for defense against cyber threats like hacking and identity theft.
- Upholding encryption ensures the confidentiality of personal and commercial communications, vital in today's digital landscape.
- Attempts to weaken encryption are seen as harmful, undermining privacy rights and aiding criminals.
- Rizvi argues that encryption protects users' privacy and security, making traceability without compromising encryption technically difficult.
- He suggests alternative methods for law enforcement to combat digital crimes without compromising encryption, such as utilizing metadata, which align with principles of data minimization endorsed by judicial precedents like the Puttaswamy judgment in India
How do other countries deal with the issue?
- Ongoing global debate between law enforcement and tech giants on user data privacy
- Governments seek access to user data for law enforcement, balancing privacy and security
- Increasing scrutiny over encryption in the US and EU, particularly to combat serious crimes like CSAM
- US refrains from enforcing laws mandating backdoors into encrypted services due to security risks
- EU regulations prioritize individual privacy and online security while accommodating law enforcement needs
- Recent UK legislative efforts to undermine end-to-end encryption faced strong opposition from leading messaging platforms
- Signal, Viber, WhatsApp emphasized encryption's critical role in protecting against online threats
- Encryption seen as indispensable for safeguarding vital institutions relying on internet technologies

Potential solution
- The resolution to the issue could lie in the adoption of India's long-awaited data privacy legislation.
- India currently lacks a cohesive data privacy framework comparable to the European Union's.
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, approved by parliament last year, is pending finalization pending post-election rule notifications.
- Once enforced, this legislation could lay a strong foundation for protecting user data and regulating technology companies' behavior.
With tensions escalating between WhatsApp and the Indian government, the resolution of this legal standoff could profoundly reshape the digital landscape within the world's largest democracy.
Inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.






















