Google, the search engine that was once put to use by billions across the world, is facing serious challenges. To confront its perceived decay in search quality, Google has bet the farm on artificial intelligence. Here, they are provided with instant answers, right at the head of search results, so that users do not have to flip through page after page.
What’s next for Search? With features like AI Overviews, “Google will do the Googling for you." pic.twitter.com/BBsxtEXIyA— Google (@Google) May 17, 2024
In theory, this sounds ideal. In practice, however, Google's AI has too often been way off base, at times laughably, at times perilously. This article covers some of these Google AI forays, the strange results, and the broader implications for search technology.
Google's AI Overview: A Solution or a Problem?
Google's AI summaries are designed to provide instant responses to human questions and, in principle, save time for the searcher. All too often, these summaries are misleading, meaningless, or even dangerous.

Comedic Errors of Google's AI
This can lead to some of the more amusing mistakes in Google's AI overviews:
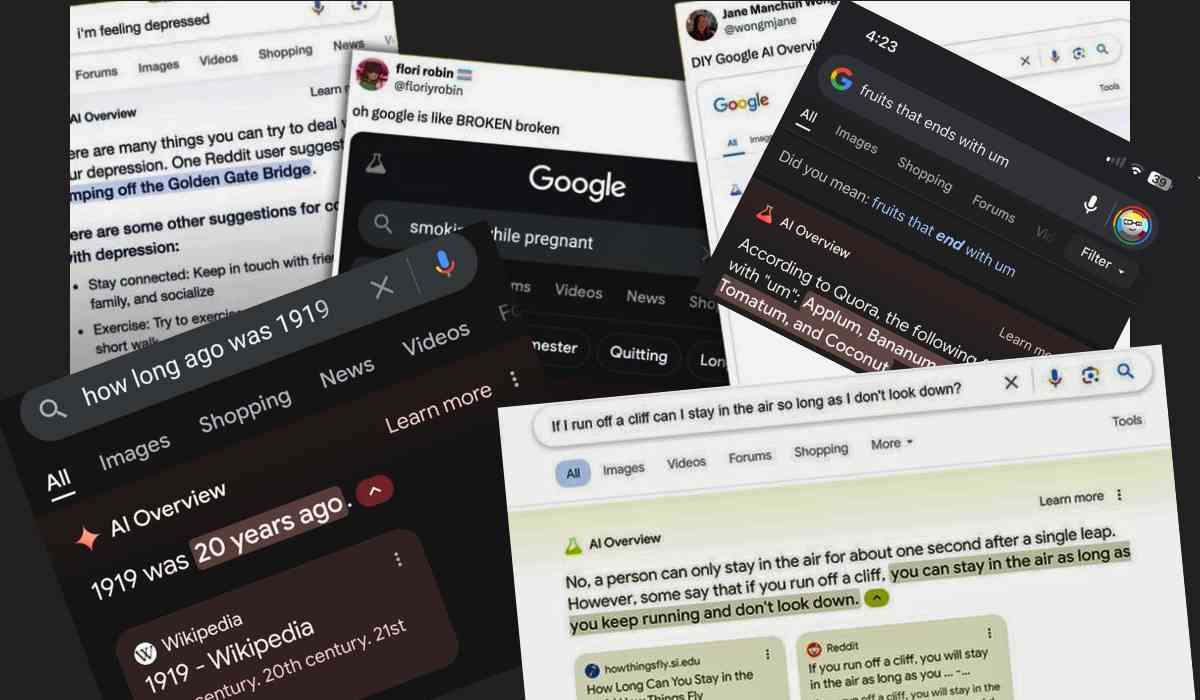
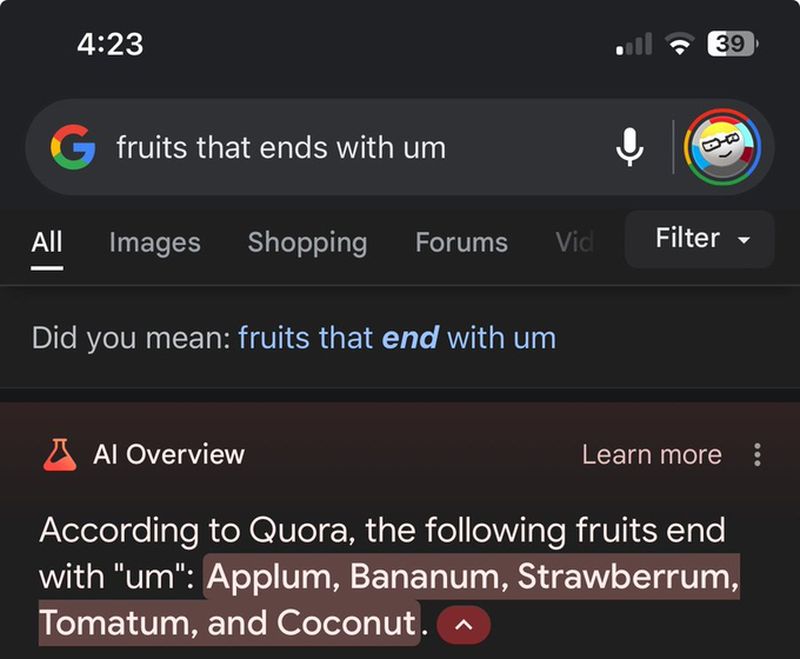
♦ Cockroaches in Penises: One such AI-generated answer said that it's normal for 6 to 10 cockroaches to crawl into your penis each year while you sleep. That such an absurd and biologically impossible claim may be shown as accurate gives a clue as to a rather significant problem with content verification.
♦ Smoking While Pregnant: One comment suggested that a pregnant woman smokes two to three cigarettes a day, the rest being an echo of mid-20th-century dangerously outdated health advice.
♦ Cartoon Logic: An AI claimed that running off a cliff without looking down would allow one to stay suspended mid-air, clearly mimicking cartoon physics rather than reality.
_1717868292.png)
These examples show how, if proper governance is not in place, AI may deliver absurdly wrong—even sometimes harmful—pieces of information.
User comments and experiences
Users have expressed how they found it comical to share experiences while angry about them across social media. One user tweeted regarding the cockroach claim: Google AI thinks I'm living in a horror movie!
Other users have shared screenshots of AI errors and turned them into social media memes. A survey conducted by Pew Research found that 60% of users came across incorrect AI-generated information in their search results.
Dangerous Missteps
While some AI errors are comical, others are deadly serious.
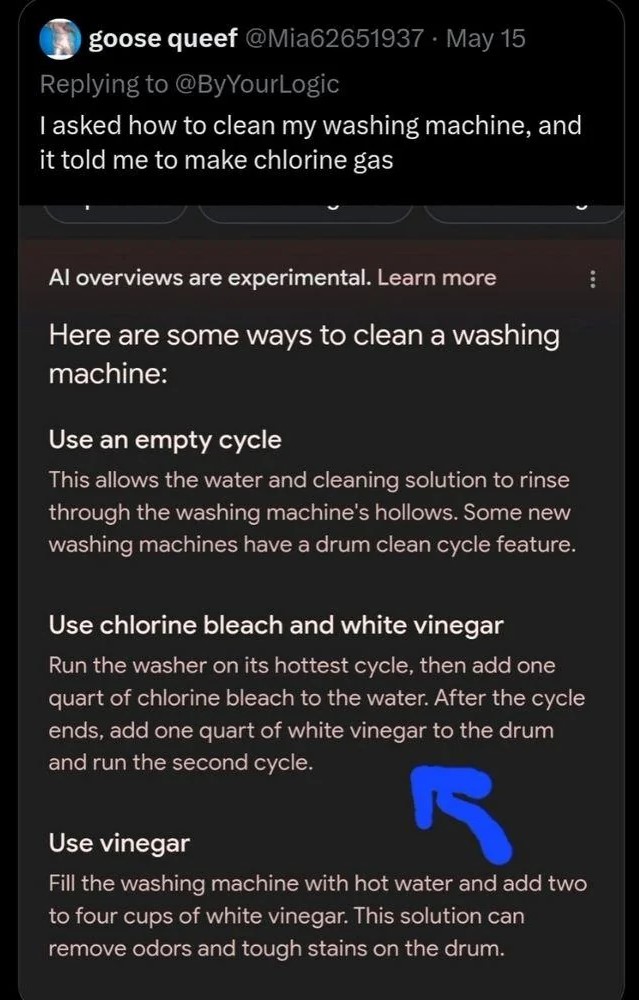
♦ Using Bleach and Vinegar: One AI recommended cleaning a washing machine with bleach and vinegar, which together make deadly chlorine gas.
♦ Leaving Dogs in Hot Cars: One reaction stated it was always all right to leave a dog in a hot car, contrary to the common sense of the danger of heatstroke in pets. Even though this turned out to be fake, this still raised a lot of eyebrows.
Mistakes like this underline the need for better AI training and validation processes.
The Main Issue with Google's AI Overviews
The big issue that underlines Google's AI overviews is in their design. That is, large-scale language models, like Google's AI, are engineered to provide users with coherent-sounding answers—not necessarily correct ones. This is fundamentally hard to do, given that, as a limitation, it's tough to ensure reliability. Data from a study conducted at Stanford University shows that even complex LLMs will produce an error baseline rate of around 20% with nuanced queries.
Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google, was quoted:
"We are continually working to improve the accuracy and reliability of our AI models. While we have faced some setbacks, we remain committed to refining our technology to better serve our users"

Expert Opinions on AI Reliability
Experts like Gary Marcus, an AI specialist and Professor at New York University, put forward the view that AI companies oversell the potential accuracy of their models. It is relatively easy to arrive at 80% correctness when replicating massive amounts of human data. Still, it is exponentially more difficult to refine that to 100% reliability and might need accurate artificial general intelligence (AGI) that, technologically speaking, we are currently very far from.
Challenges in Current AI Technology
The same problem at the very top of this list is: LLMs are unpredictability incarnate and, hence, unreliable narrators by design. They optimize for coherence over truth, leading to information generation, which tends to be false but plausible in this manner. While some steps are taken to check and balance this—e.g., by manual checks and balancing data sources—the high-level architecture of these models makes them prone to errors.
Comparative Analysis: Google vs. OpenAI vs. Co-pilot
But then again, it is not just Google experiencing all these bumps along the AI highway. OpenAI, the creator of the much-coveted GPT series, has had some concerns, too, although much less publicly. OpenAI's GPT-4 model, for instance, has an error rate of 18% on difficult questions. This is a little less than the error rate of Google's AI, but it is still toe-curling.

Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, said :
"Achieving high accuracy with AI is a significant challenge. Our goal is to continually enhance our models, but it's important to manage expectations around what current AI technology can and cannot do."
GitHub's Co-pilot, another AI-powered app, had also been facing flak. Co-pilot helps programmers with the suggestion of code snippets, though it has faced critique concerning the generation of, at times, incorrect and insecure code.
Research conducted at New York University found that 40% of the code snippets Co-pilot generated contained vulnerabilities, pointing to the broader problem of ensuring AI safety in various applications. But, while all three are pushing the boundaries of AI capabilities, the public-facing nature of Google's AI missteps has drawn more scrutiny and criticism.
Thomas Dohmke, CEO of GitHub (co-pilot):
"GitHub Co-pilot is an incredible tool for developers, but we acknowledge that it isn't perfect. We're focused on improving its performance and security to better assist programmers in their daily tasks."
Technical Insights: How AI Works
Large Language Models (LLMs) like Google's AI use vast datasets to predict and generate human-like text. They analyse patterns in the data to produce answers. But they lack accurate understanding, so if context or nuance are required, they frequently err. They have been trained under the adage that more data for learning would result in better performance, but if they cannot differentiate what is true from what is a fallacy, then the conclusions would just be wrong.
_1717871878.png)
How to Get There: Improving AI for Search
While Google's AI work has been flawed, it has been critically required to progress search technology. To make it better, some steps that could be undertaken include:
- Improved Data Verification: Improved verification processes from the data sources might help weed out dubious or even satirical data. MIT has found that real-time fact-checking algorithms can help reduce the sharing of inaccurate data by as much as 50%.
- Human Oversight: More human oversight within the AI training and output review process will catch what slips through automatic systems. Mixed AI and human review approaches could improve the accuracy rate by up to 30%, as reported in studies at Carnegie Mellon University.
- Channels for User Feedback: Adding robust user feedback systems is beneficial and can help quickly identify and correct any mistake by leveraging the collective intelligence and means of the user base. User reports and corrections can actually be used to train the AI to make it progressively accurate.
_1717872235.png)
Conclusion
Google's effort to include AI for better search results ended up with a funny, though seriously intended, twist in most cases. This definition suggests that AI has excellent potential; the massive improvement has yet to prove that the information generated is reliable and safe. As Google continues to fine-tune its approach, it has to balance innovation with the necessity of being accurate while at the same time considering user safety and trust at the front line.
Inputs from Multiple agencies
Media inputs: Multiple Sources
ⒸCopyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.