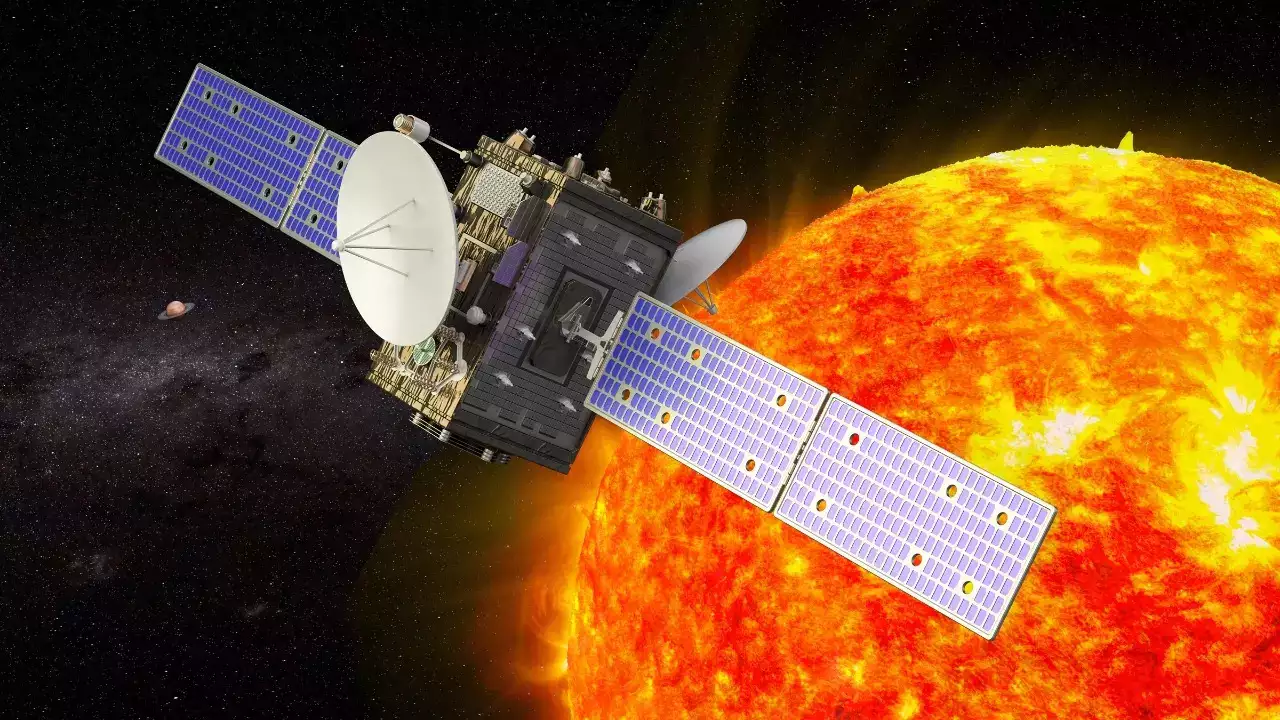
The first mission from India to explore the Sun, Aditya-L1, is scheduled to arrive at Lagrange Point 1 (L1) during the first week of January 2024, according to Minister of State for Science and Technology Jitendra Singh. The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) launched the Aditya-L1 mission in February of this year.
Aditya-L1 mission achieved a significant milestone
By recently capturing the first complete images of the Sun, the Aditya-L1 mission accomplished a noteworthy milestone. The images were taken with the Aditya-L1 instrument, the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT). In order to capture the Sun's photosphere and chromosphere within a specific wavelength range, SUIT employs a set of filters.
According to ISRO, the observations from the ADITYA-L1 mission will aid in the investigation and improvement of scientific knowledge regarding the magnetized solar environment. In turn, this will provide significant new information that will help us comprehend how solar radiation affects Earth's climate. Sunspots and 'silent' areas of the sun have been captured in the pictures that Aditya-L1 has captured thus far. The Sun's photosphere and chromosphere will be revealed through these and many more measurements in the future.
ISRO SAID ON ITS WEBSITE
The main benefit of having a satellite in the halo orbit around the L1 point is being able to watch the Sun continually without being obscured by occultation or eclipses. This will increase the benefit of real-time monitoring of solar activity and its impact on space weather. The spacecraft is equipped with seven payloads that use electromagnetic, particle, and magnetic field detectors to study the photosphere, chromosphere, and the outermost layers of the Sun, or the corona. According to ISRO's website, "Four payloads use the unique vantage point L1 to view the Sun directly, while the remaining three payloads conduct in-situ studies of particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1. This allows for significant scientific studies of the propagatory effect of solar dynamics in the interplanetary medium."
IMAGE SOURCE-X
©️ Copyright 2023. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media







