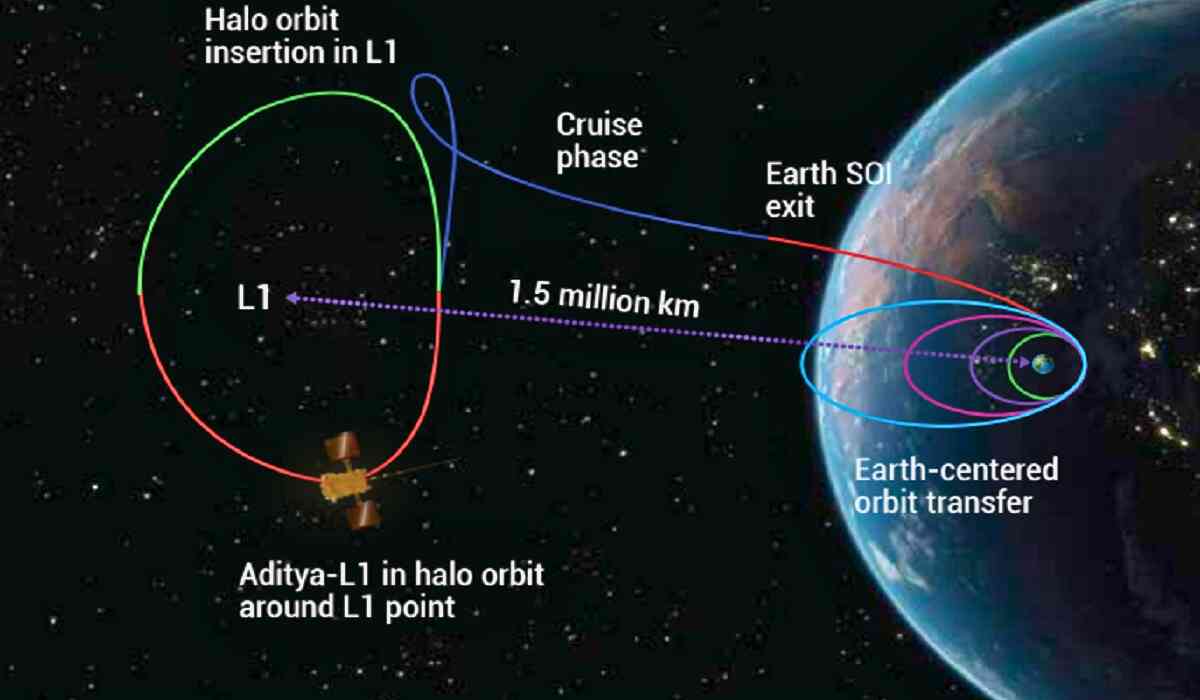
India's pioneering solar mission, known as Aditya-L1, has achieved a significant milestone by reaching the Lagrangian Point L1.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has made a noteworthy accomplishment as its solar mission, Aditya-L1, is set to reach the Lagrangian point L1 on January 6. This point, located 1.5 million km away from Earth, serves as the spacecraft's destination for uninterrupted and comprehensive solar analysis.
What is Lagrangian Point?
Lagrange Points, named after mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange, are unique positions in space where the gravitational forces of large bodies create stable zones. Spacecraft strategically use these points to conserve fuel, benefiting from a delicate balance that allows for prolonged orbits. Lagrange identified five key points; three are unstable, and two are stable, forming triangles with larger masses. (For detailed information, go to Lagrang point).
The L1 point of the Earth-Sun system affords an uninterrupted view of the sun and is currently home to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite.
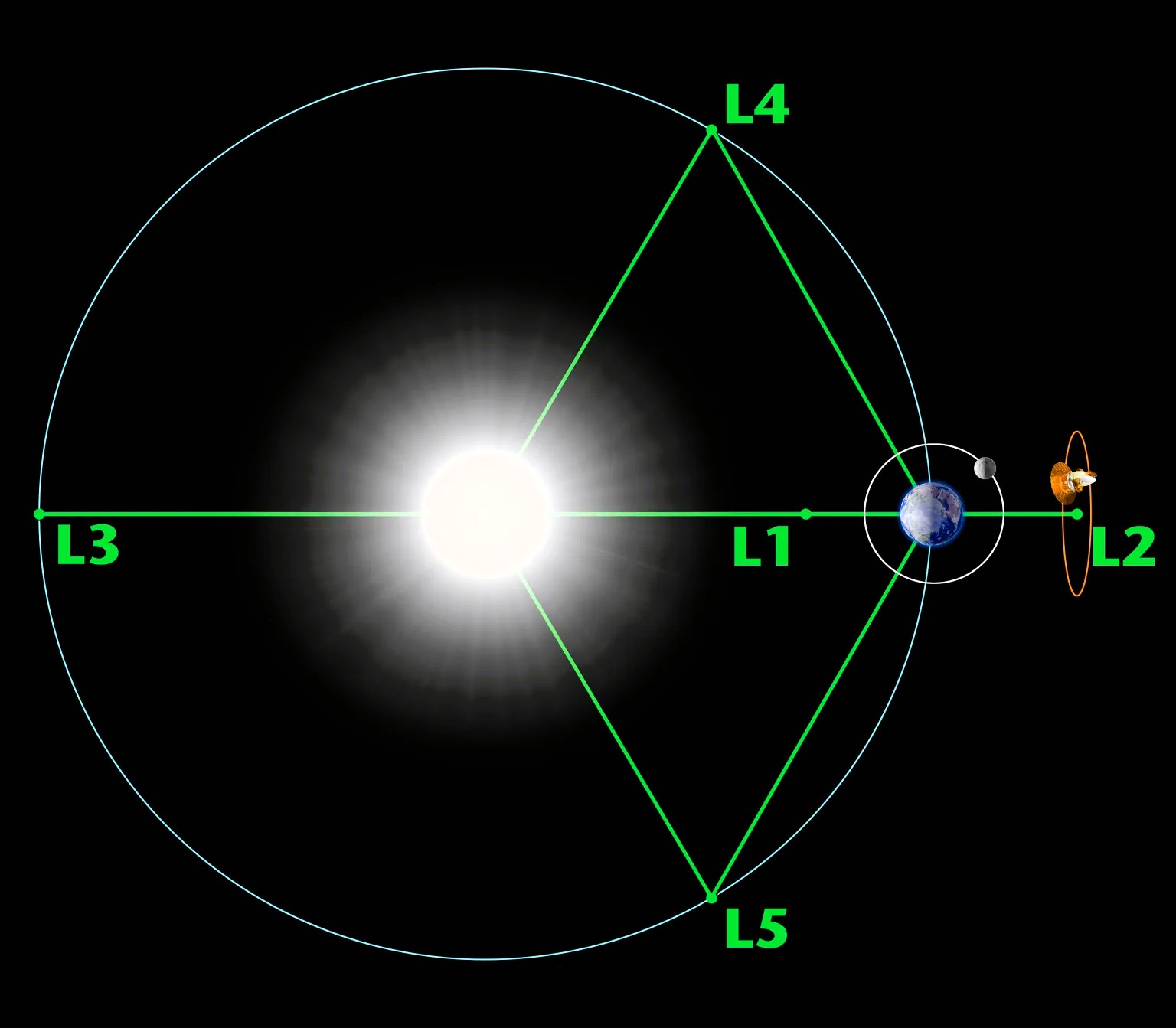
PC: NASA
Latest Solar Imaging System from Aditya-L1 Unveiled
ISRO has recently revealed the first-ever complete disk images of the Sun, which were captured in near ultraviolet wavelengths by the Aditya-L1 spacecraft. The spacecraft was launched from Sriharikota on September 2 and has provided extraordinary depictions of the Sun across a broad range of wavelengths, from 200 to 400 nm.
For more information, you may read Ever Snaps Of The Full Sun Captured By India's Aditya-L1 Mission
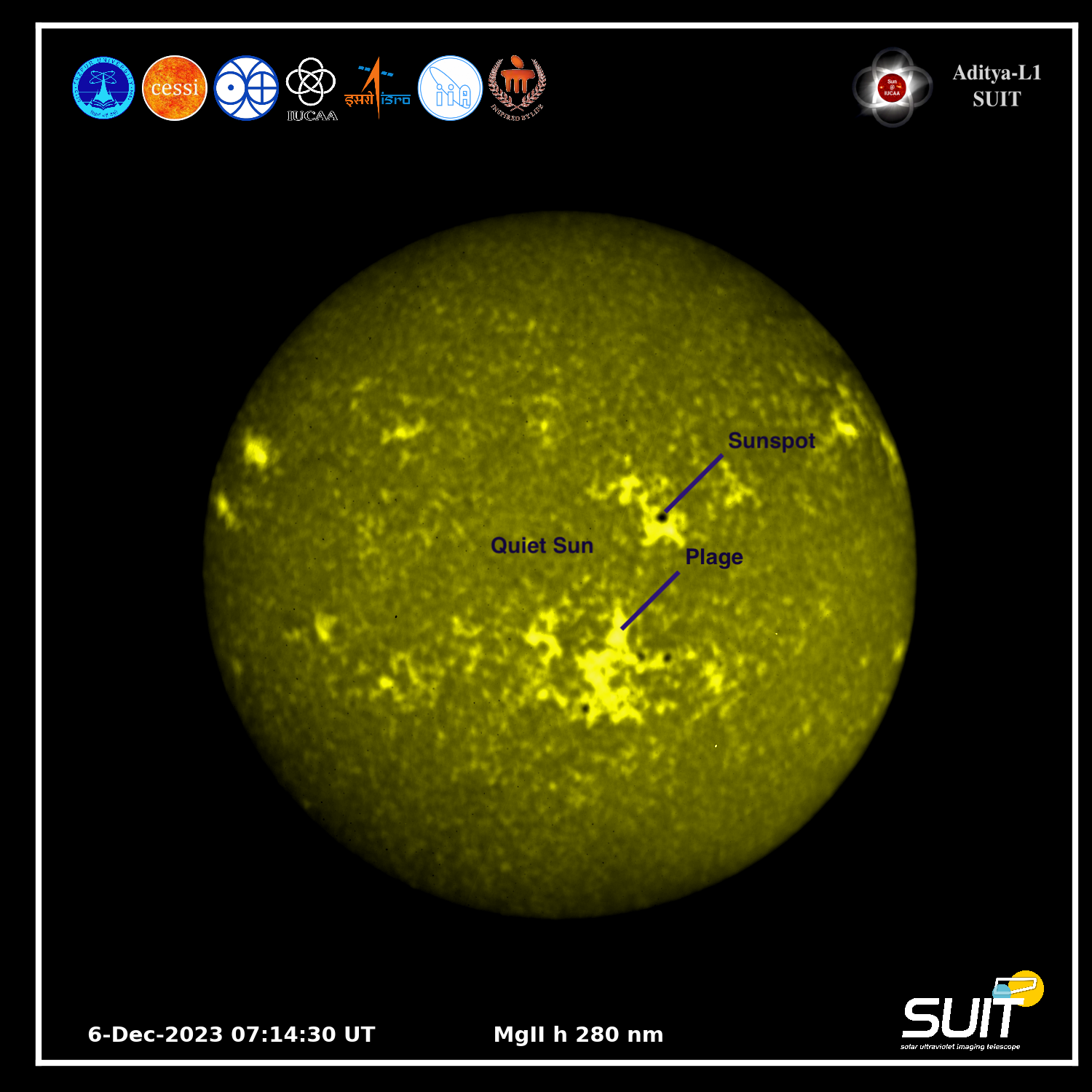
PC: ISRO
Significant orbital manoeuvres ensure uninterrupted solar observation
ISRO Chairman S Somanath graciously shared that Aditya-L1, upon reaching L1, will carefully perform a vital orbital manoeuvre to establish a stable orbit. This strategic move holds immense importance for the spacecraft's five-year mission, facilitating uninterrupted data collection that is not only valuable for India but also for the global scientific community.
VIDEO | "It's very interesting to see the growth of Gujarat over the last so many years. I have been coming here (Ahmedabad) for the last 25 years as an ISRO man. We have an ISRO centre here. And the transformation is fantastic in terms of the business, infrastructure, growth and… pic.twitter.com/qIUQh3juBZ— Press Trust of India (@PTI_News) December 22, 2023
Source: PTI (X)
Global collaboration and support
Previous reports suggested that there was a cooperative partnership between the European Space Agency (ESA) and ISRO in the solar mission. The ESA's involvement includes offering deep space communication services and assisting in the testing of crucial new flight dynamics software.
India's vision for technological advancement in space, if I may kindly state, is to make significant progress in the field of space technology with utmost dedication and commitment.
Somanath highlighted India's ambitions in space technology and presented plans for the 'Bharatiya Space Station.' This further reflects Prime Minister Narendra Modi's vision, positioning India as a technologically advanced nation in the global space domain.

Dr. S. Somanath- ISRO chairman (PC:Instagram)
The strategic focus of Indian space missions
Emphasizing India's approach, Somanath strongly emphasizes the importance of directing efforts towards areas where the nation has the potential to excel. This strategic focus plays a crucial role in India's space missions, as it aims to boost economic growth through emerging technologies and establish a prominent position within the global space community.
In summary
It can be confidently stated that India has a promising future in the field of space exploration.
As Aditya-L1 sets out on its mission to explore the Sun, India's dedication to advancing space technology shines with brilliance. Through international cooperation, meticulous planning, and a forward-looking perspective, India stands ready to play a crucial role in shaping the future of space exploration.
Ⓒ Copyright 2023. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.