On August 8, 2024, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) once again opted to maintain the status quo on policy rates, marking the ninth consecutive instance. The key benchmark repo rate was held steady at 6.5%, as the MPC continued its approach of 'withdrawal of accommodation,' even as India's economic indicators showed solid growth and signs of easing inflationary pressures.

1. Benchmark Repo Rate Held at 6.5%
For the ninth consecutive time, the RBI has kept the benchmark repo rate unchanged at 6.5%. This decision reflects the MPC's balanced approach to managing economic growth without exacerbating inflationary pressures. The MPC's decision to maintain the repo rate at 6.5% was not unanimous, with a 4:2 majority favoring the status quo. As a result, the standing deposit facility (SDF) rate remains at 6.25%, while the marginal standing facility (MSF) rate and the bank rate both stay at 6.75%. The continuity in these rates underscores the RBI's cautious approach to managing economic growth while keeping inflation in check.
2. Focus on Withdrawal of Accommodation
The RBI remains committed to its policy stance of 'withdrawal of accommodation.' This approach aims to curb inflation while simultaneously supporting economic growth. The strategy indicates that the RBI is prioritizing long-term economic stability.
3. GDP Growth Forecast Retained at 7.2% for FY25
The RBI has kept its GDP growth forecast for the fiscal year 2025 at 7.2%. This projection reflects optimism about India's economic trajectory, despite some adjustments to quarterly forecasts based on recent data.
4. Retail Inflation Projection Steady at 4.5%
The central bank has maintained its retail inflation projection at 4.5% for FY25. This steady forecast indicates the RBI's confidence in managing inflationary pressures within acceptable limits.
5. Global Economic Outlook Remains Resilient
Despite some moderation in the pace of global economic growth, the outlook remains resilient. This global context is crucial for India, as it impacts trade, investment, and overall economic performance.
6. Domestic Economic Activity Sustains Momentum
India's domestic economic activity continues to be robust, driven by strong consumption, investment, and government spending. This momentum is a positive sign for sustained economic growth.
7. Manageable Current Account Deficit
The current account deficit remains within manageable limits, reflecting a balanced trade environment and stable capital flows.
8. Forex Reserves at Historic High
India's foreign exchange reserves have reached a historic high of $675 billion. This strong reserve position provides a buffer against external shocks and enhances the country's economic stability.
9. Indian Rupee Remains Range-Bound
The Indian rupee has remained largely stable in FY25 so far, reflecting the resilience of the domestic economy and effective monetary management by the RBI.
10. Resilience of the Indian Financial System
The Indian financial system continues to gain strength and resilience. This stability is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and supporting long-term economic growth.
11. Public Repository of Digital Lending Apps
To promote orderly development in the digital lending ecosystem and address issues related to unauthorized digital lending apps (DLAs), the RBI has proposed creating a public repository of these apps. Regulated entities will be required to report and update information about their DLAs in this repository, helping consumers identify unauthorized lending platforms.
12. Introduction of 'Delegated Payments' through UPI
The RBI plans to introduce 'Delegated Payments' through the Unified Payments Interface (UPI). This move is expected to enhance the convenience and security of digital transactions, further promoting digital payments in India.
13. Proposed Steps to Speed Up Cheque Clearance
In a bid to improve the efficiency of cheque payments, the RBI has proposed measures to speed up the clearance process. Currently, cheque clearing can take up to two working days, but the proposed changes could enable cheques to be cleared within a few hours on the day of presentation.
14. Increase in UPI Tax Payment Limit
The RBI has raised the limit for tax payments through UPI from ₹1 lakh to ₹5 lakh per transaction. This increase aims to encourage more taxpayers to use digital payment methods, enhancing the ease of doing business.
15. Core Inflation Easing
Core inflation, which excludes food and fuel, has moderated to historic lows in May and June 2024, dropping from 3.2% in April to 3.1% in May-June. This trend suggests that underlying inflationary pressures are easing.
16. Food Inflation Remains a Concern
Despite the easing of core inflation, food inflation remains a significant concern. With food prices contributing to more than 75% of headline inflation in May and June, and vegetable prices alone accounting for about 35% of inflation in June, the RBI remains cautious. The central bank anticipates that high food prices may have persisted in July, though favorable base effects and improved monsoon conditions could provide some relief.
17. Next MPC Meeting Scheduled for October 2024
The next meeting of the MPC is scheduled for October 7-9, 2024. This meeting will be closely watched for any potential changes in policy rates or stance, particularly in light of evolving economic conditions.
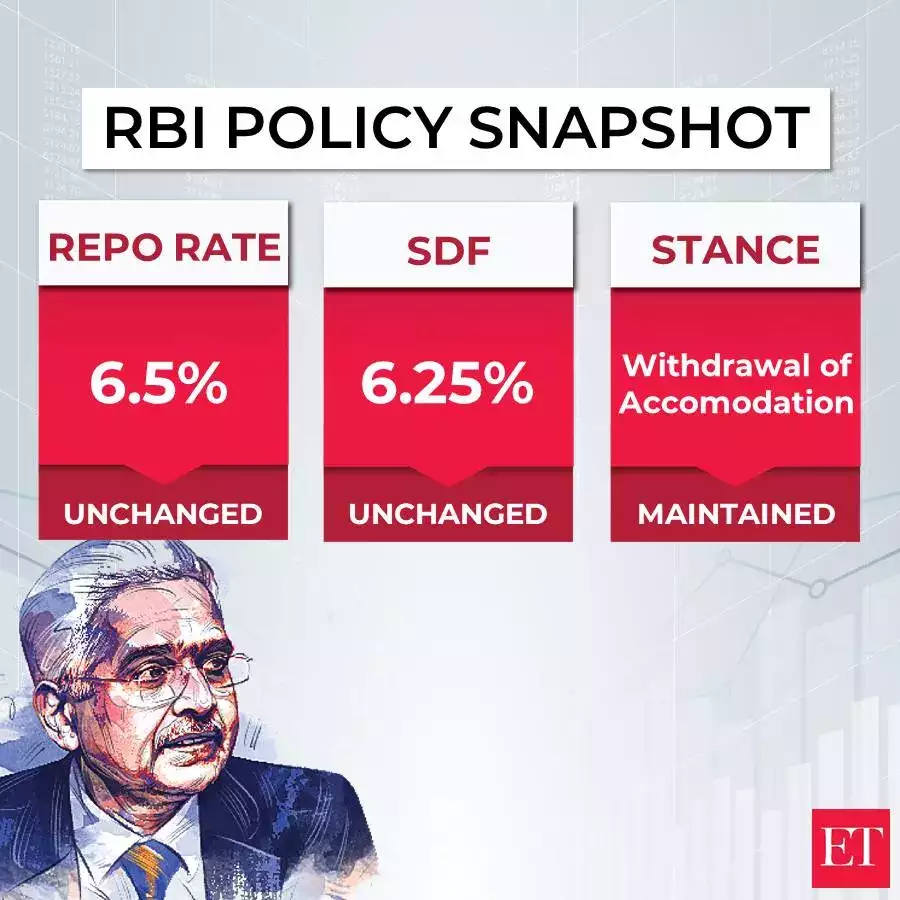
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) held its Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting in August 2024, with significant updates regarding the country's economic and monetary stance. Below is a detailed overview of the key decisions and observations from the meeting.
- Repo Rate Decision
The RBI has decided to keep the repo rate unchanged at 6.5%. This decision was reached by a 4:2 vote within the MPC. According to RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das, the focus remains on "withdrawal of accommodation," meaning the RBI aims to gradually reduce the extent of monetary support provided to the economy. There is considerable alignment between market expectations and the RBI's current policy stance.
- Inflation Trends
Headline Inflation
-
Recent Trends: Headline inflation, which had been steady at 4.8%, increased to 5.2% in June 2024. This rise was attributed primarily to food inflation, as noted by the RBI Governor.
-
Food Inflation Impact: Food prices have had a substantial impact on overall inflation, contributing to over 75% of the increase in headline inflation during May and June. Notably, vegetable prices surged sharply, contributing significantly to food inflation.
Core Inflation
- Despite the uptick in headline inflation, core inflation has been showing signs of moderation. Core inflation reached a new low, though high food prices have continued to pose challenges.

- Economic Growth and Projections
Domestic Growth
-
Current Status: Domestic economic growth remains robust, supported by steady urban consumption and increasing rural demand. The RBI Governor highlighted that GDP growth has been resilient, enabling the RBI to concentrate on managing inflation.
Future Projections
-
GDP Growth Forecast: The RBI projects GDP growth at 7.2% for the financial year 2024-25. The breakdown is as follows: Q1 GDP at 7.1%, Q2 at 7.2%, Q3 at 7.3%, and Q4 at 7.2%. For the first quarter of FY26, GDP growth is also projected at 7.2%.
- Global Economic Outlook
Global Growth
-
Current Trends: The global growth outlook remains steady. Inflation is gradually receding across major economies, and several central banks are cautiously adjusting their policies. The RBI Governor pointed out that despite some central banks tightening policies or increasing rates, the overall global economic conditions appear stable.
Financial Market Volatility
-
Market Conditions: Global financial markets have experienced volatility due to concerns over growth slowdowns and geopolitical tensions, particularly in the Middle East. This has led to fluctuations in international financial markets, but the RBI emphasizes India's strong macroeconomic fundamentals.

- Sectoral Developments
Monsoon and Agriculture
-
Agricultural Prospects: The steady growth of the southwest monsoon and improving reservoir levels are expected to positively impact the Kharif season. A good monsoon is anticipated to benefit the agriculture sector, although potential La Niña conditions may affect agricultural outcomes.
Private Investment and Corporate Activity
-
Investment Trends: Private corporate investment is on the rise, supported by an expansion in bank credit and government capex initiatives. The RBI also noted a steady increase in private investment due to favorable policy support.
Export Performance
-
Merchandise and Services Exports: Merchandise exports have expanded at a slower pace, while services exports recorded double-digit growth in May, although they moderated in June.

- Financial System Stability
Bank and Non-Banking Sector
-
System Stability: The RBI Governor highlighted the resilience and improving stability of the Indian financial system. Non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) and urban cooperatives have shown progress, while the overall financial sector remains robust and healthy.
Risks and Regulatory Measures
-
Geopolitical and Financial Risks: Geopolitical tensions and global financial market volatility pose risks. The RBI remains vigilant about these challenges and their potential impact on the Indian economy.
-
Regulatory Oversight: The RBI has proposed creating a public repository of digital lending apps to safeguard consumers and increase transparency. Additionally, the limit for tax payments via UPI will be increased to ₹5 lakh, and continuous cheque clearing is proposed to enhance the efficiency of financial transactions.

- U.S. Economic Growth and Recession Concerns
During his press conference, RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das addressed the state of the U.S. economy, highlighting the following points:
-
Current U.S. Economic Growth: Governor Das remarked that the overall economic growth in the U.S. remains strong. However, he emphasized that recent unemployment data, reflecting just one month, is insufficient for making long-term predictions about a potential recession or economic slowdown.
-
Recession Speculation: He cautioned against speculating on a U.S. recession based on short-term data, describing it as premature to draw conclusions about an impending economic downturn.
- Monitoring Data and External Shocks
Governor Das underscored the importance of vigilance regarding both domestic and international data:
-
Data Vigilance: The RBI will continue to closely monitor data from various sources, both within India and internationally, to ensure informed decision-making.
-
Resilience to External Shocks: He noted that India has enhanced its resilience against external economic shocks, a point supported by forecasts from international agencies predicting increased global trade growth.
- Liquidity Coverage and Bank Regulations
Governor Das provided updates on liquidity management and banking regulations:
-
Liquidity Coverage: A draft on liquidity coverage has been released for public feedback. Governor Das clarified that there has not been an increase in liquidity coverage, contrary to some reports.
-
Bank Decisions on Deposit Rates: The determination of deposit rates remains under the purview of individual banks. Governor Das explained that the RBI has deregulated deposit rates and encouraged banks to leverage their branch networks and innovate to attract deposits.
- Bank Practices and Innovations
Governor Das also discussed bank practices and innovations:
-
Branch Network Utilization: Banks are encouraged to utilize their branch networks effectively and explore innovative products to enhance deposit mobilization.
-
Top-Up Loans Monitoring: The RBI is addressing issues with certain banking entities breaching norms related to home equity top-up loans. There is a focus on ensuring that banks monitor the end use of these loans to prevent misuse.
- Inflation, Economic Indicators, and Foreign Investment
Further points covered included:
-
CPI Basket Review: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) basket, based on 2011-12 data, is due for a review which has been delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
Impact of Floods: Governor Das noted that while floods could temporarily impact inflation, a good monsoon is expected to positively influence the upcoming kharif and rabi seasons.
-
Global Investment Sentiment: Positive sentiment from global investors towards Indian bonds was highlighted, reflecting confidence in India's economic stability.
-
India's GDP Growth: Governor Das projected that India's GDP growth will be the highest globally, reinforcing the country's strong economic performance.
- Regulatory and Operational Updates
Additional regulatory and operational updates included:
-
Review of Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR): The review of the LCR is still in the draft stage, as mentioned by RBI Deputy Governor M. Rajeshwar Rao.
-
Government Securities and Foreign Exposure: RBI Deputy Governor Michael Patra indicated that foreign exposure to government securities stands at 4.8%, with expectations for India's weight in bond indices to increase over the next ten months.
-
Household Savings Trends: Deputy Governor Patra also discussed changes in household savings patterns, noting a high level during COVID-19 followed by a drawdown and a rise in physical savings.
- Addressing Financial Risks and System Integrity
-
Risk Management: Deputy Governor Swaminathan Janakiraman noted that loan growth in riskier segments has moderated since the November circular, with risk weights normalized post-COVID. The RBI is working with law enforcement to tackle fraudulent accounts.
-
Systemic Issues: RBI Governor Das spoke about NPCI's action to isolate technical problems in individual banks to prevent systemic spread. He also noted that while data on mule accounts is not immediately available, most banks have systems to detect and address illegal activities.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.

























