In recent weeks, the global economic landscape has been significantly impacted by the United States' decision to impose reciprocal tariffs on Indian goods. This move, aimed at reducing the U.S. trade deficit, has raised concerns about its potential effects on India's economic growth. The tariffs could lead to a slowdown in India's GDP growth, prompting expectations of deeper interest rate cuts by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to mitigate these impacts.

Understanding the Tariffs
The U.S. has implemented a 26% to 27% reciprocal tariff on Indian goods, citing high import duties imposed by India on American products. This decision affects various sectors, although essential items like pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, and energy products are exempt from these higher tariffs. The tariffs primarily target sectors such as steel, aluminum, and technology, which could reshape India’s export landscape and domestic manufacturing.
Impact on India's GDP Growth
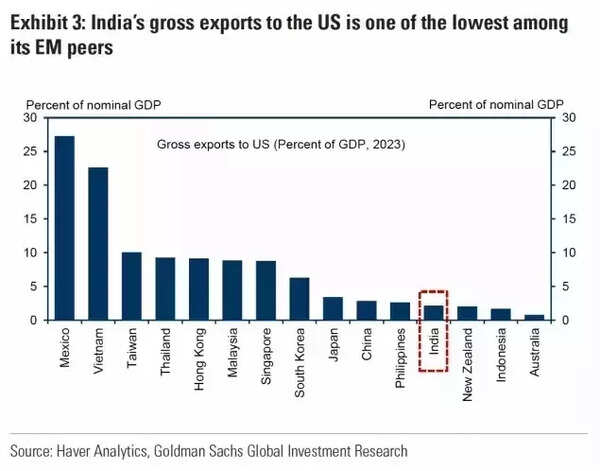
Economists estimate that these tariffs could shave off anywhere from 20 to 90 basis points (bps) from India's GDP growth this fiscal year. For instance, Goldman Sachs has revised its growth forecast down to 6.1% from a previous estimate of 6.3%. This reduction in growth is largely due to the expected decline in exports to the U.S., which accounts for about 18% of India's goods exports.
The impact of these tariffs is not uniform across all sectors. While India's reliance on services exports could provide some cushion against global trade disruptions, the overall economic slowdown could dampen business sentiment and investment. Madhavi Arora, Chief Economist at Emkay Global, suggests that the tariffs could lead to a loss of $30-33 billion in exports to the U.S., translating to a significant contraction in GDP.

Expectations of Deeper Rate Cuts
In response to the potential economic slowdown, analysts anticipate that the RBI might implement deeper interest rate cuts. The central bank has already made its first interest rate cut in five years in February, and another cut is expected during its April meeting. The rationale behind these cuts is to stimulate domestic demand by lowering borrowing costs, as inflation remains within the RBI's target range.
Citi's Chief Economist for India, Samiran Chakraborty, notes that the current economic dynamics create opportunities for the RBI to bolster growth while keeping inflation aligned with targets. With inflation expected to average 4.2% this fiscal year, the RBI has room to maneuver and support economic growth through monetary policy easing.
Opportunities Amid Challenges
While the tariffs pose significant challenges, they also present opportunities for India. Sameer Narang, Head of Economics Research at ICICI Bank, suggests that India's lower wage costs make it an attractive alternative for manufacturing, especially if infrastructure and logistics improve. This could potentially offset some of the negative impacts of the tariffs by attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) and boosting domestic manufacturing.
Moreover, India's strategic position in global trade could allow it to negotiate favorable trade agreements. The ongoing discussions between India and the U.S. on a trade deal might mitigate some of the effects of the tariffs, depending on how negotiations unfold.
Conclusion
The imposition of U.S. tariffs on Indian goods has introduced significant uncertainty into India's economic outlook. While the immediate impact is a potential slowdown in GDP growth, the RBI's proactive stance on interest rates could help mitigate these effects. As India navigates these challenges, it must also seize opportunities to strengthen its manufacturing sector and negotiate beneficial trade agreements. The coming months will be crucial in determining how effectively India can manage the ripple effects of these tariffs and maintain its economic momentum.
In the broader context, this situation highlights the complexities of global trade dynamics and the need for countries to adapt quickly to changing economic landscapes. As the world grapples with trade tensions and economic uncertainties, India's response will be a critical test of its resilience and strategic economic planning.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.

























