The Impact of Rising Oil Prices on India
India, heavily reliant on energy imports, is particularly vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices. A spike in oil prices can lead to:
- Increased inflation: Higher fuel costs drive up transportation and input expenses, leading to an overall increase in the prices of goods and services.
- Widening current account deficit (CAD): India needs to spend more foreign exchange to import oil, which can widen its CAD.
- Weakening rupee: As India pays more for imports, the rupee tends to depreciate.
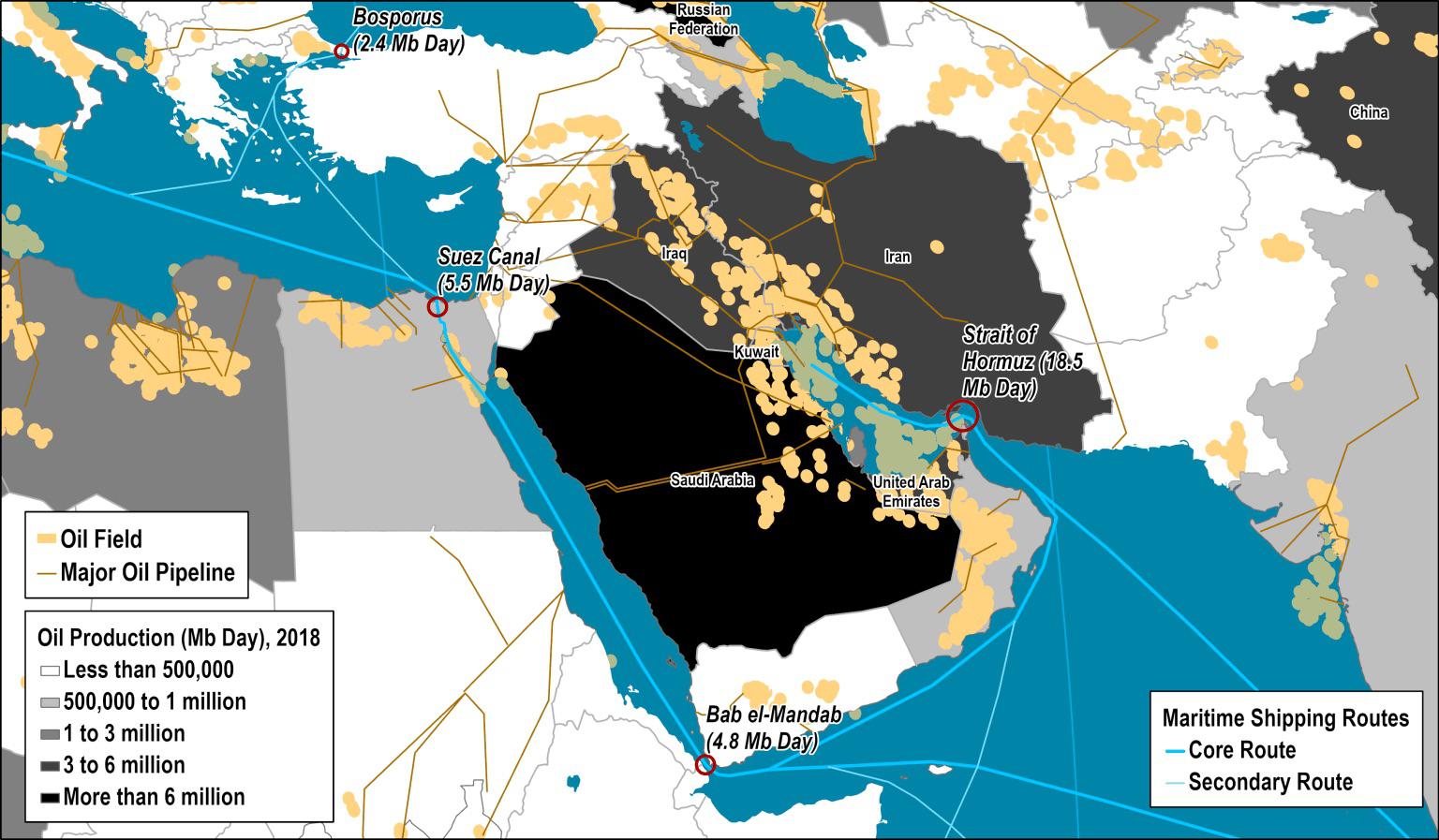
Image Source - Reddit
Middle East Role
Stiffening tensions between Iran and Israel have heightened anxiety about oil-related global supply disruptions. Iran is one of the significant producers and exporters of oil, located adjacent to a strategic strait called the Strait of Hormuz through which all such deliveries need to pass; therefore, the risk of supply disruption also heightens.
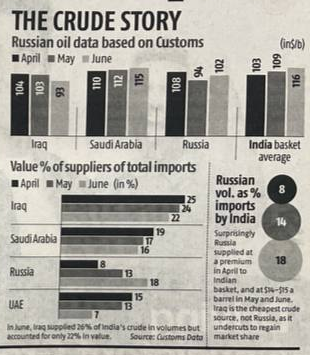
India's Economic Vulnerabilities
India's economy is already facing several challenges, including:
- Rising inflation: While inflation has been relatively contained, sustained high oil prices could push it higher.
- Widening current account deficit: India's CAD has been increasing, making it more susceptible to external shocks like rising oil prices.
- Depreciating rupee: The rupee has been under pressure, which can make imports more expensive and exacerbate inflation.

The Road Ahead
The ongoing tensions in the Middle East and the potential for further escalation pose significant risks to India's economy. The government must closely monitor the situation and take appropriate measures to mitigate the impact of rising oil prices. These measures could include these measures could include:
- Reducing dependence on oil: India can promote energy efficiency and diversify its energy sources to reduce its reliance on oil imports.
- Strengthening the rupee: The government can take steps to strengthen the rupee, such as attracting foreign investment and reducing the current account deficit.
- Controlling inflation: The government can implement measures to control inflation, such as raising interest rates or imposing price controls on essential goods.
As the global energy landscape continues to evolve, India will need to adapt and find ways to manage the challenges posed by rising oil prices and geopolitical tensions.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.

























