China, the world's second-largest economy, is grappling with a profound demographic challenge as its population has witnessed a second consecutive annual decline. The year 2023 saw a record-low birth rate and a surge in COVID-19 deaths, prompting concerns about the long-term effects on the country's economic growth. In this article, we explore the multifaceted issues contributing to China's demographic shift and the potential repercussions on its economic landscape.

Image Source: CNN
Population Decline Trends:
-
2023 Demographic Figures: The National Bureau of Statistics reported that China's population decreased by 0.2 per cent, or 2.75 million, in 2023, following a decline of 850,000 in 2022. The total number of deaths rose by 6.6 per cent to 11.1 million, reaching the highest level since 1974. Additionally, new births fell by 5.7 per cent to 9.02 million, with the birth rate plummeting to a record low of 6.39 births per 1,000 people.
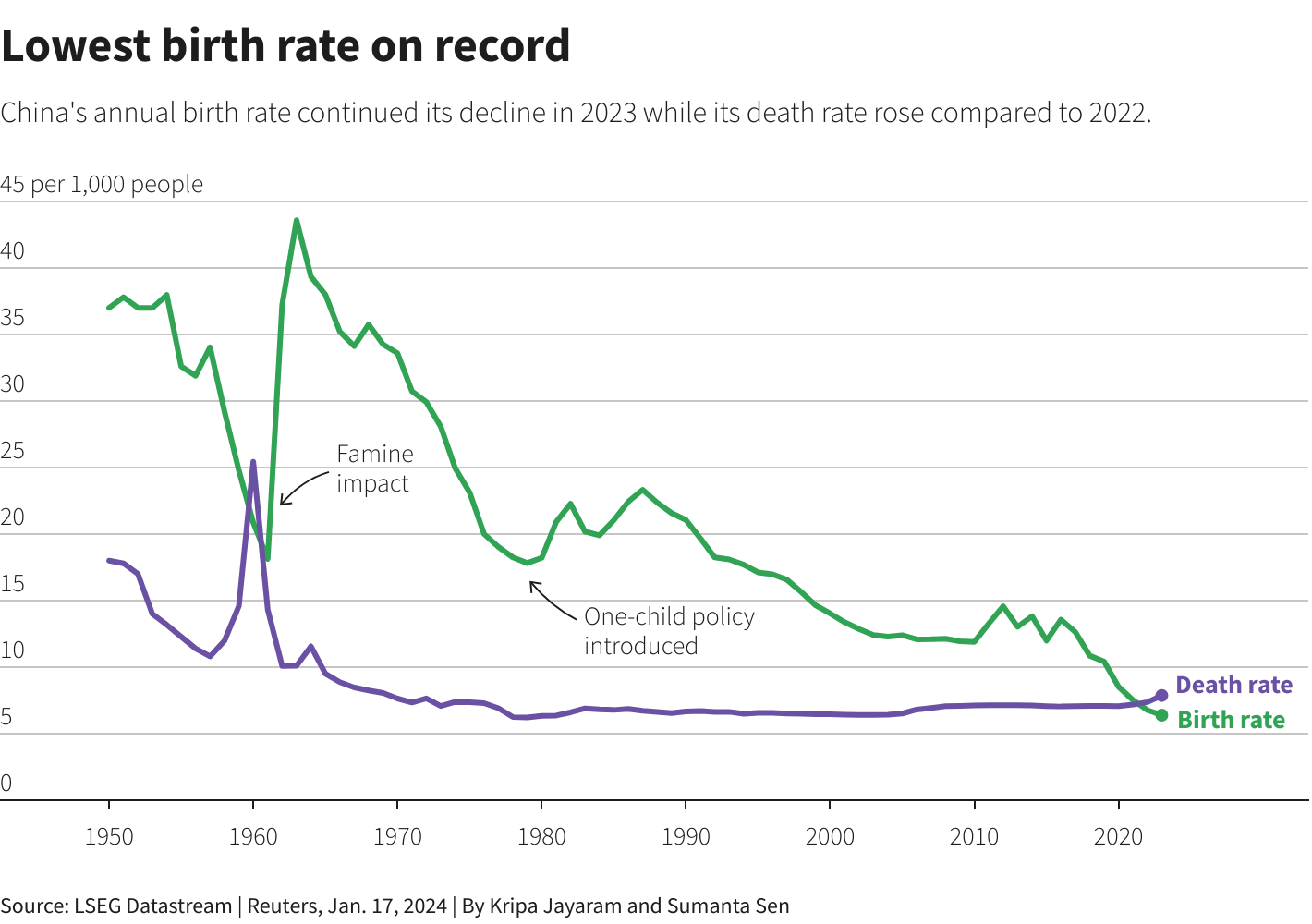
Image Source: Reuters
-
Post-One-Child Policy Challenges: The aftermath of the one-child policy, implemented from 1980 to 2015, continues to impact birth rates. The shift from population control to encouraging childbirth has proven challenging, as rising costs and economic uncertainties deter many Chinese couples from having more than one child. The country faces a surge in retirement-age population, projected to exceed 400 million by 2035, posing significant economic and social challenges.
Economic Ramifications:
-
Labor Force and Consumer Concerns: The declining birth rate contributes to a shrinking workforce, further exacerbated by a record-high youth unemployment rate in 2023. The economic consequences extend to reduced consumer demand, as high childcare and education costs dissuade couples from expanding their families.
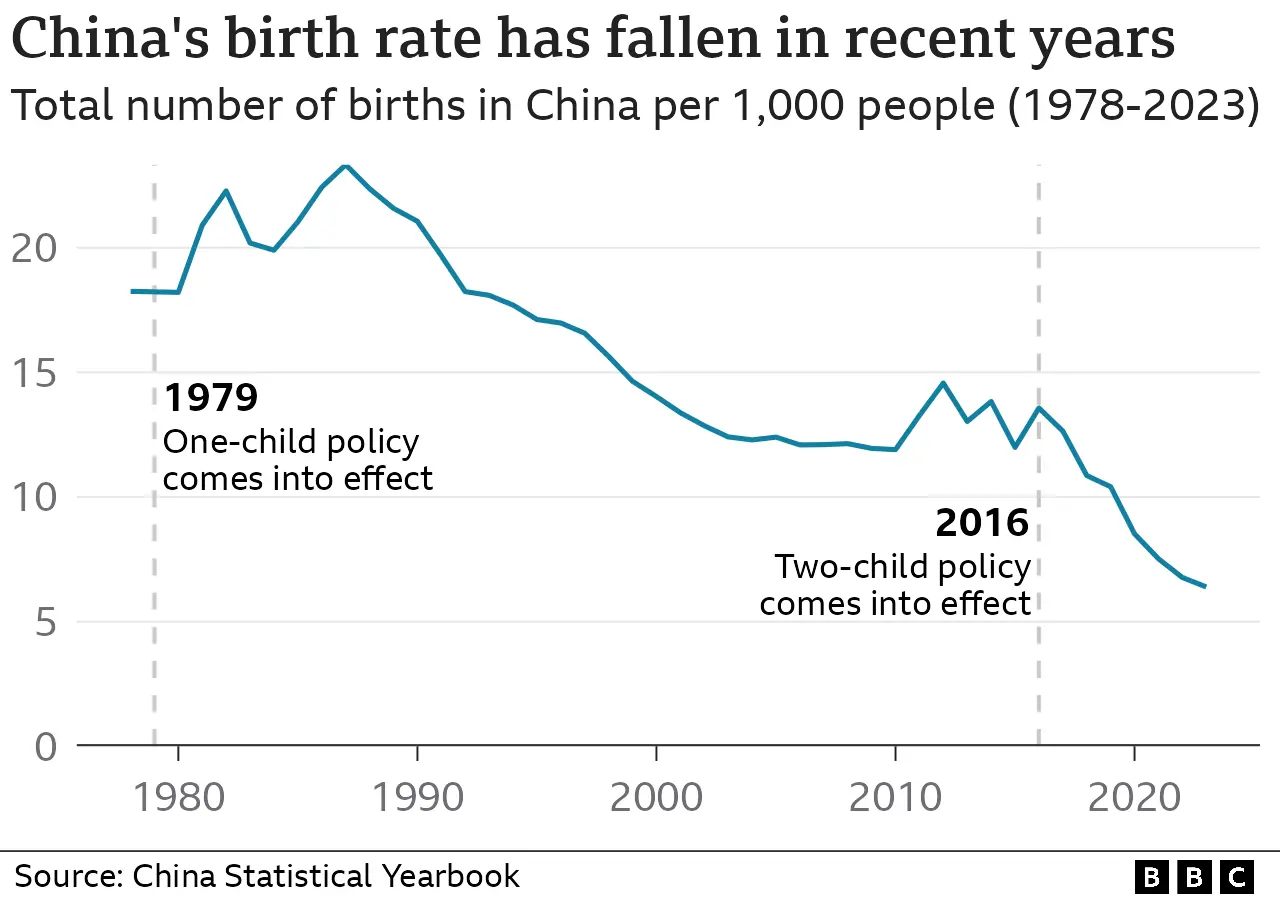
Image Source: BBC
-
Property Sector and Wealth Distribution: The real estate sector, which houses two-thirds of household wealth, is experiencing a crisis. Home sales and property investment slumped, adding pressure on an industry vital to China's economic stability. The imbalance in wealth distribution and the challenges in the property market contribute to concerns about the nation's overall growth prospects.
Pension System Challenges:
-
Aging Population and Pension Shortfall: China's retirement-age population is expected to surpass 400 million by 2035, leading to concerns about the sustainability of the pension system. The Chinese Academy of Sciences warns of the system running out of money by 2035, impacting the financial well-being of the elderly.
_1705493077.png)
Image Source: Reuters
-
Varied Economic Indicators: While China managed to achieve a 5.2% GDP growth in 2023, meeting its annual target, the economic recovery remains uneven. The property sector's struggles, coupled with challenges in consumption and a potential slowdown in GDP growth in 2024, raise questions about the sustainability of China's economic trajectory.
Global Implications:
-
China's Global Standing: China's demographic challenges have not gone unnoticed globally. India surpassed China as the world's most populous country in 2023, fueling discussions about relocating supply chains from China. Projections suggest a long-term decline in China's population, potentially impacting its geopolitical influence and economic standing.
Image Source: Le Monde
-
Need for Stimulus Measures: Mixed economic data, including positive indicators in industrial production and fixed-asset investment, point to the necessity for more stimulus measures. Policymakers face the challenge of balancing economic recovery with the ongoing demographic shifts.
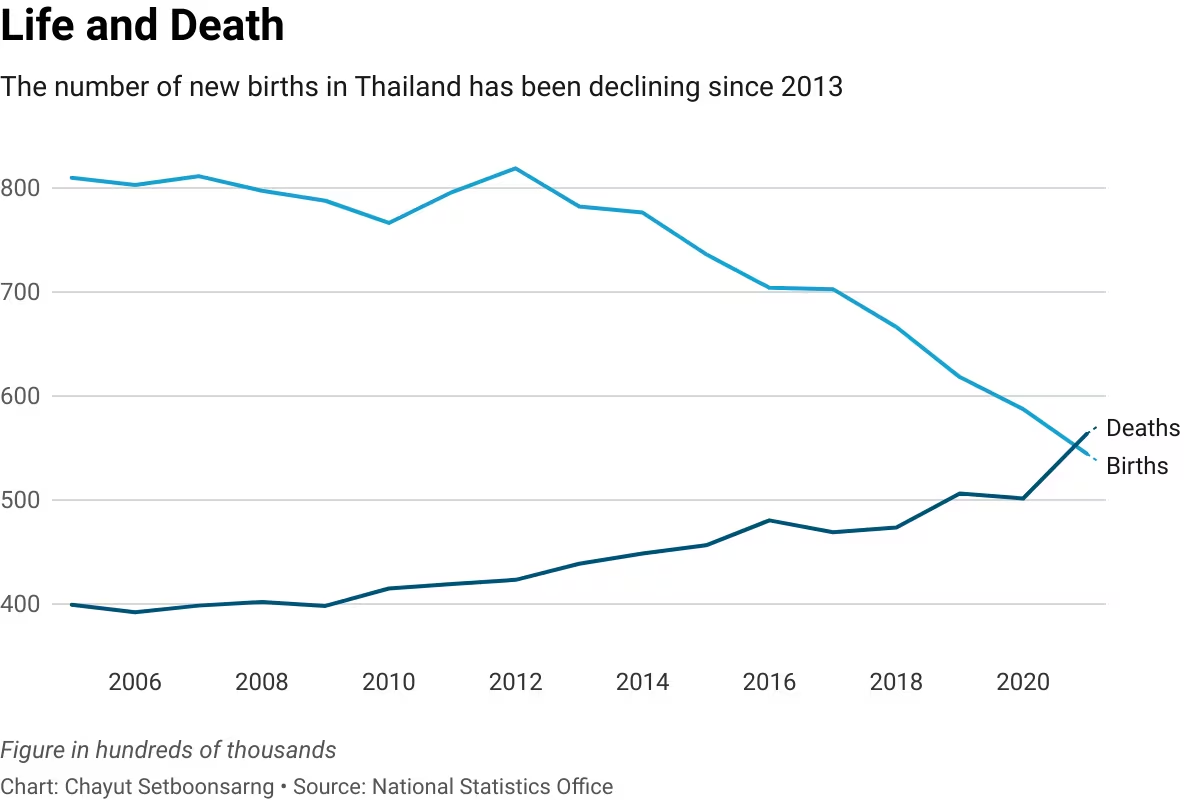
Image Source: Reuters
What does it mean for India?
A declining birth rate in China could have several implications for India, both regionally and globally. Here are some potential effects:
-
Economic Impact: A declining birth rate in China may lead to an ageing population and a shrinking workforce. This could affect China's economic growth and productivity. India, with a relatively younger population, might become a more attractive destination for foreign investments and businesses looking for a vibrant labour force.
-
Global Economic Shifts: China has been a major driver of global economic growth. If its population growth continues to slow, it may have repercussions for the global economy. India, with its large and growing population, could become a more significant player in the global economic landscape.
-
Geopolitical Dynamics: Population size and demographics can influence geopolitical power. India, with a growing population, could potentially see an increase in its geopolitical influence relative to China, especially if China's demographic challenges impact its economic and military capabilities.
-
Resource Competition: Both China and India have large populations, and their demand for resources such as energy, food, and water is substantial. As China's population growth slows, it might reduce the intensity of resource competition between the two countries. However, India would still face the challenge of meeting the needs of its growing population.
-
Global Trade Dynamics: China has been a manufacturing hub, and its declining birth rate might impact its labour force and, consequently, its manufacturing capabilities. This could open up opportunities for India to become a more significant player in global manufacturing and trade.
-
Social and Economic Challenges for China: An ageing population can bring about social and economic challenges, such as increased healthcare costs and pension obligations. This could potentially lead to a shift in China's domestic policies and priorities. India, with a younger population, might be better positioned to address similar challenges.
-
Migration Patterns: If China faces economic challenges due to demographic shifts, there might be changes in migration patterns. India could experience increased immigration or see a shift in the flow of skilled workers and professionals.
Image Source: NBC News
Demographic changes in one country often have ripple effects on the global stage, influencing economic, social, and political dynamics.
China's demographic dilemma, characterized by a declining birth rate, an ageing population, and economic uncertainties, poses significant challenges to its growth prospects. The interplay between demographic trends and economic indicators highlights the need for comprehensive policies to address labour market imbalances, stimulate consumption, and ensure the sustainability of the pension system. As China navigates these challenges, the world watches closely, recognizing the potential global implications of the demographic shifts in the world's second-largest economy.
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.























