The world's healthcare system had never had to deal with issues like the ones COVID-19 caused before. At first, medics didn't know much about COVID-19 or how to treat it, so people who had it in hospitals were taking too many drugs.
A big issue that needs to be looked into is the use of medicines too much
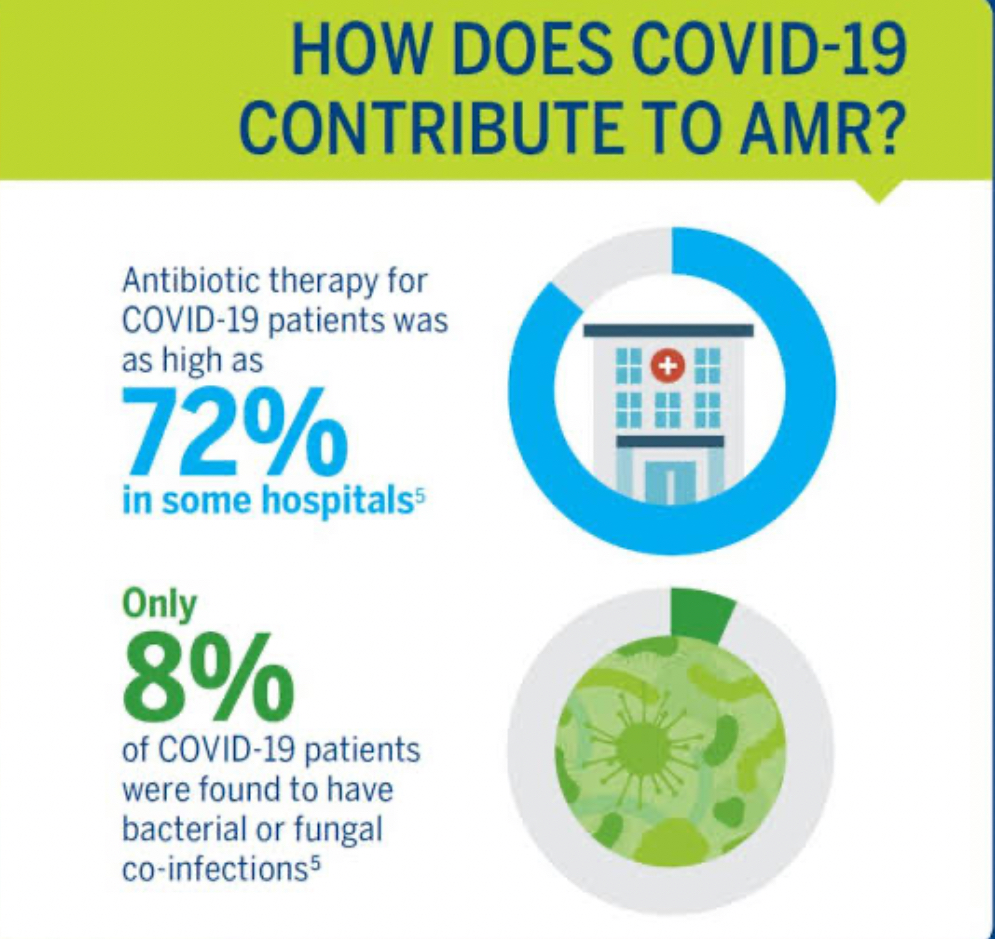
According to a new study from the World Health Organisation (WHO), up to 75% of COVID-19 hospitalised patients were given antibiotics, even though only 8% of them needed them for bacterial co-infections. Even though they mean well, some people around the world take too many drugs. This is not the right way to fight a bug.
Statistics show that this behaviour is different in different places. This was true all over the world, but the Eastern Mediterranean and Africa had the highest rates (83%). People in different parts of the world use antibiotics in different ways. This shows how important it is to have personalised drugs and better diagnostic tools.
Plans for the years 2020–2022 are another thing that worries me. It was a bad sign that more requests for medicines were coming from Africa. Still, people don't always use medicines correctly, especially in places where there aren't many options.
The severity of COVID-19 appears to have influenced changes in drug use as well. Around the world, 81% of people with major or critical cases receive antibiotics. The amounts for weak and moderate cases were not at all the same. 79% of the sick individuals in Africa received medication.
Meaning of "AWARE" Why are "watch group" medications bad?

The WHO divides drugs into three groups: reserve, watch, and access. This method checks each group's chance of AMR. It was found that the most common antibiotics used around the world are in the "watch" group. This means that germs are more likely to become resistant to them. This finding is very scary. It's important to think about how antibiotics are handled because this could speed up the spread of bacteria that can't be killed by drugs.
When people take drugs they don't need, what bad things happen?
People who aren't sick with germs can't get better with antibiotics. These are some of the risks:

Effects: A lot of bad things can happen when you take medicine. Mild sickness and diarrhoea aren't always the worst of them. Serious allergic reactions and antibiotic-associated colitis, a disease that can kill you, are.
Being more likely to get illnesses with C. diff.: The gut microbiome can get messed up when antibiotics aren't needed. This can help the bacteria Clostridium difficile (C. diff), which causes very bad diarrhoea, grow.
The threat that is coming is AMR: When you take too many drugs, some very scary things can happen. Antibiotics can kill germs after they've been exposed to them a lot of times. This means the medicines won't help with any more sicknesses.
When there were no medicines, even small illnesses could kill you. AMR could take us back to that time. This is bad for health around the world.
Call to Action: A Plan to Lower AMR
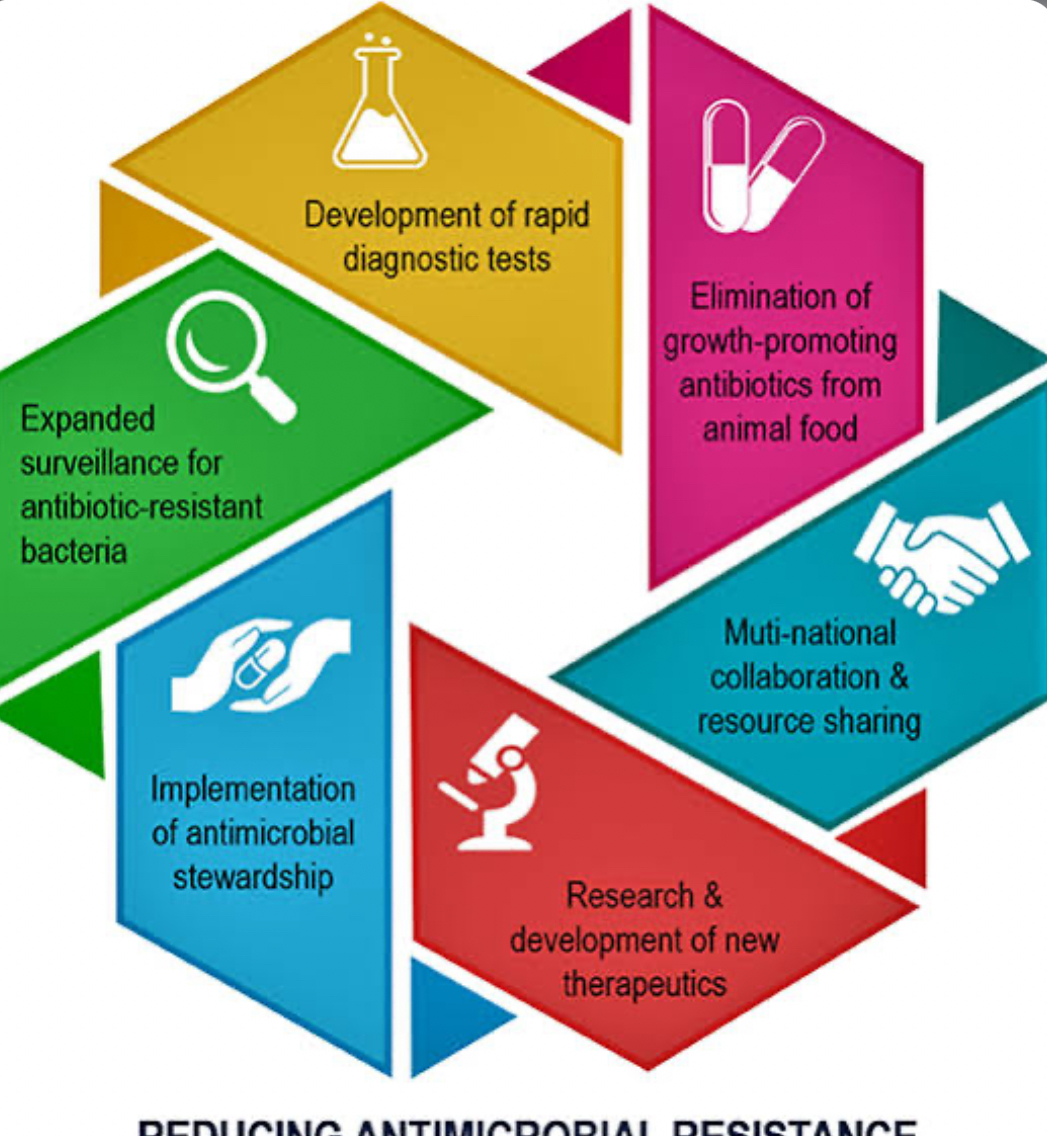
The WHO study tells us how bad the situation is. To stop COVID-19 patients from taking too many drugs and lower the risk of AMR, we need to act quickly on several fronts. These important things are possible for you:
A better way to take antibiotics will be: not to give drugs unless the doctor is sure that there is also a bacterial problem. For this to happen, people need to be able to get better tests that can tell the difference between germ- and virus-based illnesses.
Help based on facts: The WHO is still going through a lot of data to make very important rules about how to use medicines for COVID-19 patients. These rules are based on facts. Antibiotics are easy for doctors and nurses to use when there are rules like these.
Building up systems that are better at managing antibiotics: At hospitals and other healthcare facilities, strong antibiotic management systems are needed to keep an eye on how antibiotics are used, find and fix bad prescribing habits, and teach staff the right way to do things.
Public awareness: To promote responsible use in the community, people need to learn about the dangers of overusing antibiotics.
Last but not least,

Everyone in the world has decided to fight AMR. Dealing with antimicrobial resistance (AMR) quickly and in a well-planned manner is crucial. The upcoming UN General Assembly High-Level Meeting on AMR is a fantastic chance for world leaders to come together and make a detailed plan for what they need to do. A lot of people around the world need to work together, be smart about how they use medicines, and give money to research and development. Preventing the spread of bacteria unaffected by drugs will ensure the effectiveness of medicines intended to treat bacterial diseases. We need to work quickly, but if we all do it, we can make sure that, after all, medicines will still work.
Image Source: Multiple Agencies
Inputs from Agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.


















