Ultra-processed foods: the silent assassins lurking in our pantries, turning our kitchens into danger zones! It's time to kick them out and invite in the real superheroes of nutrition.
A recent extensive study spanning 30 years, featured in The BMJ, has sparked worries regarding the connection between ultra-processed foods and an elevated risk of early mortality. This research, carried out in the United States, underscores the necessity of reassessing our dietary habits for sustained health benefits. Although the researchers refrain from advocating for a total prohibition of all ultra-processed foods, they stress the significance of "limiting consumption of certain types" to foster long-term wellness.
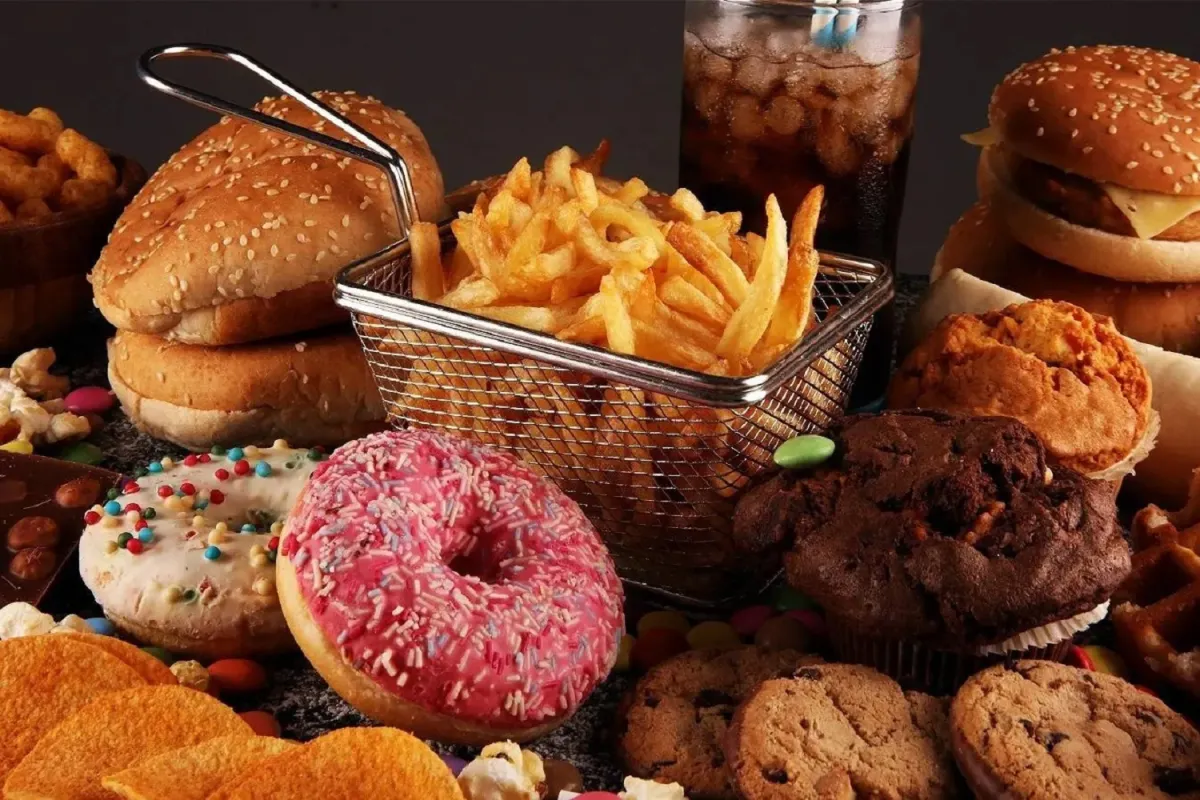

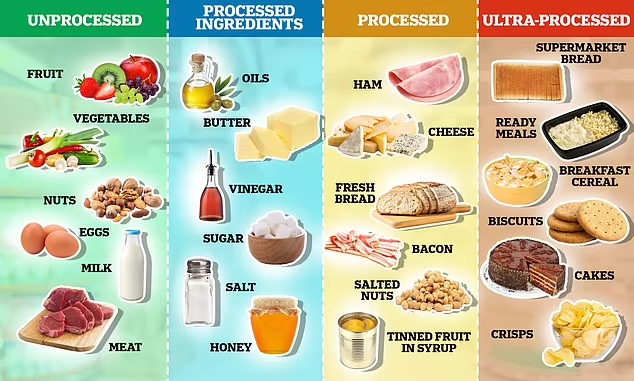
What is Ultra Processed Food?
Processed food typically contains added salt, sugar, and fat.
If a food undergoes extensive industrial processing and has five or more additional ingredients, it's classified as ultra-processed. This often involves adding flavor enhancers, emulsifiers, colors, and other additives to improve taste, shelf life, and convenience. Common processing methods include pasteurizing, canning, fermenting, freezing, and drying.
Certain processed food categories have been strongly linked to early death, including:
- Ready-to-eat meat products
- Sugary drinks
- Dairy-based desserts
- Highly processed breakfast foods
For example, raw atta is unprocessed, while atta with added salt and sugar is considered processed. If we take atta and add numerous other ingredients to make cookies, it becomes ultra-processed.
Why is this concerning for India?
In India, the rise of ultra-processed foods raises concerns due to our increasing dependency on them.
Recent data from the World Health Organization, in collaboration with the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations, highlights significant growth in India's processed food industry.
However, there's a notable shift in trends, particularly since the onset of the pandemic, with a decline in the market share of ultra-processed foods. This change may be attributed to factors such as heightened public health awareness during the pandemic and government efforts to promote healthier diets.
Nevertheless, it's important to acknowledge that the sector still experienced substantial growth, with a compound annual growth rate of 13.37% between 2011 and 2021, positioning it as one of the fastest-growing globally.
Read the WHO report here: The growth of ultra-processed foods in India
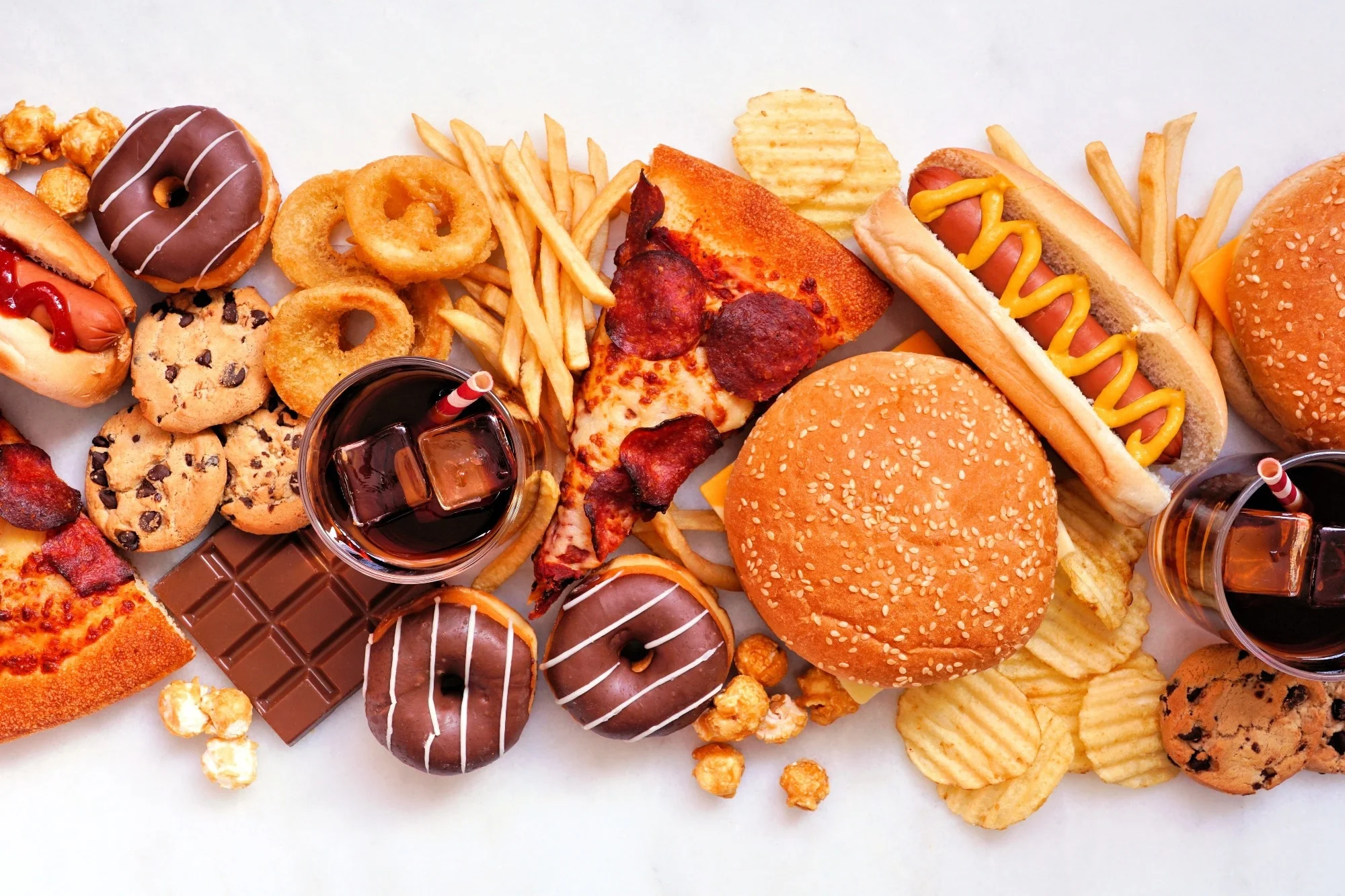

How does eating ultra-processed foods harm us?
Dangers caused by ultra-processed foods:
-
Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Ultra-processed foods often lack essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals due to heavy processing.
- They are typically high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, and sodium, contributing to poor nutritional balance.
-
Weight Gain and Obesity:
- Regular consumption of ultra-processed foods is linked to weight gain and obesity.
- These foods tend to be calorie-dense but nutrient-poor, leading to overeating and excessive calorie intake.
-
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases:
- Studies suggest that a diet high in ultra-processed foods is associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
- High levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and additives in these foods contribute to inflammation and other metabolic disturbances.
-
Digestive Issues:
- Ultra-processed foods often contain additives, preservatives, and artificial flavors that can disrupt digestive health.
- Lack of fiber in these foods can lead to constipation and other gastrointestinal problems.
-
Negative Impact on Mental Health:
- Some research indicates a correlation between ultra-processed food consumption and mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
- The high levels of added sugars and unhealthy fats may exacerbate mood swings and energy crashes.
-
Addictive Properties:
- Certain ingredients in ultra-processed foods, such as refined sugars and artificial flavors, can trigger addictive-like behaviors.
- This can lead to cravings and compulsive overeating, making it difficult to maintain a balanced diet.
-
Environmental Impact:
- The production of ultra-processed foods often involves extensive use of resources, such as water and energy, and contributes to environmental degradation.
- Packaging materials used for these foods also generate significant amounts of waste, adding to environmental pollution.
-
Social and Economic Implications:
- Dependence on ultra-processed foods can lead to socioeconomic disparities in access to healthy food options.
- Lower-income communities often have limited access to fresh, whole foods, leading to higher consumption of cheap, ultra-processed alternatives.

If not ultra-processed foods then what?
Some healthy alternatives to ultra-processed foods:
-
Swap processed snacks for wholesome options:
- Nuts: Choose almonds, walnuts, or pistachios for a dose of healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Fresh Fruits & Veggies: Enjoy a crunchy apple, carrot sticks, or a handful of berries for a natural, nutrient-rich snack.
- Greek Yogurt: Opt for plain Greek yogurt topped with fresh fruit or a drizzle of honey for a satisfying and protein-packed snack.
-
Choose whole grains over refined grains:
- Brown Rice: Swap white rice for brown rice to increase fiber intake and add essential nutrients like magnesium and selenium to your diet.
- Quinoa: Experiment with this versatile whole grain for a protein-rich alternative to processed grains like white pasta or couscous.
- Oats: Start your day with a bowl of oatmeal topped with fruit and nuts for a hearty and nutritious breakfast option.
-
Replace sugary beverages with hydrating alternatives:
- Herbal Tea: Enjoy a cup of herbal tea, such as chamomile or peppermint, for a soothing and hydrating drink without added sugars.
- Infused Water: Add slices of citrus fruits, cucumber, or mint to your water for a refreshing and flavorful alternative to soda or sweet tea.
- Sparkling Water: Choose unsweetened sparkling water with a splash of lemon or lime juice for a fizzy treat without the added sugar and calories.
-
Opt for homemade snacks over packaged ones:
- Homemade Trail Mix: Create your own trail mix with a mix of nuts, seeds, dried fruits, and a sprinkle of dark chocolate chips for a satisfying and nutritious snack.
- Veggie Chips: Make your own veggie chips by thinly slicing vegetables like sweet potatoes, beets, or kale, tossing them with olive oil and seasoning, and baking until crisp.
- Energy Bites: Whip up a batch of homemade energy bites using ingredients like oats, nut butter, honey, and seeds for a convenient and nutritious snack on the go.
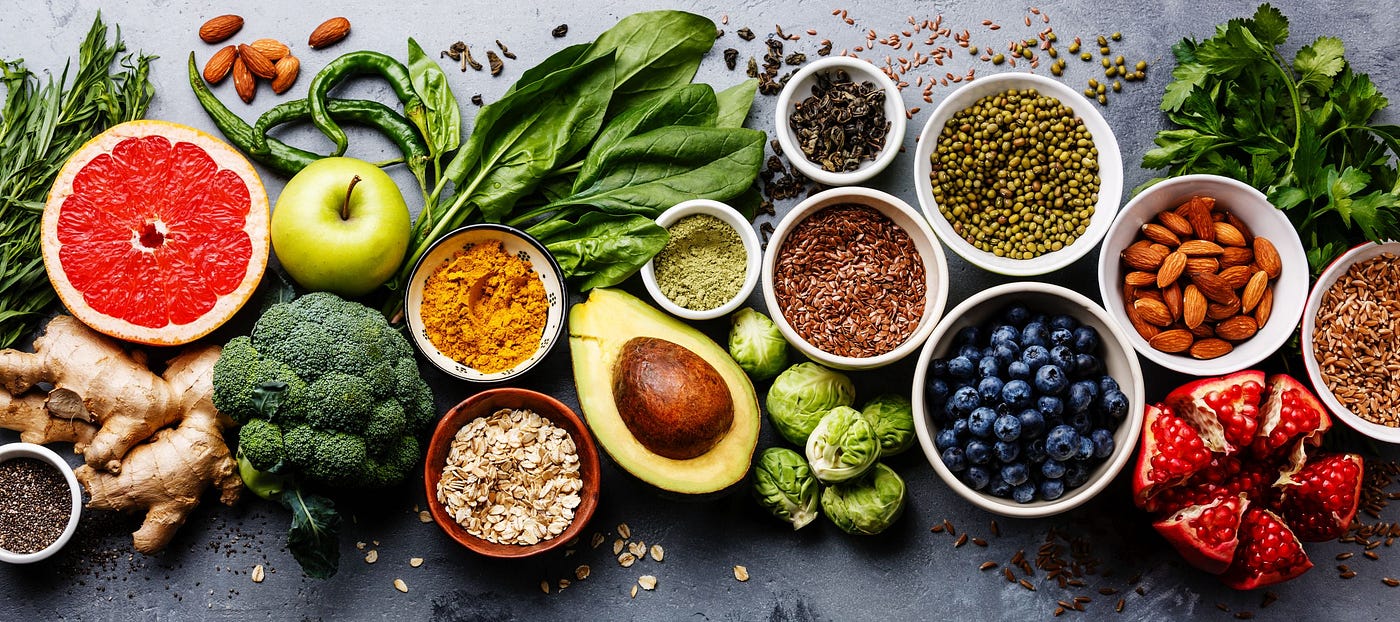

By making these swaps, you'll fuel your body with nourishing foods that support your overall health and well-being.
As we bid adieu to ultra-processed foods, let's swap the processed for the priceless - nuts over nuggets, fruits over fructose! Here's to a future where our snacks are as wholesome as our laughter, and our meals are a celebration of life, not preservatives!
You may also like to read: Unhealthy Diets Drive 56.4% Of India's Disease Burden. What Are ICMR's 17 Dietary Guidelines?
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.



















