Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to reshape the landscape of healthcare, offering unprecedented possibilities for diagnosis, treatment, and enhanced patient experiences. This article explores the various applications of AI in healthcare, its benefits, specific use cases, and the challenges that come with its integration.

Understanding AI in Healthcare
In the healthcare domain, AI involves programming computers to simulate human thinking and learning processes, thereby aiding professionals in deciphering intricate medical data. Several types of AI have gained significant applications in healthcare:
-
Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms are crucial for predictive modelling, facilitating early disease detection such as cancer. McKinsey Global Institute estimates that the utilization of ML in healthcare could generate an annual value of $100 billion across the US healthcare system.
-
Deep Learning (DL): A subset of ML, DL excels in processing vast and complex datasets, particularly in imaging data. The DL market in healthcare is projected to reach $5.2 billion by 2026.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP assists in analyzing patient records, medical notes, and prescriptions, decoding unstructured data. Studies predict that NLP will be a standard feature in 90% of data and analytics platforms by the end of 2025.
Benefits of AI Integration in Healthcare Software Solutions
The integration of AI into healthcare software solutions presents a myriad of benefits, reshaping the healthcare landscape. These advantages span from enhanced diagnostic accuracy to operational efficiency, patient experience, and research and development. Specific benefits include:
-
Improved Accuracy in Diagnostics & Predictions: AI integration enhances diagnostic accuracy and risk prediction. AI algorithms, capable of analyzing complex medical data, can surpass human capabilities in early disease detection. Google's DeepMind Health platform, for example, achieves a remarkable 94% accuracy in detecting over 50 eye diseases, potentially revolutionizing early detection.
-
Efficiency in Healthcare Operations: AI offers the opportunity to automate routine tasks, minimizing human errors and improving overall operational efficiency. Studies indicate that AI has the potential to automate around 20% of unstructured tasks in healthcare by 2022, enabling healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
-
Enhanced Patient Experience: AI's capacity for personalized care and engagement is transforming the patient experience. Predictions suggest that AI chatbots could save the healthcare industry up to $3.6 billion by 2022, automating patient interactions and ensuring 24/7 availability, thus reducing wait times.
-
Advanced Research and Drug Development: AI accelerates medical research and drug discovery by analyzing massive datasets swiftly. For instance, AI startup Insilico Medicine used AI to discover a potential new drug in just 46 days, a stark contrast to the traditional lengthy drug discovery process.
-
Cost-effectiveness and Scalability: AI integration in healthcare promises economic benefits by optimizing processes, reducing errors, and enhancing efficiencies. Accenture's report anticipates that clinical health AI applications could potentially save up to $150 billion annually for the US healthcare economy by 2026.
In light of these benefits, the integration of AI into healthcare software solutions has the potential to revolutionize the industry, making it more accurate, efficient, and patient-centric.
Use Cases of AI in Healthcare Software Solutions
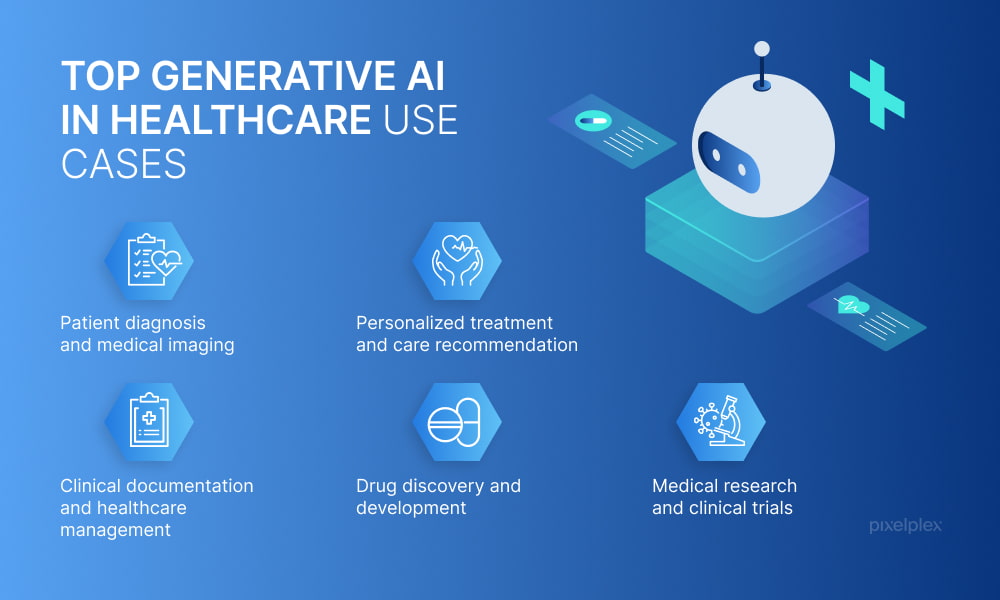
- Radiology and Medical Imaging Software
AI algorithms play a vital role in accurately analyzing medical images, such as CT scans, MRI, and X-rays. This technology improves diagnosis speed and accuracy, benefiting patient outcomes.
- Radiology AI algorithms: Evaluate X-rays and CT scans to aid in diagnosing diseases like pneumonia and tuberculosis, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
- Diagnosis and treatment: AI assists in diagnosing brain tumours, early-stage Alzheimer's, and dementia by analyzing MRI scans, contributing to improved treatment planning.
- Personalized Patient Care
AI in personalized medicine utilizes patient data, genetic information, and lifestyle factors to predict illness risks and recommend tailored treatment options.
- Treatment selection: AI assesses patient data to recommend effective chemotherapy medications for cancer patients based on genetic information.
- Patient monitoring: AI remotely monitors patients, detecting changes in conditions and providing individualized treatment options, especially for chronic diseases like diabetes.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
AI plays a crucial role in analyzing massive amounts of EHR data to uncover patterns, aid in illness prevention, and enhance treatment.
-
Data analysis: AI identifies patterns in EHR data, helping physicians identify high-risk patients and implement personalized preventative measures.
-
Fraud detection: AI detects billing fraud, improving accuracy in medical coding and resulting in cost savings.
-
Virtual assistant & chatbot: AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots offer remote patient care, guiding patients through diagnoses and reducing administrative burdens.
- Telehealth
AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots enable remote monitoring of patients, providing personalized health advice and organizing appointments.
- Personal health advice: Patients receive accurate health advice from AI-powered virtual assistants, eliminating the need to wait for consultations.
- Appointment scheduling: Virtual assistants and chatbots powered by AI organize appointments, reducing the workload on medical personnel and enhancing patient satisfaction.
The global AI in healthcare market is expected to grow from $4.9 billion in 2020 to $45.2 billion by 2026, indicating a promising future for AI in healthcare, according to MarketsandMarkets.
Challenges in AI Application in Health Services
Despite the potential benefits, challenges exist in applying AI to health services, including:

-
Data Bias: AI models may exhibit bias if trained on data that does not reflect the target population, leading to unrepresentative and discriminatory outcomes.
-
Personal Privacy: The sensitivity of health service data demands a careful balance between utilizing data for AI training and respecting patient confidentiality and consent.
-
Ethical Double Effects: Ethical considerations, particularly in biomedical applications, must carefully weigh the potential benefits and harms of AI, adhering to principles such as autonomy and justice.
-
Ethical Principles in Research and Biomedical Medicine: Adhering to principles like autonomy, benefit, non-harm, and justice is crucial in implementing AI in healthcare to ensure ethical practices.
Despite these challenges, the transformative potential of AI in healthcare can be fully harnessed through creative solutions and the adoption of best practices, promising a future of improved, affordable healthcare for all.
Image Source: OptimalVirtual Employee/Medium/Pixelplex
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.