Japan's Bold Move vs. India's Cautious Stance on Interest Rates
On January 24, 2025, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) made headlines by raising its key interest rate from 0.25% to 0.5%, the highest level since the 2008 financial crisis. This decision reflects Japan's confidence in its economic recovery amid rising wages and inflation, with core consumer inflation projected to reach 2.4% in fiscal 2025. The BOJ's move signifies a shift from years of ultra-low interest rates aimed at combating deflation and stimulating growth.In stark contrast, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has maintained its benchmark repo rate at a steady 6.5% for the eleventh consecutive meeting, aligning with market expectations while adopting a neutral policy stance. The RBI's cautious approach comes amid signs of a slowdown in economic growth, with inflation projected at 4.8% for the upcoming fiscal year.
The BOJ's decision to raise rates is seen as a response to persistent inflationary pressures and a sign of a more robust economy, while India's RBI remains vigilant, prioritizing stability amid uncertain global economic conditions.As both nations navigate their monetary policies, the contrasting approaches highlight differing economic landscapes and priorities—Japan moving towards normalization while India opts for caution amidst potential growth challenges.
How does India's interest rate compare to Japan's?
As of January 24, 2025, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) has raised its key interest rate to 0.5%, marking a significant shift in its monetary policy after years of ultra-low rates. This increase is aimed at addressing rising inflation and supporting wage growth amid a recovering economy. In contrast, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has maintained its benchmark repo rate at 6.5%, reflecting a cautious approach to economic stability amidst a slowdown.
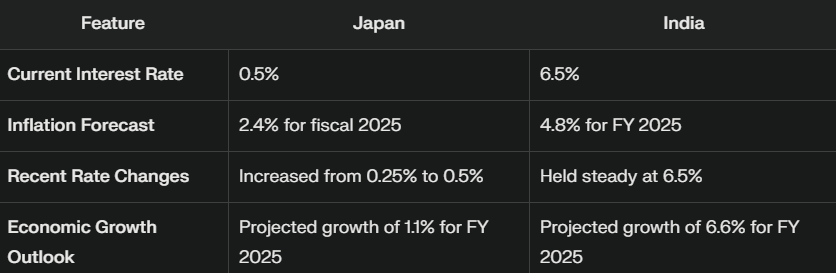
Current Interest Rates
- Japan: The BOJ's recent hike from 0.25% to 0.5% is the highest level since 2008. This decision is driven by inflationary pressures, with core inflation projected to hover around 2.4% for fiscal 2025.
- India: The RBI's steady rate of 6.5% has been in place for eleven consecutive meetings, as the bank focuses on managing inflation, which is expected to rise to 4.8% in the upcoming fiscal year
Implications of the Rate Decisions
The BOJ's decision to raise rates indicates confidence in Japan's economic recovery and aims to sustain inflation around its target level, driven by improving wage conditions and consumer spending. Conversely, India's RBI is taking a more conservative approach, focusing on stabilizing the economy while navigating external uncertainties and domestic inflation challenges.In summary, while Japan is moving towards normalization with its interest rate hike, India maintains a higher rate as it balances growth and inflation concerns, highlighting the divergent paths both economies are taking in response to their unique economic landscapes.
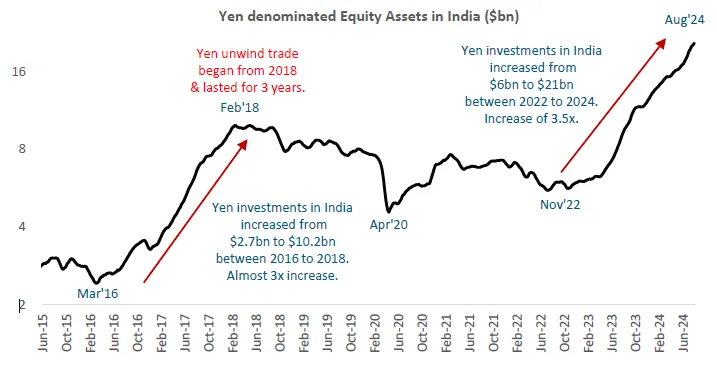
How India's and Japan's Inflation Rates Influence Their Interest Rates?
As of January 24, 2025, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) has raised its key interest rate to 0.5%, a significant increase from 0.25%. This decision is closely tied to Japan's inflation rates, which have recently stabilized around the BOJ's target of 2%, with core inflation reaching 3% in December 2024. In contrast, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has maintained its repo rate at 6.5%, reflecting a different approach to managing inflation, which is projected at 4.8% for the upcoming fiscal year.
Japan's Inflation and Interest Rate Dynamics
The BOJ's recent interest rate hike is a response to rising inflation and wage growth in Japan. The central bank noted that consumer prices have been increasing at an average rate of 2.5%, with core inflation hitting a 16-month high. This trend indicates a shift from years of deflationary pressures, prompting the BOJ to adjust its monetary policy to support economic stability and growth.
- Key Factors Influencing Japan's Rate Hike:
- Inflation reaching the desired target of 2%.
- Significant wage increases anticipated in upcoming negotiations.
- A positive economic outlook supporting consumer spending.
The BOJ aims to gradually normalize interest rates to sustain economic stability while monitoring potential market reactions and external economic conditions.
)
Image Source - Bloomberg
India's Inflation and Interest Rate Strategy?
In contrast, the RBI has opted for a more cautious approach, keeping its interest rate steady at 6.5% despite rising inflation levels. The RBI's decision reflects concerns over economic growth and external pressures that could affect domestic stability.
- Key Factors Influencing India's Steady Rate:
- Inflation projected at 4.8%, which is relatively moderate compared to Japan's current levels.
- A focus on maintaining economic growth amid global uncertainties.
- The need for stability in borrowing costs for consumers and businesses.
The RBI typically raises interest rates when inflation is high to curb spending and stabilize prices, while lower rates are used to stimulate growth during periods of low inflation. However, the current strategy aims to balance these factors without triggering adverse effects on the economy.
In summary, Japan's recent interest rate hike reflects its response to rising inflation and wage growth, signaling confidence in economic recovery. Conversely, India's steady interest rate highlights a more cautious approach as it navigates moderate inflation and seeks to maintain economic stability amidst global uncertainties. The differing strategies underscore how each country's unique economic conditions shape their monetary policies.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.
With inputs from agencies.























